Mehrgarh
| Author:Laxman Burdak, IFS (R) |
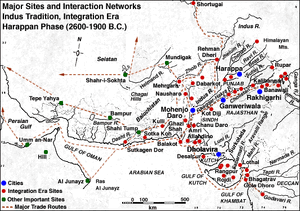
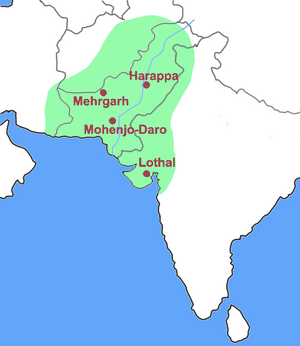
Mehrgarh (Hindi:मेहरगढ़, Urdu: مہرگڑھ), one of the most important Neolithic (7000 BCE to c. 2500 BCE) sites in archaeology, lies on the "Kachi plain" of now Balochistan, Pakistan. Mehrgarh is now seen as a precursor to the Indus Valley Civilization, displaying the whole sequence from earliest settlement and the start of agriculture, to the mature Harappan Civilisation.
Location
Mehrgarh is located near the Bolan Pass, to the west of the Indus River valley and between the now Pakistani cities of Quetta, Kalat and Sibi.
Jat clan
History
It is one of the earliest sites of Indian sub continent with evidence of farming (wheat and barley) and herding (cattle, sheep and goats) in South Asia.[1]
Early Mehrgarh residents lived in mud brick houses, stored their grain in granaries, fashioned tools with local copper ore, and lined their large basket containers with bitumen. They cultivated six-row barley, einkorn and emmer wheat, jujubes and dates, and herded sheep, goats and cattle. Residents of the later period (5500 BCE to 2600 BCE) put much effort into crafts, including flint knapping, tanning, bead production, and metal working. The site was occupied continuously until about 2600 BCE.[2] Mehrgarh is probably the earliest known center of agriculture in South Asia. [3]
In April 2006, it was announced in the scientific journal Nature that the oldest (and first early Neolithic) evidence in human history for the drilling of teeth in vivo (i.e. in a living person) was found in Mehrgarh. [4]
Period
The report, based on C-14 radio-dating, the mounds at Bhirrana village, on the banks of Ghaggar river, in Fatehabad district date back to 7570-6200 BC. The previous Pakistan-French study had put Mehrgarh site in Pakistan as the oldest in the bracket of 6400-7000 BC. Mehrgarh is located near the Bolan Pass, to the west of the Indus River Valley and between the Pakistani cities of Quetta, Kalat and Sibi.[5]
External links
References
- ↑ Hirst, K. Kris. 2005. "Mehrgarh". Guide to Archaeology
- ↑ Possehl, Gregory L. 1996. "Mehrgarh." Oxford Companion to Archaeology, edited by Brian Fagan. Oxford University Press
- ↑ Meadow, Richard H. (1996). In David R. Harris. The origins and spread of agriculture and pastoralism in Eurasia. Psychology Press. pp. 393–. ISBN 978-1-85728-538-3.
- ↑ Coppa, A. et al. 2006. "Early Neolithic tradition of dentistry: Flint tips were surprisingly effective for drilling tooth enamel in a prehistoric population." Nature. Volume 440. 6 April 2006.
- ↑ Haryana's Bhirrana oldest Harappan site, Rakhigarhi Asia's largest: ASI Rohan Dua,TNN | Apr 15, 2015
Back to Indus Valley Civilization

