Sogdiana
Sogdiana was the ancient civilization of an Iranian people and a province of the Achaemenid Empire.
Variants of name
- Sogdia
- Suguda (Old Persian)
- Sogdiana
- Σογδιανή (Ancient Greek),
- Sogdianē
- Soġd (Persian)
- Tajik: Суғд, سغد Suġd;
- Uzbek: Sơģd;
- Chinese: 粟特 Sùtè)
Jat clan
- Sogaria
- Solanki: P.C. Bagchi in, “India and Central Asia” says that the Sulikas are originally from Sogdiana in Central Asia, and came to settle in India. [1]
History
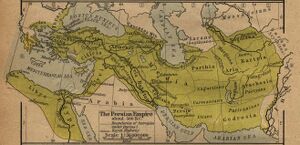
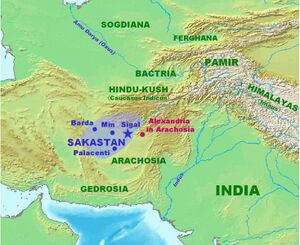
It is eighteenth in the list on the Behistun Inscription of Darius the Great (i. 16). Sogdiana is "listed" as the second of the "good lands and countries" that Ahura Mazda created. This region is listed second after Airyanem Vaejah, "homeland of the Aryans", in the Zoroastrian book of Vendidad, indicating the importance of this region from ancient times.[2] Sogdiana, at different times, included territories around Samarkand, Bukhara, Khujand, Panjikent and Shahrisabz in modern Tajikistan and Uzbekistan.
The inhabitants of Sogdiana were the Sogdians, an Eastern Iranian people who are among the ancestors of modern-day Tajik, Pashun and Yaghnobi peoples.
The Sogdian states, although never politically united, were centered around the main city of Samarkand. Sogdiana lay north of Bactria, east of Khwarezm, and southeast of Kangju between the Oxus (Amu Darya) and the Jaxartes (Syr Darya), embracing the fertile valley of the Zeravshan (ancient Polytimetus). Sogdian territory corresponds to the modern provinces of Samarkand and Bokhara in modern Uzbekistan as well as the Sughd province of modern Tajikistan.
An independent and warlike Sogdiana[3] formed a border region insulating the Achaemenid Persians from the nomadic Scythians to the north and east. The Sogdian Rock or Rock of Ariamazes, a fortress in Sogdiana, was captured in 327 BC by the forces of Alexander the Great; after an extended campaign putting down Sogdian resistance and founding military outposts manned by his Macedonian veterans, Alexander united Sogdiana with Bactria into one satrapy. The military power of the Sogdians never recovered. Subsequently Sogdiana formed part of the Hellenistic Greco-Bactrian Kingdom, founded in 248 BC by Diodotus, for about a century. Euthydemus I seems to have held the Sogdian territory, and his coins were later copied locally. Eucratides apparently recovered sovereignty of Sogdia temporarily. Finally the area was occupied by nomads when the Scythians and Yuezhis overran it around 150 BC.
Chapter xv. Voyage down the Indus to the land of Musicanus
Arrian[4] writes....THERE, at the confluence of the Acesines and Indus, he waited until Perdiccas with the army arrived, after having routed on his way the independent tribe of the Abastanians. Meantime, he was joined by other thirty-oared galleys and trading vessels which had been built for him among the Xathrians, another independent tribe of Indians who had yielded to him. From the Ossadians, who were also an independent tribe of Indians, came envoys to offer the submission of their nation. Having fixed the confluence of the Acesines and Indus as the limit of Philip’s viceroyalty, he left with him all the Thracians and as many men from the infantry regiments as appeared to him sufficient to provide for the security of the country. He then ordered a city to be founded there at the very junction of the two rivers, expecting that it would become large and famous among men.2 He also ordered a dockyard to be made there. At this time the Bactrian Oxyartes, father of his wife Roxana, came to him, to whom he gave the viceroyalty over the Parapamisadians, after dismissing the former viceroy, Tiryaspes, because he was reported to be exercising his authority improperly. Then he transported Craterus with the main body of the army and the elephants to the left bank of the river Indus, both because it seemed easier for a heavy-armed force to march along that side of the river, and the tribes dwelling near were not quite friendly. He himself sailed down to the capital of the Sogdians; where he fortified another city, made another dockyard, and repaired his shattered vessels. He appointed Peithon viceroy of the land extending from the confluence of the Indus and Acesines as far as the sea, together with all the coast-land of India. He then again despatched Craterus with his army through the country; and himself sailed down the river into the dominions of Musicanus, which was reported to be the most prosperous part of India. I-Ic advanced against this king because he had not yet come to meet him to offer the submission of himself and his land, nor had he sent envoys to seek his alliance. He had not even sent him the gifts which were suitable for a great king, or asked any favour from him. He accelerated his voyage down the river to such a degree that he succeeded in reaching the confines of the land of Musicanus before he had even heard that Alexander had started against him. Musicanus was so greatly alarmed that he went as fast as he could to meet him, bringing with him the gifts valued most highly among the Indians, and taking all his elephants. He offered to surrender both his nation and himself, at the same time acknowledging his error, which was the most effectual way with Alexander for any one to get what he requested. Accordingly for these considerations Alexander granted him an indemnity for his offences. He also granted him the privilege of ruling the city and country, both of which Alexander admired. Craterus was directed to fortify the citadel in the capital; which was done while Alexander was still present. A garrison was also placed in it, because he thought the place suitable for keeping the circumvent tribes in subjection.
External links
References
- ↑ 160-op.cit.p.146
- ↑ AVESTA: VENDIDAD (English): Fargard 1.
- ↑ Independent Sogdiana: Lane Fox (1973, 1986:533) notes Quintus Curtius, vi.3.9: with no satrap to rule them, they were under the command of Bessus at Gaugamela, according to Arrian, iii.8.3.
- ↑ Arrian Anabasis Book/6b

