Nanga Parbat
| Author:Laxman Burdak, IFS (R) |
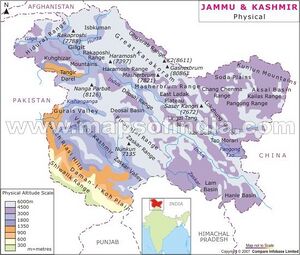
Nanga Parbat (नंगा पर्वत) known locally as Diamer (دیامر), is the ninth-highest mountain on Earth, its summit at 8,126 m above sea level.
Variants
- Diamer (दिआमिर) = Tibetan name meaning "huge mountain"
- Deo Mir (देवमिर) = Tibetan name meaning "huge mountain"
- Dayamur [1]
- Nanga Parvat (नंगा पर्वत) = lit. 'naked mountain',
Location
Nanga Parbat forms the western anchor of the Himalayan Range and is the westernmost eight-thousander. It lies just south of the Indus River in the Diamer District of Gilgit–Baltistan in Pakistani-administered Kashmir. In some places, it flows more than 7 km below the high-point of the massif. To the north is the western end of the Karakoram range.
Lying immediately southeast of the northernmost bend of the Indus river in the Gilgit-Baltistan region of Pakistan-administered Kashmir, Nanga Parbat is the westernmost major peak of the Himalayas, and thus in the traditional view of the Himalayas as bounded by the Indus and Yarlung Tsangpo/Brahmaputra rivers, it is the western anchor of the entire mountain range.[2]
Nanga Parbat is one of the 14 eight-thousanders.[3] An immense, dramatic peak rising far above its surrounding terrain, Nanga Parbat is known to be a difficult climb, and has earned the nickname Killer Mountain for its high number of climber fatalities.
Etymology
The name Nanga Parbat is derived from the Sanskrit words nagna and parvata, which, when combined, translate to "Naked Mountain".[4] The mountain is known locally by its Tibetan name Diamer or Deo Mir, meaning "huge mountain".[5]
नंगा पर्वत
नंगा पर्वत दुनिया की नौवी ऊंची चोटी है। इस की ऊँचाई 8126 मीटर है। इसे दुनिया का "क़ातिल पहाड़" भी कहा जाते है क्योंकि इसपर चढ़ने वाले बहुत से लोगों की जाने जा चुकी हैं। बीसवी सदी के पहले हिस्से में आठ हज़ार मीटर से ऊंचे पहाड़ों में इस एक पहाड़ पर सब से ज्यादा मौतें हुई हैं। नंगा परबत पाकिस्तान के गिलगित-बल्तिस्तान के क्षेत्र में है।
नंगा परबत हिमालय पर्वत शृंखला के सुदूर पश्चिमी भाग में स्थित है और आठ हज़ार मीटर से ऊंचे पहाड़ों में से सब से पश्चिमी है। यह सिन्धु नदी से ज़रा दक्षिण में और अस्तोर घाटी की पश्चिमी सीमा पर खड़ा हुआ है।
नंगा परबत के दो बड़े मुख हैं जिनपर चढ़ने वाले इस पर्वत पर चढ़ने की राह ढूंढते हैं। दक्षिण में इसका "रूपल मुख" है जो की पहाड़ के चरणों से 4600 मीटर की सीधी दीवार है। उत्तर में इसका "रखिओट मुख" है जो सिन्धु नदी की घाटी से 7000 मीटर की चढ़ाई है। रखिओट मुख की चढ़ाई रूपल मुख से वैसे ज़्यादा तो है लेकिन उसकी ढलान रूपल की दीवार से ज़्यादा आसान है। रूपल मुख को कुछ लोग विश्व की सब से ऊंची पहाड़ी दीवार कहते हैं। नंगा परबत के पश्चिम में एक तीसरा मुख है जिसे "दिआमिर मुख" कहा जाता है।
External links
References
- ↑ Alexander Cunningham: The Ancient Geography of India/Taki,p.151
- ↑ Bernstein, Jeremy (1978). Mountain passages. University of Nebraska Press. ISBN 9780803209831. "nanga parbat western anchor."
- ↑ "Nanga Parbat | mountain, Jammu and Kashmir".
- ↑ The New Encyclopaedia Britannica, Encyclopaedia Britannica, 2003, p. 501, ISBN 978-0-85229-961-6
- ↑ The Pamirs and the Source of the Oxus. (1896) George Nathaniel Curzon. Royal Geographical Society, London, p. 16.

