Uxians
| Author:Laxman Burdak, IFS (R) |
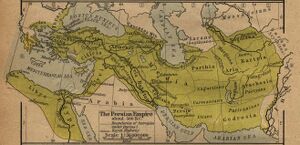
Uxians or the Uxii were a tribal confederation[1] of non-Iranian semi-nomadic people who lived somewhere in the Zagros Mountains. They were classified by Nearchus as among the four predatory peoples of the southwest along with the Mardi, Sousii, and Elymaei. They raided the settled people of Iran and raised sheep. Arrian[2] writes....that in the land of the Uxians the horse of Alexander named Bucephalas vanished.
Variants
- Uxians (Anabasis by Arrian,p. 155, 161, 174, 175, 297, 387, 398.)
Jat Gotras Namesake
- Ojla = Uxians (Anabasis by Arrian,p. 155, 161, 174, 175, 297, 387, 398.)
- Ujjihana = Uxians (Anabasis by Arrian,p. 155, 161, 174, 175, 297, 387, 398.)
History
Uxians came to the aid of Darius-III (the last king of the Achaemenid Empire of Persia) and were part of alliance in the battle of Gaugamela (331 BC) formed by Darius-III in war against Alexander the Great at Arbela, now known as Arbil, which is the capital of Kurdistan Region in northern Iraq. [3] --- The Uxii also tolled passing armies until they were defeated by Alexander the Great at the Battle of the Uxian Defile.[4] After some time, the Uxians regained independence. Some think that the tolling was a gift tradition from the Persian kings to local tribes, and wasn't forced (especially as the need for Darius to go out of his way to pay the "toll". Greek authors may have misinterpreted the practice or spun it to make Darius look weak. Achaemenid policy on people such as the Uxii involved gift giving and condensing tribal confederations together and then setting up a loyal ruler for that tribe.[5]
During Alexander's conquest of Persia, the Uxians were led by Madates. They could be divided into two groups, one which lived in the plains and was sedentary and one which lived in the mountains and was nomadic. The plain Uxians surrendered to Alexander, while the Mountain Uxians demanded a toll. The division of the Uxians into a sedentary and nomadic component is similar to many other tribes of the Middle East and Central Asia.[6]
The Uxii may have come from Khuzistan and as such are likely related to the Elymaei and Elamites.
The mother of Darius III, Sisygambis, was likely Uxian in origin, and later negotiated the release of Uxian prisoners headed by Madates.[7]
Ch.8 Description of Darius-III's Army at Arbela against Alexander
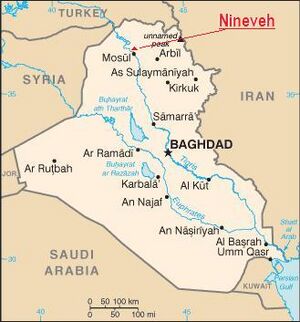
Uxians came to the aid of Darius-III (the last king of the Achaemenid Empire of Persia) and were part of alliance in the battle of Gaugamela (331 BC) formed by Darius-III in war against Alexander the Great at Arbela, now known as Arbil, which is the capital of Kurdistan Region in northern Iraq.
Arrian[8] writes....Alexander therefore took the royal squadron of cavalry, and one squadron of the Companions, together with the Paeonian scouts, and marched with all speed; having ordered the rest of his army to follow at leisure. The Persian cavalry, seeing Alexander, advancing quickly, began to flee with all their might. Though he pressed close upon them in pursuit, most of them escaped; but a few, whose horses were fatigued by the flight, were slain, others were taken prisoners, horses and all. From these they ascertained that Darius with a large force was not far off. For the Indians who were conterminous with the Bactrians, as also the Bactrians themselves and the Sogdianians had come to the aid of Darius, all being under the command of Bessus, the viceroy of the land of Bactria. They were accompanied by the Sacians, a Scythian tribe belonging to the Scythians who dwell in Asia.[1] These were not subject to Bessus, but were in alliance with Darius. They were commanded by Mavaces, and were horse-bowmen. Barsaentes, the viceroy of Arachotia, led the Arachotians[2] and the men who were called mountaineer Indians. Satibarzanes, the viceroy of Areia, led the Areians,[3] as did Phrataphernes the Parthians, Hyrcanians, and Tapurians,[4] all of whom were horsemen. Atropates commanded the Medes, with whom were arrayed the Cadusians, Albanians, and Sacesinians.[5] The men who dwelt near the Red Sea[6] were marshalled by Ocondobates, Ariobarzanes, and Otanes. The Uxians and Susianians[7] acknowledged Oxathres son of Aboulites as their leader, and the Babylonians were commanded by Boupares. The Carians who had been deported into central Asia, and the Sitacenians[8] had been placed in the same ranks as the Babylonians. The Armenians were commanded by Orontes and Mithraustes, and the Cappadocians by Ariaoes. The Syrians from the vale between Lebanon and Anti-Lebanon (i.e. Coele-Syria) and the men of Syria which lies between the rivers[9] were led by Mazaeus. The whole army of Darius was said to contain 40,000 cavalry, 1,000,000 infantry, and 200 scythe-bearing chariots.[10] There were only a few elephants, about fifteen in number, belonging to the Indians who live this side of the Indus.[11] With these forces Darius had encamped at Gaugamela, near the river Bumodus, about 600 stades distant from the city of Arbela, in a district everywhere level;[12] for whatever ground thereabouts was unlevel and unfit for the evolutions of cavalry, had long before been levelled by the Persians, and made fit for the easy rolling of chariots and for the galloping of horses. For there were some who persuaded Darius that he had forsooth got the worst of it in the battle fought at Issus, from the narrowness of the battle-field; and this he was easily induced to believe.
1. Cf. Aelian (Varia Historia, xii. 38).
2. Arachosia comprised what is now the south-east part of Afghanistan and the north-east part of Beloochistan.
3. Aria comprised the west and north-west part of Afghanistan and the east part of Khorasan.
4. Parthia is the modern Khorasan. Hyrcania was the country south and south-east of the Caspian Sea. The Tapurians dwelt in the north of Media, on the borders of Parthia between the Caspian passes. Cf. Ammianus, xxiii. 6.
5. The Cadusians lived south-west of the Caspian, the Albanians on the west of the same sea, in the south-east part of Georgia, and the Sacesinians in the north-east of Armenia, on the river Kur.
6. "The Red Sea was the name originally given to the whole expanse of sea to the west of India as far as Africa. The name was subsequently given to the Arabian Gulf exclusively. In Hebrew it is called Yam-Suph (Sea of Sedge, or a seaweed resembling wool). The Egyptians called it the Sea of Weeds.
7. The Uxians occupied the north-west of Persis, and Susiana was the country to the north and west of Persis.
8. The Sitacenians lived in the south of Assyria. ἐτετάχατο. is the Ionic form for τεταγμἑνοι ἦσαν.
9. The Greeks called this country Mesopotamia because it lies between the rivers Euphrates and Tigris. In the Bible it is called Paddan-Aram (the plain of Aram, which is the Hebrew name of Syria). In Gen. xlviii. 7 it is called merely Paddan, the plain. In Hos. xii. 12, it is called the field of Aram, or, as our Bible has it, the country of Syria. Elsewhere in the Bible it is called Aram-naharaim, Aram of the two rivers, which the Greeks translated Mesopotamia. It is called "the Island," by Arabian geographers.
10. Curtius (iv. 35 and 45) states that Darius had 200,000 infantry, 45,000 cavalry, and 200 scythed chariots; Diodorus (xvii. 53) says, 800,000 infantry, 200,000 cavalry, and 200 scythed chariots; Justin (xi. 12) gives 400,000 foot and 100,000 horse; and Plutarch (Alex., 31) speaks of a million of men. For the chariots cf. Xenophon (Anab., i 8, 10); Livy, xxxvii. 41.
11. This is the first instance on record of the employment of elephants in battle.
12. This river is now called Ghasir, a tributary of the Great Zab. The village Gaugamela was in the district of Assyria called Aturia, about 69 miles from the city of Arbela, now called Erbil.
Ch.17:Subjugation of the Uxians
Arrian[9] writes.... He (Alexander the Great) now set out from Susa, and, crossing the river Pasitigris,[1] invaded the country of the Uxians. Some of these people who inhabit the plains were under the rule of the viceroy of the Persians, and on this occasion surrendered to Alexander; but those who are called the mountaineers were not in subjection to the Persians, and at this time sent word to Alexander that they would not permit him to march with his forces into Persis, unless they received from him as much as they were in the habit of receiving from the king of the Persians for the passage through their mountains.[2] He sent the messengers back with instructions to come to the defiles, the possession of which made them think that the passage into Persis was in their power, promising them that they should there receive from him the prescribed toll. He then took the royal body-guards, the shield-bearing infantry, and 8,000 men from the rest of his army, and, under the guidance of the Susians, marched by night along a different road from the frequented one. Advancing by a route rough and difficult, on the same day he fell upon the villages of the Uxians, where he captured much booty and killed many of the people while still in their beds; but others escaped into the mountains. He then made a forced march to the defiles, where the Uxians resolved to meet him in mass in order to receive the prescribed toll. But he had already previously despatched Craterus to seize the heights, to which he thought the Uxians would retire if they were repelled by force; and he himself went with great celerity, and got possession of the pass before their arrival. He then drew up his men in battle array, and led them from the higher and more commanding position against the barbarians. They, being alarmed at Alexander's celerity, and finding themselves deprived by stratagem[3] of the position in which they had especially confided, took to flight without ever coming to close combat. Some of them were killed by Alexander's men in their flight, and many lost their lives by falling over the precipices along the road; but most of them fled up into the mountains for refuge, and falling in with Craterus, were destroyed by his men. Having received these gifts of honour[4] from Alexander, they with difficulty, after much entreaty, procured from him the privilege of retaining possession of their own land on condition of paying him an annual tribute. Ptolemy, son of Lagus, says that the mother of Darius,[5] on their behalf, entreated Alexander to grant them the privilege of inhabiting the land. The tribute agreed upon was a hundred horses, five hundred oxen, and 30,000 sheep a year; for the Uxians had no money, nor was their country fit for tillage; but most of them were shepherds and herdsmen.
1. A river flowing through Susiana, formed by the junction of the Eulaeus and Coprates.
2. Cf. Strabo, xv. 3.
3. πλεονεκτούμενοι, with dative, defrauded of. Cf. Demosthenes, 1035, 26.
4. γἐρα. An Homeric expression.
5. Named Sisygambis (Curtius, v. 11).
References
- ↑ "Achaemenid Empire, Tribal Confederations of Southwestern Persia and Seven Families". Iranian Studies. 50 (2): 173–197. doi:10.1080/00210862.2016.1243986. ISSN 0021-0862.
- ↑ The Anabasis of Alexander/5b, Ch.19
- ↑ Arrian: The Anabasis of Alexander/3a, Ch.8
- ↑ electricpulp.com. "IRAN v. PEOPLES OF IRAN (2) Pre-Islamic – Encyclopaedia Iranica". www.iranicaonline.org.
- ↑ Bahadori, Ali (2017-03-04). "Achaemenid Empire, Tribal Confederations of Southwestern Persia and Seven Families". Iranian Studies. 50 (2): 173–197. doi:10.1080/00210862.2016.1243986. ISSN 0021-0862.
- ↑ Bahadori, Ali (2017-03-04). "Achaemenid Empire, Tribal Confederations of Southwestern Persia and Seven Families". Iranian Studies. 50 (2): 173–197. doi:10.1080/00210862.2016.1243986. ISSN 0021-0862.
- ↑ Bahadori, Ali (2017-03-04). "Achaemenid Empire, Tribal Confederations of Southwestern Persia and Seven Families". Iranian Studies. 50 (2): 173–197. doi:10.1080/00210862.2016.1243986. ISSN 0021-0862.
- ↑ The Anabasis of Alexander/3a, Ch.8
- ↑ The Anabasis of Alexander/3b, Ch. 17

