Panjkora
| Author:Laxman Burdak, IFS (Retd.) |
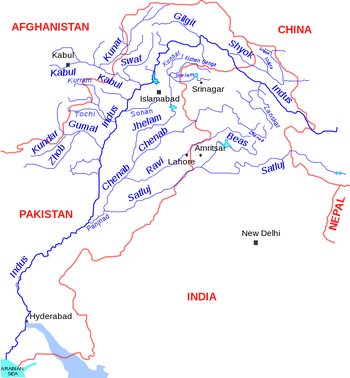
Panjkora River is a river in northern Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, northwestern Pakistan. It has been identified with Rigvedic River Gauri. Also mentioned in Mahabharata (VI.10.24) as Gauri River (गौरी) along with Swat River.[1]
Variants
- Gauri River गौरी (AS, p.310)
- Panjkora (पंजकौरा) दे. Gauri River (गौरी-2) (AS,p.517)
- River Gauri (Rigvedic)
- Gauri River (गौरी) Mahabharata (VI.10.24)
Course
It rises high in the glaciers of Hindu Kush Mountains and flows downstream south through Upper Dir and Lower Dir Districts and joins the Swat River near Chakdara, Malakand District, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. It is in the Indus River watershed basin.
Archaeology
The Panjkora Valley contains important sites of the Gandhara grave culture.
Timergara, 40 kms from Chakdara, is the site of excavated ancient graves, dating from 1500 to 600 BC. On the west side of the Panjkora River is the excavated site of Balambat. The site has been occupied continuously since 1500 BC.
History
Houses dating from 500 BC have been discovered here. Fire altars were also discovered, evidence of Yajna, a ritual practice which is part of Hinduism. The Gandhara grave culture is the earliest phase of Indo-Aryan migrations into the Indian subcontinent. It was part of the Early Vedic culture.
The Talash Valley, 13 kms from Chakdara, is full of Buddhist remains. Buddhist stupas and monasteries which have not been excavated are on both sides of the road towards Dir. At the west end of the valley is the Kat Kala Pass. Olaf Caroe identified this place with Massaga which was captured by Alexander the Great in 327BC.
There are also crumbling remains of a massive Parthian fort of the 8th to 10th centuries.
गौरी नदी
विजयेन्द्र कुमार माथुर[2] ने लेख किया है ...1. गौरी (AS, p.310) - विष्णुपुराण 2,4,55 के अनुसार क्रौंच द्वीप की एक नदी, 'गौरी कुमुद्वती चैव संध्या रात्रिर्मनोजवा,क्षांतिश्च पुंडरीका च सप्तैता वर्षं निम्नगा:'.
2. गौरी (AS, p.310) अफगानिस्तान की वर्तमान पंजकौरा नदी. यह 1. गौरी भी हो सकती है.
Visit by Xuanzang in 630 AD
Alexander Cunningham[3] writes about Pushkalavati or Peukelaotis: The ancient capital of Gandhara was Pushkalavati, which is said to have been founded by Pushkara, the son of Bharata, and the nephew of Rama.[4] Its antiquity is undoubted, as it was the capital of the province at the time of Alexander's expedition. The Greek name of Peukelaotis, or Peucolaitis, was immediately derived from Pukkalaoti, which is the Pali, or spoken form of the Sanskrit Pushkalavati. It is also called Peukelas by Arrian, and the people are named Peukalei by Dionysius Periegetes, which are both close transcripts of the Pali Pukkala. The form of Proklais, which is found in Arrian's ' Periplus of the Erythraean Sea,' and also in Ptolemy's ' Geography,' is perhaps only an attempt to give the Hindi name of Pokhar instead of the Sanskrit Pushkara.
According to Arrian, Peukelas was a very large and populous city, seated not far from the river Indus.[5] It was the capital of a chief named Astes,[6] perhaps Hasti, who was killed in the defence of one of his strongholds, after a siege of thirty days, by Hephsestion. Upon the death of Astes the city of Peukelaotis was delivered up to Alexander on his march towards the Indus. Its position is vaguely described by Strabo and Arrian as "near the Indus." But the geographer Ptolemy is more exact, as he fixes it on the eastern bank of the river of Suastene, that is, the Panjkora or Swat river, which is the very
[p.50]: locality indicated by Hwen Thsang. On leaving Parashawar the Chinese pilgrim travelled towards the north-east for 100 li, or nearly 17 miles; and, crossing a great river, reached Pu-se-kia-lo-fa-ti, or Pushkalavati. The river here mentioned is the Kophes, or river of Kabul; and the bearing and distance from Peshawar point to the two large towns of Parang and Charsada, which form part of the well-known Hasht-nagar, or "Eight Cities," that are seated close together on the eastern bank of the lower Swat river.
These towns are Tangi, Shirpao, Umrzai, Turangzai, Usmanzai, Rajur, Charsada, and Parang. They extend over a distance of fifteen miles ; but the last two are seated close together in a bend of the river, and might originally have been portions of one large town. The fort of Hisar stands on a mound above the ruins of the old town of Hashtnagar, which General Court places on an island, nearly opposite Rajur.[7] "All the suburbs," he says, " are scattered over with vast ruins."[8] The eight cities are shown in No. iv. Map. It seems to me not improbable that the modern name of Hashtnagar may be only a slight alteration of the old name of Hastinagara, or " city of Hasti," which might have been applied to the capital of Astes, the Prince of Peukelaotis. It was a common practice of the Greeks to call the Indian rulers by the names of their cities, as Taxiles, Assakanus, and others. It was also a prevailing custom amongst Indian princes to designate any additions or alterations made to their capitals by their own names. Of this last custom we have a notable instance in the famous city of Delhi ; which, besides its ancient
[p.51]: appellations of Indraprastha and Dilli, was also known by the names of its successive aggrandizers as Kot-Pithora, Kila-Alai, Tughlakabad, Firuzabad, and Shabjahanabad. It is true that the people themselves refer the name of Hashtnagar to the " eight towns " which are now seated close together along the lower course of the Swat river ; but it seems to me very probable that in this case the wish was father to the thought, and that the original name of Hastinagar, or whatever it may have been, was slightly twisted to Hashtnagar, to give it a plausible meaning amongst a Persianized Muhammadan population, to whom the Sanskrit Hastinagara was unintelligible. To the same cause I would attribute the slight change made in the name of Nagarahara, which the people now call Nang-nihar,[9] or the "Nine Streams."
In later times Pushkalavati was famous for a large stupa, or solid tower, which was erected on the spot where Buddha was said to have made an alms-offering of his eyes. In the period of Hwen Thsang's visit, it was asserted that the " eyes gift " had been made one thousand different times, in as many previous existences : but only a single gift is mentioned by the two earlier pilgrims, Fa-Hian in the fifth century, and Sung-Yun in the sixth century.
References
- ↑
- शशिकान्तां शिवां चैव तदा वीरवतीम अपि
- वास्तुं सुवास्तुं गौरीं च कम्पनां स हिरण्वतीम Mahabharata (VI.10.24)
- ↑ Aitihasik Sthanavali by Vijayendra Kumar Mathur, p.310
- ↑ The Ancient Geography of India/Gandhara, p. 49-51
- ↑ Wilson's ' Vishnu Purana,' edited by Hall, b. iv. c. 4.
- ↑ Arrian, - 'Indica,' i.
- ↑ Arrian, ' Anabasis,' It. 22.
- ↑ Journ. Asiat. Soc. Bengal, 1836, p. 479.
- ↑ ibid 1836, p. 394.
- ↑ Baber's ' Memoirs,' p. 141. — Wood's ' Journey to the Source of the Oxus,' p. 167. — Macgregor's 'Greography of Jalalabad,' in Journ. Asiat. Soc. Bengal, xi. 117, and xiii. 867.

