Bijapur Karnataka
| Author:Laxman Burdak, IFS (R) |
Bijapur (बीजापुर), officially known as Vijayapura,[1] is a city and district of Karnataka state of India. Bijapur city is well known for its historical monuments of architectural importance built during the rule of the Adil Shahi dynasty.
Contents
Variants
- Bijapur Karnataka बीजापुर, कर्नाटक (AS, p.634)
- Vijayapura officially name [2]
- Vijapura officially name [3]
Location
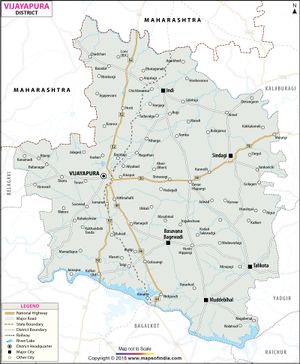
Bijapur is located 530 km northwest of the State Capital Bangalore and about 550 km from Mumbai and 384 km west of the city of Hyderabad.
History
The Bijapur city was established in the 10th-11th centuries by the Kalyani Chalukyas and was known as Vijayapura (City of victory). The city was passed to Yadavas after Chalukya's demise. In 1347, the area was conquered by the Bahmani Sultanate. After the split of the Bahmani Sultanate, the Bijapur Sultanate ruled from the city. Relics of the Sultanates' rule can be found in the city, including the Bijapur Fort, Bara Kaman, Jama Masjid, and Gol Gumbaz.
Early history: Bijapur district is historically, traditionally and legendarily, one of the richest districts in the state. The evidence found here reveals that it was an inhabited place since the Stone Age. Many places of this district have legendary history. The history of this district is divided into four periods, from the Chalukya acquisition of Badami till the Muslim invasion.
Early Western Chalukya period lasting from about A.D. 535 to about A.D.757.
Rastrakuta period from A.D. 757 to A.D.973
Kalachuri and Hoysala period from A.D. 973 to about A.D.1200
Devagiri Yadava period from A.D.1185 to the Muslim conquest of Devagiri in A.D. 1312.
Bahmani and Bijapur Sultanates: Bijapur came under Muslim influence, first under Allaudin Khalji, the Sultan of Delhi, towards the end of the 13th century, and then under the Bahamani kings of Bidar in 1347. In 1347, when the Bahamani dynasty was established, it included southern and eastern parts of Bijapur district. The supremacy of the Bahaman's may be said to have ceased by 1489. At that time five Shahi Dynasties were born and one of them was "Bijapur". The Mughal emperor Aurangazeb conquered Bijapur in 1686 and it was under Mughal rule up to 1723.
In 1724 the Nizam of Hyderabad established his independence in the Deccan and included Bijapur within his dominions. However, his acquisition on this portion was of brief duration, in 1760 it went into the hands of Marathas.
In 1518, the Bahmani Sultanate split into five splinter states known as the Deccan sultanates, one of which was Bijapur, ruled by the kings of the Adil Shahi dynasty (1490–1686). The city of Vijayapura owes much of its greatness to Yusuf Adil Shah, the founder of the independent state of Bijapur.
The rule of this dynasty ended in 1686, when Bijapur was conquered during the reign of Mughal badshah (emperor) Aurangzeb, who has in 1684 turned Bijapur into a subah (imperial top-level province).
British Colonial period: In 1724 the Nizam of Hyderabad established his independence in the Deccan, and included Bijapur within his dominions. In 1760, the Nizam suffered a defeat by the Marathas, and ceded the region of Bijapur to the Maratha Peshwa.
After the 1818 defeat of the Peshwa by the British in the Third Anglo-Maratha War, Bijapur passed into the hands of the British East India Company, and was assigned to the Maratha princely state Satara.
In 1817, war broke out between the British and the Marathas. By 1818, the whole of Bijapur was occupied by the British and was included in the territory assigned to the Raja of Satara. In 1848 the territory of Satara was obtained through the failure of heir and the British rule started. Till 1884, the Bijapur district had headquarters at Kaladagi. Bijapur was made headquarters in 1885.
Post-Independence: After Independence, the movement for re-organisation of States gained further momentum and on 1 November 1956 a separate "Mysore State" was formed. By the wish of the people it was renamed as "Karnataka". Thus, the district Bijapur along with other Kannada speaking areas became a part of "Karnataka State" on 1 November 1956.
Central government had approved the request to rename the city in October 2014 from Bijapur to "Vijayapura" on 1 November 2014.[4]
बीजापुर, कर्नाटक
विजयेन्द्र कुमार माथुर[5] ने लेख किया है .....बीजापुर (AS, p.634): शोलापुर-हुबली रेलपथ पर शोलापुर से 68 मील दूर स्थित है। नगर का प्राचीन नाम 'विजयपुर' कहा जाता है। 11वीं शती के बौद्ध अवशेष हाल ही की खोज में यहाँ प्राप्त हुए हैं, जिससे इस स्थान का इतिहास पूर्व-मध्यकाल तक पहुँचता है। किंतु बीजापुर का जो अब तक इतिहास ज्ञात है, वह प्रायः 1489 ई. [p.635]:से 1686 तक के काल के अंदर ही सीमित है। इन दो सौ वर्षों में बीजापुर में आदिलशाही वंश के सुल्तानों का आधिपत्य था। इस वंश का प्रथम सुल्तान 'यूसुफ़ आदिल ख़ाँ' था, जो 'अल्तूनिया' का निवासी था। इसने बहमनी राज्य के नष्ट-भ्रष्ट होने पर यहाँ स्वाधीन रियासत स्थापित की। बीजापुर का निर्माण तालीकोटा के युद्ध (1556 ई.) के पश्चात् विजय नगर के ध्वंसावशेषों की सामग्री से किया गया था। आदिलशाही सुल्तान शिया थे, और ईरान की संस्कृति के प्रेमी थे। इसीलिए उनकी इमारतों में विशालता और उदारता की छाप दिखाई पड़ती है।
मराठों और शिवाजी की ऐतिहासिक गाथाओं के संबंध में बीजापुर का नाम बराबर सुनाई देता है। बीजापुर के सुल्तान की सेनाओं को कई बार शिवाजी ने परास्त करके अपने छिने हुए क़िले वापस ले लिए थे। बीजापुर के सरदार अफ़ज़ल ख़ाँ को प्रतापगढ़ के क़िले के पास शिवाजी ने बड़े कौशल से मारकर मराठा इतिहास में अभूतपूर्व ख्याति प्राप्त की थी। 1686 ई. में मुग़ल सम्राट और औरंगज़ेब ने बीजापुर की स्वतंत्र राज्यसत्ता का अंत कर दिया और तत्पश्चात् बीजापुर मुग़ल साम्राज्य का एक अंग बन गया।
बीजापुर में आदिलशाही शासन के समय की अनेक उल्लेखनीय इमारतें हैं जो उसकी तत्कालीन समृद्धि की परिचायक हैं। यहाँ की सभी इमारतें प्राचीन क़िले या पुराने नगर के अंदर स्थित हैं।
गोल गुम्बद मुहम्मद आदिलशाह (1626-1656) का मक़बरा है। इसके फर्श का क्षेत्रफल 18337 वर्गफुट है जो रोम के पेथिंयन सेंट पीटर-गिर्जे के गुम्बद से कुछ ही छोटा है। इसकी ऊँचाई फर्श से 175 फुट है और इसकी छत में लगभग 130 फुट वर्ग स्थान घिरा हुआ है। इस गुंबद का चाप आश्चर्यजनक रीति से विशाल है। दीवारों पर इसके धक्के की शक्ति को कम करने के लिए गुम्बद में भारी निलंबित संरचनाएं बनी हैं, जिससे गुम्बद का भार भीतर की ओर रहे। यह गुम्बद शायद संसार की सबसे बड़ी उपजाप वीथि (Whispering Gallery) है। जिसमें सूक्ष्म शब्द भी एक सिरे से दूसरे तक आसानी से सुना जा सकता है।
इब्राहिम द्वितीय (1580-1627) का रौजा मलिक सदल नामक ईरानी वास्तु विशारद का बनाया हुआ है। गोलगुंबज के विपरीत इसकी विशेषता विशालता अथवा भव्यता में नहीं वरन् पत्थर की सूक्ष्म कारीगरी तथा तक्षणशिल्प में है। इसमें खिड़कियों की जालियाँ अरबी अक्षरों के रूप में काटी गई हैं जिससे ऐसा प्रतीत होता है कि इसमें जो पत्थर लगे हैं वे बिना किसी आधार के टिके हैं। कुछ वास्तुविदों का कहना है कि भवन का निर्माणशिल्प सर्वोत्कृष्ट कोटी का है। [p.636]:
जामा मस्जिद: जामा मस्जिद 1576 ई. में बननी शुरू हुई थी। 1686 ई. में औरंगज़ेब ने इसमें अभिवृद्धि की किंतु यह अपूर्ण ही रह गई है। इसके फर्श में 2250 आयत बने हैं। इसकी ऊँचाई 240 फुट और चौड़ाई 130 फुट है। इसमें लंबे बल में पाँच और चौड़े बल में 9 दालान हैं। मध्य का स्थान विशाल गुम्बद से ढका है। जिसकी भीतरी चौड़ाई 96 फुट है। प्रांगड़ पूर्व–पश्चिम 187 फुट है। इसमें उत्तर-दक्षिण की ओर एक बरामदा है। पूर्व के कोने में दो मीनारें बनाई जाने वाली थी, किंतु केवल उत्तरी मीनार ही प्रारंभ हो सकी।
गगन महल: गगन महल (1561 ई.) का केंन्द्रीय चाप भी 61 फुट चौड़ा है किंतु यह इमारत अब खंडहर हो गई है। इसकी लकड़ी की छत को मराठों ने निकाल लिया था।
असर मुबारक महल भी मुख्यतः काष्ठ निर्मित है। सम्मुखीन भाग खुला हुआ है। छत दो काष्ठ स्तम्भों पर आधारित है। इसके भीतर भी लकड़ी का अलंकरण है और चित्रकारी की हुई है। मिहतर महल
मिहतर महल में जो एक मसजिद का प्रवेश द्वार है, पत्थर की नक़्क़ाशी का सुंदर काम प्रदर्शित है। खिड़कियों के पत्थरों पर अनोखे बेल बूटे और कंगनियों के आधार-पाषाणों पर मनोहर नक़्क़ाशी, इस भवन की अन्य विशेषताएँ हैं।
अन्य इमारतें: बीजापुर की अन्य इमारतों में बुखारा मसजिद, अदालत महल, याकूत दबाली की मसजिद, खवास ख़ाँ और मसजिद, छोटा चीनी महल और अर्श-महल उल्लेखनीय है। बीजापुर की वास्तुकला आगरा और दिल्ली की मुग़लशैली से भिन्न है। किंतु मौलिकता और निर्माण कौशल में उससे किसी अंग में न्यून नहीं। यहाँ की इमारतों में हिन्दू प्रभाव लगभग नहीं के बराबर है। किंतु ईरानी निर्माण शिल्प की छाप इनकी विशाल तथा विस्तीर्ण संरचनाओं में स्पष्ट रूप से देखी जा सकती है।
बीजापुर परिचय
उत्तरी कर्नाटक (भूतपूर्व मैसूर) राज्य का एक शहर है। बीजापुर नगर का प्राचीन नाम 'विजयपुर' कहा जाता है। मध्य कालीन मुस्लिम स्थापत्य कला का यह महत्त्वपूर्ण स्थल, पहले विजयपुर कहलाता था। बहमनी राजवंश की प्रांतीय राजधानी बनने से पहले, 1294 तक, एक शाताब्दी से भी अधिक समय तक यादव वंश के अंतर्गत यह एक महत्त्वपूर्ण नगर था।
स्थापना: बहमनी राजवंश के पतन के बाद बने 5 नये राज्यों में बीजापुर का विशेष स्थान था। इस स्वतंत्र राज्य की स्थापना 1489 ई. में यूसुफ़ आदिलशाह ने की। यह धार्मिक रूप से सहिष्णु एवं न्यायप्रिय शासक था। इसके दरबार में ईरान, मध्य एशिया, तुर्किस्तान से विद्वानों का आना-जाना लगा रहता था। इसके बाद के 3 उत्तराधिकारी 'इस्माईल आदिलशाह' (1510 सें 1534 ई.), 'इब्राहिम आदिलशाह' (1535 से 1558 ई.), 'अली आदिलशाह प्रथम' (1558 से 1580) अयोग्य थे। इब्राहिम आदिलशाह ने फ़ारसी के स्थान पर 'हिन्दवी' (दक्कनी उर्दू) को राजभाषा बनाया और शासन में अनेक हिन्दुओं को नियुक्त किया। अली आदिलशाह का विवाह अहमदनगर के 'हुसैन निज़ामशाह' की पुत्री चाँदबीबी से हुआ था।
उद्योग और व्यापार: उद्योगों में कपास की ओटाई, तिलहन की मिलें, साबुन, रसायन और रंगरेज़ी से संबंधित उद्योग शामिल हैं।
संदर्भ: भारतकोश-बीजापुर