Transoxiana
| Author:Laxman Burdak, IFS (Retd.) |
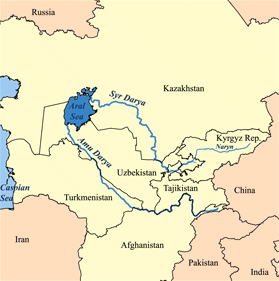
Transoxiana (also spelled Transoxania), known in Arabic and Persian sources as Mawarannahr (Arabic: ماوراء النهر mā warāʔa an-nahr "what (is) beyond the (Oxus) river"), is the ancient name used for the portion of Central Asia corresponding approximately with modern-day Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, southern Kyrgyzstan and southwest Kazakhstan.
Location
Geographically, it is the region between the Amu Darya (Ancient Greek: Ώξος Ōxos) and Syr Darya rivers.[1] The area had been known to the Romans as Transoxania (Land beyond the Oxus), to the Arabs as Mawarannahr (Land Beyond the River), and to the Iranians as Turan, a term used in the Persian national epic Shahnameh.[2]
The region was one of the satrapies of the Achaemenid dynasty of Persia under the name Sogdiana.
History
The name Transoxiana stuck in Western consciousness because of the exploits of Alexander the Great, who extended Greek culture into the region with his conquests of the 4th century BC; Transoxiana was the most north-eastern point of the Hellenistic culture until the Arabic invasion. During the Sassanid Empire, it was often called Sogdiana, a provincial name taken from the Achaemenid Empire, and used to distinguish it from nearby Bactria.
The Chinese explorer Zhang Qian, who visited the neighbouring countries of Bactria and Parthia along with Transoxiana in 126 BC, made the first known Chinese report on this region. Zhang Qian clearly identifies Parthia as an advanced urban civilisation that farmed grain and grapes, made silver coins and leather goods.[3] It was ruled successively by Seleucids, Greco-Bactrian Kingdom, Parthian Empire and Kushan Empire before Sassanid rule.
In Sassanid times, the region became a major cultural and scientific centre due to effective royal authority and the wealth derived from the Northern Silk Road. Sassanid rule was interrupted by the Hephthalite invasion at the end of the 5th century and didn't return to the Sassanids until 565. Many Persian nobles and landlords escaped to this region after the Muslim invasion. Before the Muslim invasion it was also ruled by Gokturks. Following the Arab conquest, the area became known as Ma wara'un-Nahr (Arabic, "what is beyond the river").
Part of this region was conquered by Qutayba ibn Muslim between 706 and 715 and loosely held by the Umayyads from 715 to 738. The conquest was consolidated by Nasr ibn Sayyar between 738 and 740, and continued under the control of the Umayyads until 750, when it was replaced by the Abbasids. The Tang Dynasty also controlled the eastern part of the region until about the same time, when a civil war occurred.
Genghis Khan invaded Transoxiana in 1219 during his conquest of Khwarezm. Before his death in 1227, he assigned the lands of Western Central Asia to his second son Chagatai, and this region became known as the Chagatai Khanate.
In 1369, Timur, of the Barlas tribe, became the effective ruler and made Samarkand the capital of his future empire. Transoxiana was known to be flourishing in the mid-14th century.[4]
Ram Sarup Joon[5] writes: It has been mentioned in Malfuzat Temuri that is the time of Temuri's invasion of India, Jats were the first to intercept him many Jats were killed in the encounter. Timur had for long harboured an animosity against the Jats. Timur was from Chughtaiya (Saktaya) the capital of which was in Trans Oxiana. A great Jat king Kokaltas invaded Khurasan and occupied it. After that he invaded Trans Oxiana. The king fled away. But the nephew of that Amir Timur was a clever and far sighted man. He offered due apologies on behalf of his uncle and admitted the suzerainty of Kokaltas, who had one Lakh (100,000) brave Jats in his army. King Kokaltas died issue less in 1380. Timur occupied the throne and also married a Jat Rajkumari. But Jats did not accept the rule of Timur. A mutiny flared up and continued for long time. Finally Timur managed to suppress it, carried out a mass massacre of the Jats and drove out the remnants from the country. By 1349 he succeeded in finally establishing himself, but still he was not free from Jat troubles. He writes in Timur Nama, that he did not intend to kill so many Jats, because they were handsome, stalwart people, but he had to do so. It is written in MulfuZai Temur P 429 that when he invaded India, he was interrupted by the Jats who took a heavy toll of his army. It is also mentioned in Todd's Rajasthan with reference to Tazke-babri that at the time of Babar's invasion of India a large number of Jats resisted him at Thanesar and most of them were slain.
Major cities
Transoxiana's major cities and cultural centres are Samarkand and Bukhara. Both are in the southern portion of Transoxiana, (though still to the north of the Amu Darya itself, on the river Zeravshan), and the majority of the region was dry but fertile plains. Both cities remained centres of Persian culture and civilisation after the Islamic conquest of Iran, and played a crucial role in the revival of Persian culture with establishment of the Samanid dynasty.
External links
References
- ↑ Encyclopædia Britannica online
- ↑ Mapping Mongolia: Situating Mongolia in the World from Geologic Time to the Present, Paula L.W. Sabloff, P.62
- ↑ Silk Road, North China, C. Michael Hogan, The Megalithic Portal, ed. A. Burnham (2007)
- ↑ The Timurid Empire
- ↑ History of the Jats/Chapter IX, p. 150

