Geats
| Author:Laxman Burdak, IFS (R) |
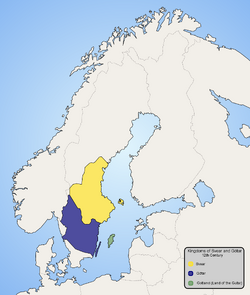
| Distribution of Geats |
| Distribution of Swedes |
| Distribution of Gutes |
Geats (गीट, जीट, गेट, याट, जाट,गोथ, गोटर, जोटर) were a large North Germanic tribe who inhabited Götaland ("land of the Geats") in modern southern Sweden from antiquity until the late Middle Ages. They are one of the progenitor groups of modern Swedes, along with Swedes (the tribe) and Gutes. The name of the Geats also lives on in the Swedish provinces of Västergötland and Östergötland, the Western and Eastern lands of the Geats, and in many other toponyms.
The Swedish dialects spoken in the areas that used to be inhabited by Geats form a distinct group, Götamål.
Variants
- Geat (गीट, जीट)
- /ɡiːts (गीट), ˈɡeɪəts, jæts/ GHEETS, GAY-əts, YATS;[1][2]
- Old English: gēatas [ˈjæɑtɑs] (जीट)
- Old Norse: gautar [ˈɡɑu̯tɑr] (गोटर)
- Swedish: götar [ˈjø̂ːtar]) (जौटर)
- sometimes called Goths (गोथ)[3]
- Gutar (गुटर)
- Goutai (Γου̑ται) (गौटई, जौटई)
- Geatas (गीट, जीट)
- Gautoi (गौटोई, जौटोई)
Etymology
The etymology of the name Geat (Old English Geatas, from a Proto-Germanic *Gautaz, plural *Gautōz) is similar,[4]although not identical, to that of Goths and Gutar (*Gutô, plural *Gutaniz). The names derive from different ablaut grades of the Proto-Germanic word *geutaną, meaning "to pour".[5] They are generally accepted as having originated as heiti for "men (of the tribe)", with the literal meaning "they who pour their seed".[6] (For more information see Goths § Etymology.) The names could also allude to watercourses in the land where they were living,[7] but this is not generally accepted to be the case, partly because that would mean that the names' similarity would be coincidental.[8]
A more specific theory about the word Gautigoths is that it means the Goths who live near the river Gaut,[9]today's Göta älv (Old Norse: Gautelfr).[10] It might also have been a conflation of the word Gauti with a gloss of Goths.[11] In the 17th century the name Göta älv, 'River of the Geats', replaced the earlier names Götälven and Gautelfr.[12]The etymology of the word Gaut (as mentioned above) derives from the Proto-Germanic word *geutan, and the extended meaning of "to pour" is "flow, stream, waterfall", which could refer to Trollhättan Falls or to the river itself.[13]
The short form of Gautigoths was the Old Norse Gautar, which originally referred to just the inhabitants of Västergötland, or the western parts of today's Götaland, a meaning which is retained in some Icelandic sagas.[14]
History
Early history: The earliest known surviving mention of the Geats appears in Ptolemy (2nd century AD), who refers to them as Goutai. In the 6th century, Jordanes writes of the Gautigoths and Ostrogoths (the Ostrogoths of Scandza); and Procopius refers to Gautoi. The Norse Sagas know them as Gautar; Beowulf and Widsith as Gēatas.[15] Beowulf and the Norse sagas name several Geatish kings, but only Hygelac finds confirmation in Liber Monstrorum where he is referred to as "Rex Getarum" and in a copy of Historiae Francorum where he is called "Rege Gotorum". These sources concern a raid into Frisia, ca 516, which is also described in Beowulf. C. 551, some decades after Hygelac's raid, Jordanes described the Geats as a nation which was "bold, and quick to engage in war".[16]
The Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain included many North Germanic people who were losers in the brutal tribal warfare of Scandinavia. The place-name -gate marks the site of Geatish settlement, often alongside strategically important Roman roads and nearby Visigothic and/or Jutish settlements.[17]Defeated Jutes like Hengest and his brother Horsa fled to Kent, while Geats defeated by encroaching Swedes moved to Yorkshire where they founded Gillingshire by the Tees, originally the settlement of the Geatlings.[18]It has also been suggested that East Anglia was settled by Geats at this time,[19] or by Wulfings who also came from Götaland, bringing the traditions of Beowulf with them.[20]
Any peace that eventually settled in southern Scandinavia was most likely due to exhaustion, and a Danish archaeologist has summarized that in the mid-6th century, and after, Scandinavia "went down to hell".[21] Scandinavian wares appear to have stopped arriving in England, c. 550, suggesting that contact was broken.[22]
According to Procopius there were 13 "very numerous nations" on the Scandinavian peninsula in the 6th century, which is supported by recent archaeological analyses. Several scholars consider this to be a reasonable number of independent kingdoms at the time, with each consisting of one or more tribes, as reported by Jordanes.[23] However, by 1350, these 13 kingdoms had been reduced in number to only two, Norway and Sweden.[24] The Geats were one of the largest tribes,[25]
Procopius and Jordanes both mention the Geats, but after them, foreign sources about Scandinavia are scarce until the 9th century, when Anglosaxon and Frankish sources does shed some light on the area. In these, the Geats are absent, which has led some scholars to conclude that they were no longer an independent nation and had been subsumed by the Swedes.[26] Norwegian and Icelandic scaldic sources from the 10th century does however indicate that they were still politically independent, sometimes opposing Norwegian kings. Their absence in older sources have instead been suggested to be due to them being an inland people.[27]
The nature and the processes of how Geats and Swedes came to form one kingdom have been much debated among Swedish scholars. The scarcity and sometimes debated veracity of sources has left much room open for interpretation. The oldest medieval Swedish sources present the Swedish kingdom as having remaining differences between provinces, in laws as well as in weights and measurements.[28]Some scholars have argued that the Geats were subjugated by the Swedes, and have suggested various dates for such an event, from the sixth to the 9th century.[29] Others have wanted to see a more gradual merging, and that the Geats were slowly subsumed into the more powerful kingdom of Sweden, and in many respects they maintained their own cultural identity during the Middle Ages.[30] Still others have put emphasis on how it was individual rulers, not ethnic groups, that were driving the process towards a unified kingdom, and that the process was very complicated.[31]
Papal letters from the 1080s style the recipients as "king of the Swedes" or "king of the West Geats". In another papal letter from the 1160s, the title rex Sweorum et Gothorum is first attested.[32] The Swedish kings began the custom of styling themselves as also the king of the Geats in the 1270s.[33]
Society
The Geats were traditionally divided into several petty kingdoms, or districts, which had their own things (popular assemblies) and laws. The largest one of these districts was Västergötland (West Geatland), and it was in Västergötland that the Thing of all Geats was held every year, in the vicinity of Skara. Despite the name, the thing was only for the inhabitants of Västergötland and Dalsland. The equivalent in Östergötland was Lionga thing.
Unlike the Swedes, who used the division hundare, the Geats used hærrad (modern Swedish härad), like the Norwegians and the Danes. Surprisingly, it would be the Geatish name that became the common term in the Swedish kingdom. This is possibly related to the fact that several of the medieval Swedish kings were of Geatish extraction and often resided primarily in Götaland. In Västergötland and Dalsland, there were also a higher-level division where one or more hærrad made up a bo linked to a kongsgård.
Goths
Geatas was originally Proto-Germanic *Gautoz and Goths and Gutar (Gotlanders) were *Gutaniz. *Gautoz and *Gutaniz are two ablaut grades of a Proto-Germanic word *geutan with the meaning "to pour" (modern Swedish gjuta, modern German giessen). The word comes from an Indo-European root meaning to pour, offer sacrifice.[34] There were consequently two derivations from the same Proto-Germanic ethnonym.[35]
It is a long-standing controversy whether the Goths were Geats. Both Old Icelandic and Old English literary sources clearly separate the Geats (Isl. Gautar, OEng Geatas) from the Goths/Gutar (Isl. Gotar, OEng. Gotenas); but the Gothic historian Jordanes wrote that the Goths came originally to Dacia from the island of Scandza. Moreover, he described that on this island there were three tribes called the Gautigoths (cf. Geat/Gaut), the Ostrogoths (cf. the Swedish province of Östergötland) and Vagoths (Gutar?) ‒ this implies that the Geats were Goths rather than vice versa. The word Goth is also a term used by the Romans to describe related, culturally linked tribes like the Tervingi and the Greuthungs, so it may be correct to label Geats as Goths.
Scandinavian burial customs, such as the stone circles (domarringar), which are most common in Götaland and Gotland, and stelae (bautastenar) appeared in what is now northern Poland in the 1st century AD, suggesting an influx of Scandinavians during the formation of the Gothic Wielbark culture.[36] Moreover, in Östergötland, in Sweden, there is a sudden disappearance of villages during this period.[37] Contemporary accounts beginning in the fourth century further associated these groups with the earlier Getae of Dacia, but this is now disputed.
Götaland theory
The Götaland theory (Swedish "Västgötaskolan") is a disparate group of theories, which have attempted to prove that some events and even places that are traditionally placed around Mälaren, especially ones that are associated with the formation of medieval Sweden, instead should be located to Västergötland. The methods ranged from relatively scholarly efforts to dowsing.[38] This "school" was brought to prominence in the 1980s following a TV series by Dag Stålsjö. While some serious scholars have attempted to place more emphasis on the Geats in the early history of Sweden than was traditional, Västgötaskolan has never reached any acceptance.
Identity of the Gēatas
The generally accepted identification of Old English Gēatas as the same ethnonym as Swedish götar and Old Norse gautar is based on the observation that the ö monophthong of modern Swedish and the au diphthong of Old Norse correspond to the ēa diphthong of Old English.
Thus, Gēatas is the Old English form of Old Norse Gautar and modern Swedish Götar. This correspondence seems to tip the balance for most scholars. It is also based on the fact that in Beowulf, the Gēatas live east of the Dani (across the sea) and in close contact with the Sweon, which fits the historical position of the Geats between the Danes and the Swedes. Moreover, the story of Beowulf, who leaves Geatland and arrives at the Danish court after a naval voyage, where he kills a beast, finds a parallel in Hrólf Kraki's saga. In this saga, Bödvar Bjarki leaves Gautland and arrives at the Danish court after a naval voyage and kills a beast that has been terrorizing the Danes for two years (see also Origins for Beowulf and Hrólf Kraki).
Jutish hypothesis
There is a hypothesis that the Jutes also were Geats, and which was proposed by Pontus Fahlbeck in 1884. According to this hypothesis the Geats would have not only resided in southern Sweden but also in Jutland, where Beowulf would have lived.
The Geats and the Jutes are mentioned in Beowulf as different tribes, and whereas the Geats are called gēatas, the Jutes are called ēotena (genitive) or ēotenum (dative).[39] Moreover, the Old English poem Widsith also mentions both Geats and Jutes, and it calls the latter ȳtum.[40] However, Fahlbeck proposed in 1884 that the Gēatas of Beowulf referred to Jutes and he proposed that the Jutes originally also were Geats like those of southern Sweden.[41] This theory was based on an Old English translation of Venerable Bede's Ecclesiastical History of the English People attributed to Alfred the Great where the Jutes (iutarum, iutis) once are rendered as gēata (genitive) and twice as gēatum (dative)[42] (see e.g. the OED which identifies the Geats through Eotas, Iótas, Iútan and Geátas). Fahlbeck did not, however, propose an etymology for how the two ethnonyms could be related.[43]
Fahlbeck's theory was refuted by Schück who in 1907 noted that another Old English source, the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, called the Jutes īutna, īotum or īutum.[44] Moreover, Schück pointed out that when Alfred the Great's translation mentions the Jutes for the second time (book IV, ch. 14(16)) it calls them ēota and in one manuscript ȳtena.[45] Björkman proposed in 1908 that Alfred the Great's translation of Jutes as Geats was based on a confusion between the West Saxon form Geotas ("Jutes") and Gēatas ("Geats").[46]
As for the origins of the ethnonym Jute, it may be a secondary formation of the toponym Jutland, where jut is derived from a Proto-Indo-European root *eud meaning "water".[47]
Gutnish hypothesis
Since the 19th century, there has also been a suggestion that Beowulf's people were Gutes (from the island of Gotland in Sweden). According to the poem, the weather-geats or sea-geats, as they are called are supposed to have lived east of the Danes/Dacians and be separated from the Swedes by wide waters. Some researchers have found it a little far-fetched that wide waters relates to Vänern in Västergötland or Mälaren. The weather in weather-geats, and sea-geats marks a people living at a windy, stormy coast by the sea. The Geats of Västergötland were historically an inland people, making an epithet such as weather- or sea- a little strange. Moreover, when Beowulf dies he is buried in a mound at a place called Hrones-naesse, meaning "the cape of whales". Whales have for obvious reasons never lived in Vänern, where, according to Birger Nerman, Beowulf is buried. However, an expanse of water separates the island of Gotland from the Swedes. The island lies east of Denmark/Dacia and whales were once common in the Baltic Sea where Gotland is situated. The name of the Gutes in Swedish, Gutar, is an ablaut-grade of the same name as that of the Geats in Beowulf. These facts made the archaeologist Gad Rausing come to the conclusion that the weather-Geats may have been Gutes. This was supported by another Swedish archaeologist Bo Gräslund. According to Rausing, Beowulf may be buried in a place called Rone on Gotland, a name corresponding to the Hrones in Hrones-naesse. Not far from there lies a place called Arnkull corresponding to the Earnar-naesse in Beowulf, which according to the poem was situated closely to Hrones-naesse.
This theory does not exclude the ancient population of Västergötland and Östergötland from being Geats, but rather holds that the Anglo-Saxon name Geat could refer to West-geats (Västergötland), East-geats (Östergötland) as well as weather-geats (Gotland), in accordance with Jordanes account of the Scandinanian tribes Gautigoth, Ostrogoth and Vagoth.
Jat History
Mangal Sen Jindal[48] writes ...The Southern portion of Sweden as 'Gotland' wherein the name of a city is 'Goteborg'. In Baltic Sea, there is a big island which used to be a trade centre of importance sometime back is named 'Gothland', The words are definitely connected with Jats or Goths.
See also
References
- ↑ "Geat". Merriam-Webster Dictionary.
- ↑ "Geat". The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language (5th ed.). HarperCollins.
- ↑ E.g. Microsoft Encarta (on Swedish history), translations from Old Norse
- ↑ Hellquist, Elof. "göt". Svensk etymologisk ordbok (in Swedish).
- ↑ "887-888 (Nordisk familjebok / Uggleupplagan. 10. Gossler - Harris)". runeberg.org.
- ↑ Svenskt ortnamnslexikon, Språk- och folkminnesinstitutet, Uppsala 2003, pages 103 och 92 (articles "Götaland" and "Gotland").
- ↑ An interpretation of both names of Götaland and Gotland according to the etymology sentences in their respective articles in Nationalencyklopedin.
- ↑ Hellquist, Elof. "göt". Svensk etymologisk ordbok (in Swedish).
- ↑ "887-888 (Nordisk familjebok / Uggleupplagan. 10. Gossler - Harris)". runeberg.org.
- ↑ Nationalencyklopedin, the article (in Swedish) about Klarälven, which says that Klarälven was called Gautelfr in records from the 13th century. See also Nationalencyklopedin, the article "Göta älv" (in Swedish).
- ↑ Götar in Svenska Akademiens Ordbok.
- ↑ "887-888 (Nordisk familjebok / Uggleupplagan. 10. Gossler - Harris)". runeberg.org.
- ↑ "887-888 (Nordisk familjebok / Uggleupplagan. 10. Gossler - Harris)". runeberg.org.
- ↑ "887-888 (Nordisk familjebok / Uggleupplagan. 10. Gossler - Harris)". runeberg.org.
- ↑ Michael Alexander's 1995 (Penguin Classics) edition of Beowulf mentions a variant: Gēotas
- ↑ Larsson, Mats G. (2004). Götarnas riken. Stockholm: Atlantis. p. 43.
- ↑ Margary, Ivan D. (1973). Roman Roads in Britain, 3rd ed. London: Baker.
- ↑ Shippey, Tom (2018). Laughing Shall I Die. London: Reaction Books Limited. p. 56. ISBN 978-1-78023-909-5.
- ↑ Farrel, R.T. (1972). Beowulf, Swedes and Geats (PDF). Viking Society for Northern Research, University College, London. p. 269.
- ↑ Newton, Sam (1993). The Origins of Beowulf, and the Pre-Viking Kingdom of East Anglia. D. S. Brewer, Cambridge.
- ↑ Shippey, Tom (2018). Laughing Shall I Die. London: Reaction Books Limited. p. 56. ISBN 978-1-78023-909-5.
- ↑ Farrel, R.T. (1972). Beowulf, Swedes and Geats (PDF). Viking Society for Northern Research, University College, London. p. 269.
- ↑ Iversen, Frode (2020). "Between Tribe and Kingdom – People, Land, and Law in Scandza AD 500–1350". Rulership in 1st to 14th century Scandinavia. De Gruyter. p. 250. doi:10.1515/9783110421101-004. ISBN 9783110421101. S2CID 213596339.
- ↑ Iversen, Frode (2020). "Between Tribe and Kingdom – People, Land, and Law in Scandza AD 500–1350". Rulership in 1st to 14th century Scandinavia. De Gruyter. pp. 245–304. doi:10.1515/9783110421101-004. ISBN 9783110421101. S2CID 213596339.
- ↑ Iversen, Frode (2020). "Between Tribe and Kingdom – People, Land, and Law in Scandza AD 500–1350". Rulership in 1st to 14th century Scandinavia. De Gruyter. p. 295. doi:10.1515/9783110421101-004. ISBN 9783110421101. S2CID 213596339
- ↑ Ståhl, Harry (1976). Ortnamn och ortnamnsforskning. Uppsala: Almquist & Wiksell. p. 131.
- ↑ Sawyer, Peter (1991). När Sverige blev Sverige. Viktoria Bokförlag, Alingsås. p. 12.
- ↑ Ståhl, Harry (1976). Ortnamn och ortnamnsforskning. Uppsala: Almquist & Wiksell. p. 131.
- ↑ Ståhl, Harry (1976). Ortnamn och ortnamnsforskning. Uppsala: Almquist & Wiksell. p. 131.
- ↑ Farrel, R.T. (1972). Beowulf, Swedes and Geats (PDF). Viking Society for Northern Research, University College, London. p. 270.
- ↑ Sawyer, Peter (1991). När Sverige blev Sverige. Viktoria Bokförlag, Alingsås. pp. 9–10.
- ↑ Sawyer, Peter (1991). När Sverige blev Sverige. Viktoria Bokförlag, Alingsås. pp. 58–59.
- ↑ Harrison, Dick (2002). Sveriges historia: Medeltiden. Liber, Stockholm. pp. 58, 70–74.
- ↑ "god" in The Oxford English Dictionary Online. (2006).
- ↑ cf. Serbs and Sorbs, Polans and Poles, Slovenes and Slovaks in Slavic languages.
- ↑ "The Goths in Greater Poland" (in Polish). Muzarp.poznan.pl.
- ↑ Oxenstierna, Graf E.C. : Die Urheimat der Goten. Leipzig, Mannus-Buecherei 73, 1945 (later printed in 1948).
- ↑ Larsson, Mats G. (2004). Götarnas riken. Stockholm: Atlantis. pp. 33–34, 90.
- ↑ Nerman, Birger (1925). Det Svenska Rikets Uppkomst. Stockholm: Ivar Haeggström. p.108
- ↑ Nerman, Birger (1925). Det Svenska Rikets Uppkomst. Stockholm: Ivar Haeggström. p.108
- ↑ Nerman, Birger (1925). Det Svenska Rikets Uppkomst. Stockholm: Ivar Haeggström. p.109
- ↑ Nerman, Birger (1925). Det Svenska Rikets Uppkomst. Stockholm: Ivar Haeggström. p.108-9
- ↑ Nerman, Birger (1925). Det Svenska Rikets Uppkomst. Stockholm: Ivar Haeggström. p.109
- ↑ Nerman, Birger (1925). Det Svenska Rikets Uppkomst. Stockholm: Ivar Haeggström. p.109
- ↑ Nerman, Birger (1925). Det Svenska Rikets Uppkomst. Stockholm: Ivar Haeggström. p.110
- ↑ Nerman, Birger (1925). Det Svenska Rikets Uppkomst. Stockholm: Ivar Haeggström. p.110
- ↑ Hellquist, Elof (1922). "Jut-, Jute". Svensk etymologisk ordbok (in Swedish). Project Runeberg.
- ↑ History of Origin of Some Clans in India/Jat From Jutland, p. 2
Back to Variants of Jat

