Rahatgarh
| Author:Laxman Burdak, IFS (R) |
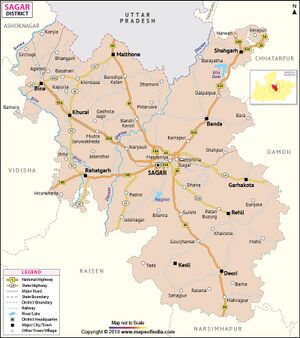


Rahatgarh (राहतगढ़) is a town in Sagar district in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. Author (Laxman Burdak) visited Rahatgarh on 23.08.1990 while on tour from Damoh to Bhopal, Got held up near Rahatgarh due to flood in Bina River.
Origin
Variants
Location
Rahatgarh situated on NH 146, Connecting Sagar and Bhopal. Rahatgarh is located at 23.78°N 78.37°E. It has an average elevation of 461 metres. The town is also notable for the Rahatgarh waterfall.
Villages in Rahatgarh Tahsil
Town: 1 Rahatgarh
Villages:
1 Aeran Mirzapur, 2 Bahadurpur, 3 Bakena, 4 Bamhori Seth, 5 Bamura, 6 Barbatu, 7 Barodiya Ballahh, 8 Basiya Bhoti, 9 Basiya Gange, 10 Basoda, 11 Batyaoda, 12 Behrol, 13 Behta Alinagar, 14 Berkhera, 15 Berkheri, 16 Berkheri Bhoti, 17 Berkheri Gopal, 18 Bhabhukawari, 19 Bhaisa, 20 Bhulna Bhangarh, 21 Bichpuri, 22 Bilaspur, 23 Bilha Kuwakheda, 24 Binaiki, 25 Chakerpur, 26 Chandan Hari, 27 Chandrapur, 28 Chauki, 29 Chhirkheda, 30 Dabri, 31 Darkoli, 32 Daudpur, 33 Dhagarniya, 34 Dhanora, 35 Dhekri, 36 Fatehpura, 37 Gada, 38 Gadaghat, 39 Gambhiriya, 40 Gamiriya, 41 Gawari, 42 Gazikheda, 43 Gungucha, 44 Hanotiya Kalan, 45 Harwanshpura, 46 Hinotiya Khurd, 47 Hirankheda, 48 Huran Kutguwn, 49 Jaitpura, 50 Jalandhar, 51 Jamundhana, 52 Jhila, 53 Johariya Sheikh, 54 Kakruwa, 55 Kalyanpur Bir, 56 Kalyanpur Mal, 57 Karaiya, 58 Karaiya Hazari, 59 Kathoda Fazalpur, 60 Katighati, 61 Kenera, 62 Khajuriya, 63 Khari Gumariya, 64 Khatakheri, 65 Khejramafi, 66 Khiriya Jhila, 67 Khiriya Kajiwara, 68 Kishunpur, 69 Kituwa, 70 Koluwa, 71 Koluwa, 72 Lachkyai, 73 Lalbag, 74 Luharra, 75 Mad Deora, 76 Magoriya, 77 Mahuna Gujar, 78 Manak Chauk, 79 Manesiya, 80 Mankapur, 81 Manki Salaiya, 82 Mardanpur, 83 Masaniya, 84 Menwara Kalan, 85 Menwara Khurd, 86 Mirkhedi, 87 Mohasa, 88 Mudiya Meda, 89 Nadanwara, 90 Nanau, 91 Nayakheda, 92 Nivodiya, 93 Norja, 94 Osankheri, 95 Pachoha, 96 Pachpipra, 97 Padarsoi, 98 Parasari Khurd, 99 Parasari Tyonda, 100 Parasri Kalan, 101 Parsora, 102 Patan, 103 Patheriya Bedni, 104 Pekhlon, 105 Pepalkhedi, 106 Pipariya Chor, 107 Pipariya Ghat, 108 Pipariya Khas, 109 Piparkhedi, 110 Pipra, 111 Rajoli, 112 Rajwans, 113 Ramchayari, 114 Rasulpur, 115 Rupau, 116 Rusalla, 117 Rusalla, 118 Sagoni Umariya, 119 Saikheda, 120 Semra Charkhara, 121 Semra Jhila, 122 Semra Meda, 123 Senpa, 124 Shikarpur, 125 Sihora, 126 Sonpur, 127 Sothiya, 128 Sumredi, 129 Tatarpur, 130 Tila Buzurg, 131 Umariya Semra,
Source - https://www.census2011.co.in/data/subdistrict/3448-rahatgarh-sagar-madhya-pradesh.html
History
Originally built by Sultan Muhamad Khan (Circa 17th Century AD), Rahatgarh Fort is situated on the top of north west peak along the range of hills near the town itself. It can be approached by means of a long winding passage, and the walls of the fortification are approximately 100 m thick.
An inscription of the Paramara king Jayavarman II, dated 28 August 1256 CE, was issued at Rahatgarh and discovered on a stone slab by Alexander Cunningham during the 1870s. The 14-line inscription is written in Sanskrit prose.[1] The inscription drafts a royal document of Maharajadhiraja ("great king") of Dhara. As the inscription is partially damaged, different scholars have read the name of the king as "Jayasimhadeva" or "Jayavarmadeva".[2]
It is possible that Jayavarman captured the area from the Chandelas. [3]
A small town 60 km west of Sagar on Bhopal Sagar Road renowned for its battlement ramparts, its gates and its ruins of palaces temples and mosques. It is picturesquely situated on the steep bank of the Bina River which is crossed at this point by a fine bridge of fourteen arches, completed in 1863. Close to the town stands the famous fort of Rahatgarh. It outer wall consists of 26 enormous towers, some of which were used as dwellings connected by curtain walls and enclosing a space of 66 acres. Two miles away from the fort is a waterfall nearly 50 feet high in picturesque surroundings.[4]
Places of Interest
2 Bhalkund Waterfall
राहतगढ़
राहतगढ़ (AS, p.796): मध्य प्रदेश के सागर ज़िले का एक ऐतिहासिक स्थान है। गढ़मंडला नरेश संग्राम शाह (मृत्यु 1541 ई.) के बाबनगढ़ों में से राहतगढ़ एक है। अकबर ने गढ़मंडला की रानी वीरांगना दुर्गावती के निधन के पश्चात् उसके पुत्र वीरनारायण के उत्तराधिकारी चंद्रशाह को गोंडवाना का राजा बनाने के पश्चात् जो किले लिये थे उनमें से यह भी था। [5]
राहतगढ़ परिचय
राहतगढ़ भारत के मध्य प्रदेश राज्य के सागर ज़िले में स्थित एक नगर है। यह इसी नाम की तहसील का मुख्यालय भी है। राहतगढ़ बीना नदी के किनारे बसा हुआ है। सागर-भोपाल मार्ग पर सागर से लगभग 40 किमी की दूरी पर स्थित यह कस्बा स्थित है। यहां से NH-146 गुजरता है वर्तमान में राहतगढ़ एक नगर पंचायत है। प्राचीन किला, जलप्रपात एवं भगवान विश्वनाथ के बीना नदी के घाट बनेनी घाट पर स्थित मंदिर के कारण प्रसिद्ध पिकनिक स्थल के रूप में विख्यात है। यह नगर राहतगढ़ के किले के नीचे एवं बीना नदी के किनारे पर स्थित है। राहतगढ़ किला सुरक्षात्मक द्रष्टि से काफी महत्वपूर्ण है बीना नदी पार करके मालवा बुंदेलखंड को जोड़ने के लिए अंग्रेजों ने 14 कमानी का एक सुन्दर पुल सन (1853) में "आर्क तकनीक पर आधारित' बनवाया था। इसकी लागत उस समय लगभग 56000 रूपये आई थी। वर्तमान में इस पुल के ठीक बाजू से एक नवीन पुल का निर्माण कर दिया गया है, एवं पुराना पुल जिसको "बड़े पुल" के नाम से जाना जाता था आज भी शान से अच्छी हालत में बीना नदी के दोनों किनारों को जोड़े खड़ा हुआ है।
इतिहस: 11 वीं शताब्दी के एक खंडित शिलालेख पर गढ़पेहरा के डांगी वंश के राजा निहालशाह के उपराहद मंडल की स्थिति के बारे में स्पष्ट जानकारी तो नहीं है, परन्तु कुछ इतिहासकार इसे राहतगढ़ मानते हैं।
कालांतर में गढ़ामंडला राज्य जिसमे 350 गाँव सम्मिलित थे और एक विशाल गढ़ था, के रूप में भी इसका उल्लेख मिलता है। बाद में गौंड़ राजाओं के शासन का यहाँ उल्लेख मिलता है। गोंड शासक संग्रामशाह द्वारा विजित 52 गढ़ो में से राहतगढ़ एक था। नवाब यार मुहम्मद खान (1726 से 1742) के समय भोपाल राज्य के 'दीवान बीजल राम' ने इसे भोपाल राज्य में मिला लिया।
सन 1799 में एक पिंडारी मुखिया द्वारा राहतगढ़ को लूटा गया। इस लूट का उल्लेख 'मेमोयर ऑफ़ सेन्ट्रल इण्डिया' नाम की एक प्रसिद्द पुस्तक में रोचक ढंग से किया गया है।
इसके बाद यह किला एवं नगर सन 1807 में सिंधिया राज्य में विलय हो गया।
सन 1818 में नगर का प्रबंध अंग्रेजों के अधीन आ गया। 1857 के प्रथम स्वतंत्रता संग्राम में राहतगढ़ किला अंग्रेजों के लिए रणनीतिक महत्व का रहा।
External links
References
- ↑ Trivedi, Harihar Vitthal (1991). Inscriptions of the Paramāras (Part 2). Corpus Inscriptionum Indicarum Volume VII: Inscriptions of the Paramāras, Chandēllas, Kachchapaghātas, and two minor dynasties. Archaeological Survey of India. p. 190. doi:10.5281/zenodo.1451755.
- ↑ Trivedi, Harihar Vitthal (1991). Inscriptions of the Paramāras (Part 2). Corpus Inscriptionum Indicarum Volume VII: Inscriptions of the Paramāras, Chandēllas, Kachchapaghātas, and two minor dynasties. Archaeological Survey of India. p. 191. doi:10.5281/zenodo.1451755.
- ↑ Harihar Vitthal Trivedi (1991). Inscriptions of the Paramāras (Part 2). Corpus Inscriptionum Indicarum Volume VII: Inscriptions of the Paramāras, Chandēllas, Kachchapaghātas, and two minor dynasties. Archaeological Survey of India. pp. 190–191. doi:10.5281/zenodo.1451755.
- ↑ https://sagar.nic.in/en/tourist-place/rahatgarh/
- ↑ Aitihasik Sthanavali by Vijayendra Kumar Mathur, p.796

