Taman
| Author:Laxman Burdak, IFS (R) |
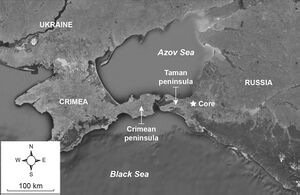
Taman is a peninsula and a locality in the present-day Krasnodar Krai of Russia.
Location
Taman borders the Sea of Azov to the North, the Strait of Kerch to the West and the Black Sea to the South.
Variants
- Taman Peninsula/Taman peninsula (Russian: Тама́нский полуо́стров, Tamanskiy poluostrov)
- Sindike Chersonesus/Sindikè chersònesus (Greek: Σινδική χερσόνησος, peninsula of the Sindi)
Etymology
One version of the origin of the name "Taman" claims its Circassian origin from "temen", a swamp that corresponds to the nature of the area.
Jat clans
Need further research find connection:
History
The area has evolved over the past two millennia from a chain of islands into today's peninsula. In ancient times the peninsula was known to the Greeks as Sindikè chersònesus (Greek: Σινδική χερσόνησος, peninsula of the Sindi) and Pontic Greek colonies of Hermonassa and Phanagoria stood on the peninsula, as did the later city of Tmutarakan.[1]
The Maeotae and Sindi settled in the area from ancient times. In the classical period it became part of the Bosporan kingdom; its inhabitants included Sarmatians, Greeks, Anatolian settlers from Pontus, and Jews. In the 4th century CE the area fell to the Huns; it was later the capital of Great Bulgaria and fell to the Khazars in the mid-7th century. Following the breakup of the Khazar Khaganate in c. 969, the peninsula formed part of a Khazar Jewish successor state under a ruler named David. By the late 980s it came largely into the possession of the Kievan Rus and of the Russian Principality of Tmutarakan before falling to the Kipchaks c. 1100. The Mongols seized the area in 1239 and it became a possession of Genoa, along with Gazaria in Crimea, in 1419.
In 2018, archaeologists discovered the remains of ancient Greek musical instruments, a harp and a lyre. The instruments discovered while examining an ancient necropolis located near the Volna settlement. Archaeologists say that a Greek polis existed there from the second quarter of the 6th century BC to the 4th century AD, which belonged to the Bosporan Kingdom.[2]
Jat History connections
Hukum Singh Panwar (Pauria)[3] writes that The Russian archaeologists discovered innumerable graves of the Saka Kings and chieftains in the Kuban, north of the Caucasus (7th-6th century B.C.), in the Crimea, in south Russia, in the Taman peninsula, in the Dnieper Valley as far up as Kiev, as well as in the Don, Donetz and Volga basins as far westwards as the Urals, in the Dunube basin as far west as Hungary and in what used to be East Prussia and is now Western Poland (6th-5th century B.C.)107. Excavations of the Royal Scythian tombs by M.P. Gryazhnov, S.I. Rudenko and others at Pazyryk and other sites in the Western Altai and nearer to lake Baikal (6th-4th century B.C. contemporary of Herodotus's Royal Scythians of South Russia) were most interesting and informative[4].
107. Lister. op.cit., pp. 70f
References
- ↑ "Greek colonization in the northern Black Sea area". German Archaeological Institute.
- ↑ Russian archaeologists discover ancient Greek musical instruments near Crimea
- ↑ The Jats:Their Origin, Antiquity and Migrations/The identification of the Jats,p.318
- ↑ Artamonov, M.I.; 'Frozen Tombs of the Scythians', in the Scientific American, May, 1965, Vol. 212, No.5, pp. 100-109.
Back to Places

