Ramanathapuram
| Author:Laxman Burdak, IFS (R) |
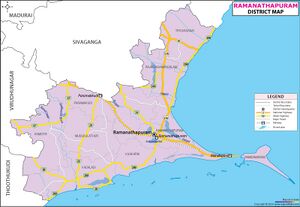
Ramanathapuram (रामनाथपुरम्), also known as Ramnad, is a city and district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is located on Ram Van Gaman Path.
Origin
Variants
- Ramanathapuram (रामनाथपुरम्) (AS, p.427)
- Ramnad (रामनाद)
- Ramanada रामनाद, मद्रास, (AS, p.790)
History
The region is well known since Puranic ages. The estate of Ramnad included the holy island city of Rameswaram, from where, legend has it that the god Rama launched his invasion of Ravana's Lanka. On the conclusion of the war and Rama's success in it, he appointed a Sethupathi or "lord of the bridge" to guard the way to the island. The "bridge" referred to here is the legendary Adam's Bridge or Rama's Bridge which was believed to have been constructed by Rama. The chieftains of Ramnad were entrusted with the responsibility of protecting the bridge, hence the appellation.
Historically, for a short period, this area had been under the Chola Dynasty when Rajendra Chola I brought it under his territory in 1063 AD.
In the late 12th and early 13th century, this province was ruled by Hazrat Sulthan Syed Ibrahim shaheed of Ervadi. Later on His heirs were ruling the province following a peace treaty with the Sethupathis. From then, until the early 15th century the present territories of Ramanathapuram district — comprising the taluks Tiruvadanai, Kilakarai, Paramakudi, Kamuthi, Mudukulathur, Ramanathapuram and Rameswaram — were included in the Pandyan Empire.
During the 14th and 15th centuries, the traditional chieftain of the region who belonged to the Maravar caste was officially recognized as Sethupathi by the Nayak king of Madurai. The chieftain of Ramnad, in return, recognized the sovereignty of the Nayak king over his lands. When the power of the Nayak kings of Madurai began to decline in the late 17th century, the chieftains of Ramnad asserted their independence. In the late 17th century, Raghunatha Kilavan crowned himself king of Ramnad and changed his seat from Pogalur to Ramnad close to the east coast. He erected massive fortifications to protect his capital. In 1725, the king of Tanjore claimed the northern part of the Ramnad kingdom (the Aranthangi region) up to the river Pambar in return for his services during the civil war in Ramnad. A vassal of Ramnad who was amongst the victors in the civil war took over the westerly located Sivaganga region, thereby leaving only three-fifths of the kingdom actually in the hands of the king of Ramnad. At the beginning of the 18th century, family disputes over succession resulted in the division of Ramanathapuram. With the help of the King of Thanjavur in 1730, one of the chieftains deposed the Sethupathi and became the Raja of Sivaganga.
दर्भशयनम्
विजयेन्द्र कुमार माथुर[1] ने लेख किया है ...दर्भशयनम् (मद्रास) (AS, p.427) रामनाद अथवा रामनाथपुरम् से 6 मील दूर है. समुद्र यहां से 3 मील है. कहा जाता है कि समुद्र को पार करने के लिए श्री रामचंद्र ने समुद्र से 3 दिन तक प्रार्थना की थी और इसी स्थान पर कुश-आसन पर शयन कर उन्होंने व्रत का अनुष्ठान किया था जिसके कारण इस स्थान को दर्भशयन कहते हैं. बाल्मीकि रामायण में इस घटना का वर्णन इस प्रकार है-- 'तत: सागरबेलायां दर्भानास्तीर्यराघव:, अंजलिं प्राङ्गमुख: कृतवा प्रतिशिश्ये महोदधे', युद्ध कांड 21,1 अर्थात तब समुद्र के तीर पर कुश या दर्भ बिछाकर रामचंद्र पूर्व की ओर समुद्र को हाथ जोड़कर सो गए. 'स त्रिरात्रौषितस्तत्रनयज्ञो धर्मवत्सल: उपासत तदाराम: सागरं सरितांपतिम्', युद्ध कांड 27,11 अर्थात नीतज्ञ, धर्मपरायण राम ने विधिपूर्वक तीन रात वहाँ रहकर सरितापति समुद्र की उपासना की.
रामेश्वरम् से कुछ दूर दक्षिण में एक स्थान है, जिसे ‘दर्भशयनम्’ कहते है; यहीं पर राम ने पहले समुद्र में सेतु बांधना शुरू किया था। इस कारण यह स्थान आदि सेतु भी कहलाता है। [2]
रामनाद
रामनाद (AS, p.790) मद्रास (वर्तमान चेन्नई, तमिलनाडु) स्थित एक ऐतिहासिक स्थान है। रामनाद नरेश, रामेश्वर द्वीप के परंपरागत शासक माने जाते हैं। यह स्थान रामेश्वरम के मार्ग में है। यहाँ से 5 मील की दूरी पर 'त्रिपुलानी' और 10 मील पर 'देवीपाटन' के प्रसिद्ध प्राचीन मंदिर स्थित हैं।

