Surkh Kotal
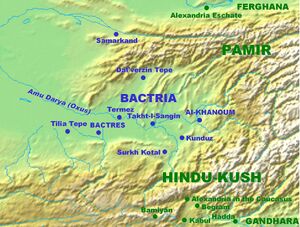
Surkh Kotal (Hindi: सुर्ख कोतल , Persian: سرخکوتل; Pashto: سور کوتل) is an ancient archaeological site located in the southern part of the region of Bactria, about 18 km north of the city of Puli Khumri, the capital of Baghlan Province of Afghanistan.[1]
Variants of name
Location
It is the location of monumental constructions made during the rule of the Kushans. Huge temples, statues of Kushan rulers and the Surkh Kotal Inscription, which revealed part of the chronology of early Kushan emperors (also called Great Kushans) were all found there. The Rabatak inscription which gives remarkable clues on the genealogy of the Kushan dynasty was also found in the Robatak village just outside the site.
History
राजकीय संग्रहालय मथुरा में कुषाण प्रतिमाएं
राजकीय संग्रहालय मथुरा[2] भारतीय कला को मथुरा की एक विशेष देन है। भारतीय कला के इतिहास में यहीं पर सर्वप्रथम हमें शासकों की लेखों से अंकित मानवीय आकारों में बनी प्रतिमाएं दिखलाई पड़ती हैं।[3] कुषाण सम्राट वेमकटफिश, कनिष्क एवं पूर्ववर्ती शासक चष्टन की मूर्तियां माँट नामक स्थान से पहले ही मिल चुकी हैं। एक और मूर्ति जो संभवत: हुविष्क की हो सकती है, इस समय गोकर्णेश्वर के नाम से मथुरा मे पूजी जाती है। ऐसा लगता है कि कुषाण राजाओं को अपने और पूर्वजों के प्रतिमा-मन्दिर या देवकुल बनवाने की विशेष रूचि थी। इस प्रकार का एक देवकुल तो माँट में था और दूसरा संभवत: गोकर्णेश्वर में। इन स्थानों से उपरोक्त लेखांकित मूर्तियों के अतिरिक्त अन्य राजपुरुषों की मूर्तियां भी मिली हैं, पर उन पर लेख नहीं है[4]। इस संदर्भ में यह बतलाना आवश्यक है कि कुषाणों का एक और देवकुल, जिसे वहां बागोलांगो (bagolango) कहा गया है, अफ़ग़ानिस्तान के सुर्ख कोतल नामक स्थान पर था। हाल में ही यहाँ की खुदाई से इस देवकुल की सारी रूपरेखा स्पष्ट हुयी है।
Excavation
The site of Surkh Kotal, excavated between 1952 and 1966 by Prof. Schlumberger of the Délégation Archéologique Française en Afghanistan, is the main site excavated of the Kushan Empire. Some of the site's sculptures were transferred to the National Museum of Afghanistan (also known as the 'Kabul Museum'), the rest of the site was completely looted during the Afghan Civil War. The most famous artifacts of this site are the Surkh Kotal inscriptions, the statue of King Kanishka and the fire altar. The statue of the king was destroyed during the Taliban wave of iconoclasm in February–March 2001, but has been restored by French conservationists. The three artifacts are currently on display in the Afghan National Museum.
Archaeology
A major Kushan dynastic shrine complex on top of a hill overlooking the Baghlan plain. It is approached by a monumental brick and masonry staircase, flanked by four massive erraces, cut out of the hillside. The temple itself - possibly a fire temple - is in the centre of a paved courtyard, and consists of a masonry altar with four Hellenistic column bases at each corner, in a sanctuary with massive mud walls. The most important finds have been inscriptions. The most noteable one is the foundation inscription, a monumental inscription in the Bactrian anguage, made up of a series of stone blocks that originally lined the front of the third terrace. The other main inscription is the Nokonzoko inscription, an elaborate, very controversial inscription in three versions, that describes the construction and restoration of the complex, also in the Bactrian language. Other finds include a life-size headless statue of Kanishka, several more inscriptions, many coins and various sculptural fragments in stone and stucco.[5][6]
The translation of inscriptions
Here are translations of the inscriptions from Surkh Kotal by J. Harmatta. They were originally in the Bactrian language and written in Greek script. For possible interpretations of their meanings, see Harmatta's article.:[7]
The "unfinished inscription" (SK2) has been translated as:
- "Era-year 299, on the 9th [day] of [month] Dios, King of Kings Ooëmo Takpiso, the majesty, the Kuṣāṇa, had the canal d[ug here]."
Unfortunately, the fragments of an inscription from the period of Kanishka's reign contain only about one fifth (124 letters altogether) of the original inscription. They have been translated as:
- the lord, K[ing of Kings], the mighty Kaneṣko . . .]
- [in the] first [era ye]ar T [an officer of the king] c[ame] here.
- Then [this stronghold and the sanctuary] were built by him in four years.
- [And] when the st[rongho]ld was com[pleted, then this fa]çade [and] the stairs l[eading th]ere [were built by him. Moreover, the canal was wh]olly bu[tressed with stones so that p[ure water was [provid]ed [by him in the can]al for the ab[ode of the gods. Thus he] to[ook care of the sanctuary].
- [Moreover, this stronghold and the canal were built by So-and-So by the order of the king]. Then So-and-So inscribed this façade and the stairs leading there.
The text of SK 4 (A, B, M) runs:
- This stronghold is the 'Kaneṣko' Oanindo sanctuary which the lord king made the namebearer of Kaneṣko.
- At that time when the stronghold was first completed, then its inner water to drink was missing, therefore the stronghold was without water. And when the water-flow disappeared from the canal, then the gods wished themselves away from the abode. Then they were led to Lrafo, [namely] to Andēzo. Afterwards the stronghold became abandoned.
- Then, when Nokonzoko, the karalrango, the king's favourite who is much devoted towards the king, Son of God, the patron, the benefactor, the merciful as well, who wishes glory, all-winning strength from pure heart, came here to the sanctuary in the 31st Era-year, in the month Nīsān, then he took care of the stronghold. Then he had a well dug, thus he provided water. Thereafter he buttressed [the well] with stones so that the fine, pure water should not be missing for the stronghold. And when for them the water-flow would disappear from the canal, even then the gods, should not wish themselves away from their abode, thus the stronghold should not become abandoned for them.
- Moreover, he appointed an inspector over the well, he placed a helper there, so that a separate [inspector] took good care of the well and a separate inspector of the whole stronghold.
- Moreover, this well and the façade were made by Xirgomano, the karalrango, by the order of the king. [B: Moreover, this well was made by Borzomioro, son of Kozgaṣko, citizen of Hastilogan, attendant of Nokonziko, the karalrango, by order of the king.]
- Moreover, Eiiomano inscribed [this] together with Mihramano, the son of Bozomihro [Device 5] jointly [Device 2]. (A: Device 1 jointly, Device 2, B: Liiago, Device 3, Adego, Device 4).
Jat clans
- Anda (from Andēzo of Inscription)
- Maan (See Xirgomano, Eiiomano, Mihramano in inscription)
- Panwar (Burzmihr Puhr of Inscription)
Jat History
Bhim Singh Dahiya[8] mentions the famous Surkh Kotal inscription written in Greek and relating to the year 31 of Saka ara. Here the work done was the repair of a sanctuary built by Kanishka. The inscription was recorded by two persons whose names are given as Mihra Mān and Burzmihr Puhr. Here again the two persons who are of course, important officers of the empire were two Jats from the Mān and Puhr/Pawar clans. Again the names here are decidedly Iranian. [9]
दलीप सिंह अहलावत[10] ने लिखा है - जाट्स दी ऐन्शन्ट रूलर्ज पृ० 40 पर लेखक बी० एस० दहिया ने लिखा है कि “सम्राट् कनिष्क (सन् 120 से 162 ई० तक) के बनाए धार्मिक स्थान की मरम्मत करते समय यूनानी भाषा में लिखा हुआ एक प्रसिद्ध सुर्ख कोतल शिलालेख प्राप्त हुआ था। यह शिलालेख दो व्यक्तियों ने लिखा था जिनके नाम मिहरमान और बुर्जमिहर पुहर लिखे हैं। उस साम्राज्य के ये दोनों महत्वपूर्ण पदाधिकारी थे। उनके ये नाम ईरानी भाषा में थे। दोनों जाट थे। एक का गोत्र मान तथा दूसरे का गोत्र पंवार था।” [11]
References
- ↑ Cultural Property Training Resource Afghanistan
- ↑ राजकीय संग्रहालय मथुरा
- ↑ व्यक्ति प्रतिमाओं के विशेष अध्ययन के लिए देखिये: T.G.Aravamuthan, Portrait Sculpture in South India ,London, 1931
- ↑ C.M.Keiffer, Kushana Art and the Historical Effigies of Mat and Surkh Kotal, Marg, Vol 15, Number 2, March 1962, p.43-48
- ↑ Source: Warwick Ball, Archaeological Gazetteer of Afghanistan, 1982, n. 1123
- ↑ Cultural Property Training Resource Afghanistan
- ↑ "Languages and literature of the Kushan Empire" János Harmatta. (1994). In: History of civilizations of Central Asia, Volume II, pp. 427-432. UNESCO Publishing. Paris. ISBN 92-3-102846-4.
- ↑ Bhim Singh Dahiya, Jats - The Ancient Rulers, p.40
- ↑ BSOAS, Vol XXIII, pt. I , pp 47-55
- ↑ Jat History Dalip Singh Ahlawat/Chapter III,p.301
- ↑ Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies (University of London) vol. XXIII, Pt. 1, PP 47-55)।

