Amasya
| Author:Laxman Burdak, IFS (R) |
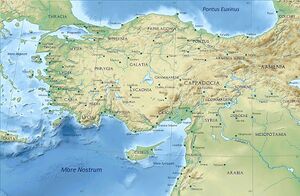
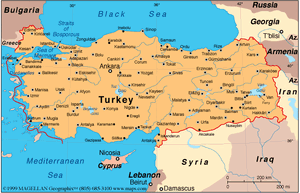
Amasya is a city in northern Turkey and is the capital of Amasya Province, in the Black Sea Region. It was called Amaseia or Amasia in antiquity.[1] Amasya was birth-place of the geographer Strabo.
Variants
- Amaseia (Ἀμάσεια)
- Amasia (Pliny.vi.3)
- Amassia
- Turkish pronunciation: [aˈmasja]
Location
Amasya stands in the mountains above the Black Sea coast, set apart from the rest of Anatolia in a narrow valley along the banks of the Yeşilırmak River.
Etymology
According to Strabo the Greek name Ἀμάσεια comes from Amasis, the queen of the Amazons, who were said to have lived here. The name has changed little throughout history: Ἀμάσεια, Amaseia, Amassia and Amasia are all found on ancient Greek and Roman coinage and continue to be used in modern Greek. Armenian: Ամասիա, Ottoman Turkish اماسیه, and modern Turkish Amasya all represent the same pronunciation.
History
Antiquity: Archaeological research shows that Amasya was first settled by the Hittites and subsequently by Phrygians, Cimmerians, Lydians, Greeks, Persians, and Armenians.
Hellenistic period: An independent Pontic kingdom with its capital at Amaseia was established by the Persian Mithridatic dynasty at the end of the 4th century BC, in the wake of Alexander's conquests. In the 1st century BC, it briefly contested Rome's hegemony in Anatolia. By 183 BC, the city was settled by Greeks, eventually becoming the capital of the kings of Pontus from 333 BC to 26 BC.
Today, there are prominent ruins including the royal tombs of Pontus in the rocks above the riverbank in the centre of the city. Ancient district in northeastern Anatolia adjoining the Black Sea.
Roman-Byzantine period: Amaseia was captured by a force led by the Roman Lucullus in 70 BC from Armenia and was quickly made a free city and administrative center of his new province of Bithynia and Pontus by Pompey. By this time, Amaseia was a thriving city, the home of thinkers, writers and poets, and one of them, Strabo, left a full description of Amaseia as it was between 60 BC and 19 AD. Around 2 or 3 BC, it was incorporated into the Roman province of Galatia, in the district of Pontus Galaticus. Around the year 112, the emperor Trajan designated it a part of the province of Cappadocia.[2][3] Later in the 2nd century it gained the titles 'metropolis' and 'first city'. After the division of the Roman Empire by emperor Diocletian the city became part of the East Roman Empire (the Byzantine Empire). At this time it had a predominantly Greek-speaking population.
Amaseia was also referenced in the first book of the Alexiad. Amaseia was the town where Emperor Alexios I Komnenos received the Norman general Ursel as a captive from the Turkic general Tutach. Ursel had, according to the book, looted and pillaged the Eastern provinces of the Byzantine Empire until the at-the-time General Alexios convinced Tutach to capture him. Alexios agreed that he would pay "...such a sum of money as no one ever gained before." to Tutach for the capture of Ursel, however Alexios had no cash to give and the Emperor was unable to fund it, so he attempted to raise money from the people of Amaseia, however this caused serious unrest. However, after a speech by Alexios, he arranged a mock-blinding of Ursel which promptly caused the people to contribute funds. However, this is likely to be biased.[4]
Saints Theodore of Amasea (died by 319), a warrior saint, and the local bishop Asterius of Amasea (died c. 410), some of whose polished sermons survive, are notable Christian figures from the period.
In 2013, a 24-square-meter christian mosaic belonging to the floor of a chapel was discovered, near a site where an illegal archaeological dig had been attempted. The mosaic, depicts apples, an apple tree, partridges and many geometric figures.[5]
Although near the Black Sea, this area is high above the coast and has an inland climate, well-suited to growing apples, for which Amasya province, one of the provinces in north-central Anatolia Turkey, is famed. It was the home of the geographer Strabo and the birthplace of the 15th century Armenian scholar and physician Amirdovlat Amasiatsi. Located in a narrow cleft of the Yeşilırmak (Iris) river, it has a history of 7,500 years with many traces still evident today.
In antiquity, Amaseia was a fortified city high on the cliffs above the river. It has a long history as a wealthy provincial capital, producing kings and princes, artists, scientists, poets and thinkers, from the kings of Pontus, through Strabo the geographer, to many generations of the Ottoman imperial dynasty. With its Ottoman-period wooden houses and the tombs of the Pontus kings carved into the cliffs overhead, Amasya is attractive to visitors.
During the early Ottoman rule, it was customary for young Ottoman princes to be sent to Amasya to govern and gain experience. Amasya was also the birthplace of the Ottoman sultans Murad I and Selim I. Traditional Ottoman houses near the Yeşilırmak and the other main historical buildings have been restored; these traditional Yalıboyu houses are now used as cafes, restaurants, pubs and hotels. Behind the Ottoman wooden houses one can see the rock tombs of the Pontic kings.
In recent years, there has been much investment in tourism, and therefore more foreign and Turkish tourists have visited the city.
Geography
Situated between the Black Sea and inner Anatolia in a region of fertile plains irrigated by the Tersakan, Çekerek and Yeşilırmak rivers, Amasya lies in a beautiful narrow river valley, bounded by almost vertical cliffs and the high peaks of the Canik and Pontus mountains. Despite the mountainous location, it is not far above sea level. This makes its climate more temperate.[citation needed]
Five bridges cross the river, and most of the town lies on the southern bank, spread along the river. The climb up to the higher ground is very steep, making the valley walls virtually uninhabitable. The town is shaped like the letter 'v' as it follows a sharp bend in the river.
The legend of Ferhat and Shirin
In its Turkish version, this classic tale of oriental folklore is held to have taken place in Amasya. The nearby mountain Ferhat is named for Farhad (Turkish spelling Ferhat), the hero of the legend, who for love of the princess Shirin (Turkish spelling Şirin) tried to win her father's favour and permission by tunnelling through the mountain to bring spring water to his palace. Sadly, while he was working he was sent the false information that Shirin had died; upon which he threw himself onto the rocks in his grief. And his beloved princess died soon after. The story has since become a play by Nâzım Hikmet, a novel by Talip Apaydın, and an opera by Arif Melikov.[
Mention by Pliny
Pliny[6] mentions...Cappadocia1 has in the interior Archelais,2 a colony founded by Claudius Cæsar, and past which the river Halys flows; also the towns of Comana,3 watered by the Sarus, Neocæsarea,4 by the Lycus,5 and Amasia,6 in the region of Gazacene, washed by the Iris. In Colopene it has Sebastia and Sebastopolis;7 these are insignificant places, but still equal in importance to those just mentioned.
1 The boundaries of Cappadocia varied under the dominion of the Persians, after the Macedonian conquest, and as a Roman province under the emperors.
2 Founded by Archelaüs, the last king of Cappadocia. In Hamilton's Researches, the site has been assumed to be the modern Ak-serai, but that place is not on the river Halys, as Leake supposes. It is, however, considered that Ak-serai agrees very well with the position of Archelais as laid down in the Itineraries, and that Pliny may have been misled in supposing that the stream on which it stood was the Halys.
3 Also called by the name of Chryse, or "Golden," to distinguish it from another place of the same name in Pontus. It is generally supposed that the town of Al-Bostan, on the Sihoon or Sarus, is on or near the site of this Comana.
4 Now called Niksar, according to D'Anville, though Hardouin says that it is Tocat. Parisot remarks, that this place belonged rather to Pontus than to Cappadocia.
5 A small tributary of the Iris, or Yeshil-Irmak, mentioned in the next Chapter.
6 Both to the west of Neo-Cæsarea. According to Tavernier, as quoted by Hardouin, the modern name of Sebastia is Sivas.
7 Still called Amasia, or Amasiyeh, and situate on the river Iris, or Yeshil Ermak. It was at one time the residence of the princes of Pontus, and the birth-place of the geographer Strabo. The remains of antiquity here are very considerable, and extremely interesting.
References
- ↑ "Amasya" in The New Encyclopædia Britannica. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 313.
- ↑ Strabo Geographica, (12.561).
- ↑ Mitchell, Stephen (1996), "Amaseia", in Hornblower, Simon; Spawforth, Anthony (eds.), Oxford Classical Dictionary (3rd ed.), Oxford: Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-521693-6
- ↑ "The Alexiad, translated by Elizabeth A. S. Dawes | Anna Comnena; Dawes, Elizabeth A. S. (trans.)".
- ↑ "1,800-year-old mosaic reveals symbol of Black Sea province". hurriyetdailynews. 21 July 2020.
- ↑ Natural History by Pliny Book VI/Chapter 3
Back to Jat Places in Turkey

