Chaul Maharashtra
| Author:Laxman Burdak, IFS (R) |
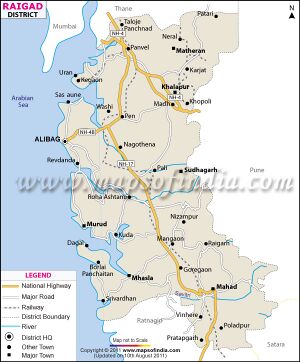
Chaul (चौल) is a ruined, former city of Portuguese, in Raigad District of Maharashtra.
Location
It is located 60 km south of Mumbai, in Raigad District of Maharashtra state in western India. The important towns located on the banks of Kundalika are Kolad, Korlai, Chaul, Roha and Salav.
Jat clans
History
In 1508, the Egyptian Mamluks, allied with the Gujarat Sultanate vanquished the Portuguese in the Battle of Chaul. The first Portuguese settlement at Chaul took place in 1521 with the construction of the first fort on the south bank of the Kundalika River. In October 1531, the Portuguese erected a new square stone fortress, named Santa Maria do Castello, which contained a church and dwellings for 120 men. A town developed around the fortress, but a 1558 treaty precluded fortifying the town. The town was destroyed in a 1570-71 siege by the Nizam Shahi Sultan of Ahmadnagar, but a treaty was concluded which lifted the siege, and the town was rebuilt and surrounded by walls and bastions.
A fort (Korlai fort) was built on the Morro de Chaul, a rocky promontory on the north side of the river opposite the town. The town withstood several further attacks, and its defence works were expanded in 1613.
Chaul was part of Portuguese India's Northern Province, which by the mid 17th century extended for 100 km along the coast of present-day Maharashtra and Gujarat, from Chaul in the south to Daman in the north. The headquarters of the northern province was at Baçaim (modern Vasai) north of Bombay.
During the later 17th and early 18th centuries Portuguese India declined economically and politically, and Chaul lost its former importance. As the power of the Mughal Empire declined in the early 18th century, the Marathas expanded their control of central and western India. The Portuguese colony of Kalyan was captured by the Marathas in 1720, and in 1737 the Maratha general Angria began a concerted campaign to capture the remaining Portuguese territories. Chaul and the Morro de Chaul came under siege in March 1739, but the siege was raised in October. After the capture of Baçaim in 1740, a peace treaty was concluded, and on 18 September 1740, Chaul was ceded by treaty to the Marathas. The city was subsequently abandoned and left in ruins.
The village of Korlai, near the ruins of Chaul, is still home to speakers of Portuguese Creole.
Korlai Fort
Korlai Fort is situated near Korlai Village in Murud taluka. Korlai Fort (also called Morro or Castle Curlew[1]), known in Portuguese as Fortaleza do Morro de Chaul, is a Portuguese fortification in the town of Korlai,[2] Maharashtra, India. It was built on an island (Morro de Chaul)[3] which guards the way to the Revdanda Creek. It was meant as a companion to the fort at Chaul. At this strategic position the Portuguese could use it to defend their province which stretched from Korlai to Bassein. Vestiges of the Portuguese occupation are manifested in the distinct dialect of the Korlai villages inhabitants which is a Luso-Indian Portuguese Creole called Kristi.
Rail: The nearest railway station is at Roha which is 42 km from the fort.
Road: Korlai is around 117 Km south of Mumbai via State Highway 104 and 24 km from Alibag via State Highway 91.
Kundalika River
The Kundalika is a small river flowing from the hills of Sahyadri to the Arabian Sea. This river originates at a small town called Bhira in the Indian state of Maharashtra, 150 km south east of Bombay (Mumbai).
The important towns located on the banks of Kundalika are Kolad, Korlai, Chaul, Roha and Salav.
A historical trade route called Savalya Ghat descends in Kundalika Valley from Tamhini Ghat Road. Beautifully carved staircases exist at some places, and there are two small water cisterns. This river was a means of trade in ancient times. There are many forts on the hills along the river, including Surgad, Avchitgad, Birwadi fort, Korlai fort and Revdanda.
Devkund Waterfall
Devkund Waterfall is located near Bhira, in Raigad district. The waterfall is a type of 'plunge' waterfall in nature pouring in massive amounts of water on the rocky surface underneath of Kundalika river. Devkund Waterfall is a popular spot for one day picnics.[4][5]
चौल
पुर्तगाली भारत का पूर्व शहर, चौल शहर अब एक खंडहर के रूप में है। यह मुंबई से लगभग 60 किमी दूर स्थित है, महाराष्ट्र में दक्षिण की ओर यह रायगढ़ जिले के अंतर्गत आता है। इतिहास इस तथ्य का गवाह है कि पुर्तगाली पहले चौल में, लगभग 500 साल पूर्व, 1521 में आये। शहर, बाद में अहमदनगर के निजाम शाही सुल्तान के द्वारा 1570 में नष्ट कर दिया गया था। चौल के शहर बाद में 1613 में पुनः बनाया गया। घूमने के स्थान यह पर्यटन स्थल अलीबाग के पास स्थित है और कई राजवंशों के उत्थान और पतन का गवाह है। शहर पुर्तगाली खंडहर, पुराने चर्चों और आराधनालयों के साथ भरा हुआ है। चौलो काडू लाइटहउस कोरलाई पोर्ट के निकट है और देखने लायक है। कोरलाई फोर्ट, चौल किले के साथ दो ऐतिहासिक स्थान हैं जो आपको अतीत में ले जाते हैं। एक प्रकृति प्रेमी को रेवडंडा समुद्र तट को अवश्य देखना चाहिए, जो एक सुंदर स्थान है जहाँ पर अपने निष्क्रिय विचारों में डूब क्षितिज को देखा जा सकता है। दत्ता मंदिर न केवल एक महत्वपूर्ण धार्मिक जगह है, बल्कि इसकी ऐतिहासिक प्रासंगिकता भी है। इस जगह के ऊपर से दृश्य मोहक है। [6]
External links
References
- ↑ "Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society". v4. Bombay Natural History Society. 1889: 291.
- ↑ Kapadia, Harish (2004). Trek the Sahyadris. Indus Publishing. p. 72. ISBN 81-7387-151-5.
- ↑ Indica. Saint Xavier's College, Bombay Heras Institute of Indian History and Culture. 2004.
- ↑ Devkund waterfalls
- ↑ The Secret Devkund Waterfalls On The Mumbai-Panvel-Goa Road Are Not So Secret Anymore
- ↑ https://hindi.nativeplanet.com/chaul/#overview

