Koraput
| Author:Laxman Burdak, IFS (R) |
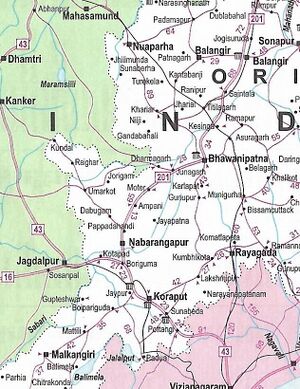
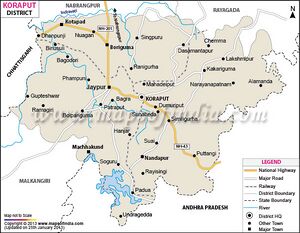
Koraput (कोरापुट) is a city and district of Odisha, India. In October, 1992, Koraput district was divided, resulting in the creation of Malkangiri, Rayagada and Nabarangpur districts. Before the bifurcation then Koraput District had been the second largest district in India.
Location
It is located along the Eastern Ghats.
Origin
The District of Koraput derives its name from its headquarters, the present town of koraput. In ancient times, when the Nalas were ruling over this tract, Pushkari, the modern Umerkote was the capital city.[1]
Administration
Koraput district is divided into 2 sub-divisions and 14 blocks. The 2 sub-divisions are Koraput and Jeypore.
Blocks in Koraput sub-division 1. Koraput 2. Semiliguda 3. Nandapur 4. Pottangi 5. Dasmanthpur 6. Lamtaput 7. Laxmipur 8. Narayanapatna 9. Bandugaon
Blocks in Jeypore sub-division 1. Jeypore 2. Boipariguda 3. Kotpad 4. Kundra 5. Boriguma
History
Koraput belonged to the Atavikas, a feudatory of the powerful Kalinga Empire (Ancient Odisha) who valiantly fought the Kalinga War in the 3rd century BCE. Kalinga regained its former glory during the Mahameghabahan Dynasty in the first century BCE. The third king of this dynasty Kharavela made the Kalinga empire and the Atavika land was very strong under his rule.
The successive dynasties – the Satavahanas (2nd century CE), Ikshvakus (3rd century CE) had headquarters at Pushkari, near the modern town of Umerkote. The Kesaribeda excavations bear testimony to the rule of King Bhabadatta Varma and King Arathapati. The inscriptions of Podagarh refer to king Skandavarma.
The overlord Nala kings are traced to the kings who ruled from Gwalior in Madhya Pradesh. Their rapid growth landed them in the Odia regions of Bastar and Koraput. Around the 10th century CE a Nala king Bhimesen was ruling over a region now located in Koraput and Ganjam District.
The Koraput area including present-day Narabangpur District was a small principality of Tri Kalinga under the Ganga era of the 5th century CE. The patches of Utkala, Kalinga and Kosala were brought under the control of the Ganga kings of Odisha. This dynasty became prominent during the 11th century CE with the rise of Somanakshi. Their suzerainty extended from the modern Sambalpur, Sonepur to the Bastar and Koraput regions and they enjoyed control until the beginning of the 14th century CE.
The Matsya family ruling over the Oddadi region of modern Jeypore dominated the next generation. The best known kings included Bhanudeva and Narasingha Dev, as is known from the Odia inscription of Simhachalam in Visakhapatnam district of Andhra Pradesh.
The next dynasty belonged to the Sailavansis, who ruled over Vindhya during the 14th century CE. The earliest king Ganga Raju was ruling over Nandapur, a former capital of the Maharaja of Jeypore. Nandapur is famous for the throne of 32 steps erected in the line of king Vikramaditya of Ujjain. Jainism and Shaktism grew side by side in the kingdom of Nandapur.
The last king of Sailavansa, Pratap Ganga Raju was succeeded by Vinayak Dev of Surya Vansa which lasted until the time of the British Empire. Vinayak Dev was said to be married to the daughter of the last ruler of Silavansi Paratap Ganga Raju. He and his six succeeding generation of kings had only one son each and on advice from astrologers the headquarters of the kingdom was switched from Nandapur to Jeypore.
During the Anglo-French conflict, Vikram Dev I (1758–1781 CE) was successful in driving out the French from Malkangiri area and the Marathas from the Umerkote belt. They were succeeded by the brave Odia king Ramachandra Dev II (1781–1825) while his other two sons Jagannath and Narasingh Dev were placed in charge of Nabarangpur and Gudari regions. Jagannath Dev’s son Arjun Dev and Narasingha Dev’s son Chaitanya Dev were issueless. Hence, Nabarangpur and Gudari were remerged to Jeypore kingdom.
During the 20th century Ramachandra Dev IV (1920–31) was an honourable lieutenant in World War I. He was issueless and was succeeded by a benevolent, aged, scholar king Vikram Dev IV, the son of Krishna Chandra Dev. During this period the Boundary Commission headed by Sir O’Donnel was entrusted with the task of writing the different Oriya speaking tracts. The Commission went round Jeypore, Paralakhumendi, Ganjam, and Visakhapatnam before finalizing its decision. The state of Orissa was formed on 1 April 1936 with Koraput as one of the six districts. In 1951 Vikram Dev IV died at 82 and the Estate Abolition Act was passed the next year. The Estate of Jeypore was taken over by the Government of Odisha.
Koraput is one of the most popular tourist spot in Odisha. There are a number of interesting sites that are rated highly in the list of tourist attractions in India. The most popular tourist spots in Koraput include:
Rivers
References
Back to Jat Kingdoms in Ancient India/Jats in Buddhism
Back to Orissa

