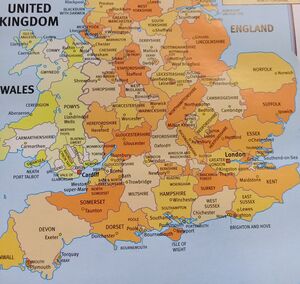
West Midlands
| Author:Laxman Burdak, IFS (R) |
West Midlands is the second most ethnically diverse region of the UK (London being the most diverse). The West Midlands is one of nine official regions of England at the first level of International Territorial Level for statistical purposes. It covers the western half of the area traditionally known as the Midlands.
Location
The West Midlands region consists of the counties of Herefordshire, Shropshire, Staffordshire, Warwickshire, West Midlands and Worcestershire. The region has seven cities Birmingham, Coventry, Hereford, Lichfield, Stoke-on-Trent, Wolverhampton and Worcester.
Midlands
The Midlands are a part of England that broadly correspond to the Kingdom of Mercia of the Early Middle Ages, bordered by Wales, Northern England and Southern England. The Midlands were important in the Industrial Revolution of the 18th and 19th centuries. They are split into the West Midlands and East Midlands. The region's biggest city, Birmingham – often considered the social, cultural, financial and commercial centre of the Midlands, – is the second-largest city and metropolitan area in the United Kingdom.
History
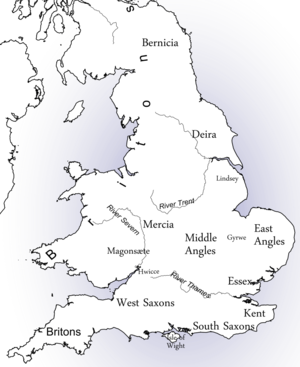
Further information: Mercia
Geography
The West Midlands region is geographically diverse, from the urban central areas of the West Midlands conurbation to the rural counties of Herefordshire, Shropshire and Worcestershire which border Wales. The region is landlocked, however, the longest river in the UK, the River Severn, traverses the region southeastwards, flowing through the county towns of Shrewsbury and Worcester, and the Ironbridge Gorge, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Staffordshire is home to the industrialised Potteries conurbation, including the city of Stoke-on-Trent, and the Staffordshire Moorlands area, which borders the southeastern Peak District National Park near Leek. The region also encompasses five Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty, the Wye Valley, Shropshire Hills, Cannock Chase, Malvern Hills, and parts of the Cotswolds. Warwickshire is home to the towns of Stratford upon Avon, birthplace of writer William Shakespeare, Rugby, the birthplace of Rugby football and Nuneaton, birthplace to author George Eliot.
The official region contains the ceremonial counties of Herefordshire, Shropshire, Staffordshire, Warwickshire, West Midlands and Worcestershire.
There is some confusion in the use of the term "West Midlands", as the name is also used for the much smaller West Midlands county and conurbation which is in the central belt of the Midlands and on the eastern side of the West Midlands Region. It is also still used by various organisations within that area, such as West Midlands Police and West Midlands Fire Service.
The highest point in the region is Black Mountain, at 703 metres (2,307 ft) in west Herefordshire on the border with Powys, Wales.
The region contains five Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONBs), including the Shropshire Hills, Malvern Hills and Cannock Chase, and parts of the Wye Valley and Cotswolds. The Peak District national park also stretches into the northern corner of Staffordshire.
Ethnicity
The West Midlands is the second most ethnically diverse region of the UK (London being the most diverse). This is in large part due to the West Midlands conurbation, which is highly diverse. The ethnic makeup of the West Midlands as a whole as measured by the 2011 census was as follows:
| Ethnic group | 1991[1] | 2001[2] | 2011[3] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |
| White: Total | 4,725,824 | 91.8% | 4,674,296 | 88.74% | 4,633,669 | 82.7% |
| White: British | 4,537,892 | 86.15% | 4,434,333 | 79.2% | ||
| White: Irish | 73,136 | 1.38% | 55,216 | 1.0% | ||
| White: Irish Traveller/Gypsy | - | - | 4,734 | 0.1% | ||
| White: Other | 63,268 | 1.2% | 139,386 | 2.5% | ||
| Asian or Asian British: Total | 297,829 | 5.8% | 401,672 | 7.62% | 604,435 | 10.8% |
| Asian or Asian British: Indian | 158,731 | 178,691 | 3.39% | 218 439 | 3.9% | |
| Asian or Asian British: Pakistani | 98,612 | 154,550 | 2.93% | 227,248 | 4.1% | |
| Asian or Asian British: Bangladeshi | 19,415 | 31,401 | 0.59% | 52,477 | 0.9% | |
| Asian or Asian British: Chinese | 9,588 | 16,099 | 0.3% | 31,274 | 0.6% | |
| Asian or Asian British: Asian Other | 11,483 | 20,931 | 0.39% | 74,997 | 1.3% | |
| Black or Black British: Total | 102,206 | 2% | 104,032 | 1.97% | 182,125 | 3.3% |
| Black or Black British: Caribbean | 78,082 | 82,282 | 1.56% | 86,794 | 1.6% | |
| Black or Black British: African | 5305 | 11,985 | 0.22% | 64,253 | 1.2% | |
| Black or Black British: Other | 18,819 | 9,765 | 0.18% | 31,078 | 0.6% | |
| Mixed : Total | 73,225 | 1.39% | 131,714 | 2.4% | ||
| Mixed: White and Caribbean | 39,782 | 0.75% | 68,533 | 1.2% | ||
| Mixed: White and African | 3,683 | - | 9,232 | 0.2% | ||
| Mixed: White and Asian | 18,160 | 0.34% | 32,561 | 0.6% | ||
| Mixed: Other Mixed | 11,600 | 0.22% | 21,388 | 0.4% | ||
| Other: Total | 24,328 | 0.47% | 14,083 | 0.26% | 49,904 | 0.9% |
| Other: Arab | - | - | 18,079 | 0.3% | ||
| Other: Any other ethnic group | 24,328 | 0.47% | 14,083 | 0.26% | 31,825 | 0.6% |
| Total | 5,150,187 | 100% | 5,267,308 | 100% | 5,601,847 | 100% |
Jat History
Bharatpur (भरतपुर) is a village Aston in England. Aston is a ward of Central Birmingham, England. Located immediately to the north-east of Central Birmingham, Aston constitutes a ward within the metropolitan authority.
Origin: The fort of Bharatpur is the only fort in India which was never physically captured by the British. The British were impressed by the bravery of Jats of Bharatpur. So they named this village after Bharatpur.
Ram Sarup Joon[4] writes that ... On 7th Jan. 1805 Lord Lake explored every possible avenue to penetrate the fort. A large number of British Officers and soldiers were killed in this action, the supply of rations and ammunition ran short and they failed in capturing the fort. They employed 5 inch and 7 inch guns but these did not make much impression on the thick mud walls. After two days, they succeeded in creating a break in the Southern Wall and the fort was charged by four Indian units and 1,500 British troops. The Jats repulsed this attack after inflicting heavy casualties. Colonel Maitland and 400 troops were killed. The British advanced for the third time and attacked the fort under the covering fire of heavy Artillery. The troops bravely crossed the mote and tried to scale the walls of the fort. As they came up the Jats kept killing them till the mote was filled with dead bodies, General Smith and Col Meeker, commanders of the British troops requested Lord Lake to sign a peace treaty with Jats.
ब्रिटेन पर जूट्स, सेक्सन्स एंगल्स की विजय (410 ई० से 825 ई०)
दलीप सिंह अहलावत[5] लिखते हैं: जूट्स, सेक्सन्स और एंगल्स लोग जर्मनी की एल्ब नदी के मुहाने और डेन्मार्क के तट पर रहते थे। ये लोग बड़े बहादुर थे तथा लूटमार किया करते थे। ये क्रिश्चियन धर्म के विरोधी थे।
ब्रिटेन से रोमनों के चले जाने के बाद ब्रिटेन के लोग बहुत कमजोर और असहाय थे। इन लोगों पर स्काटलैंड के केल्टिक कबीलों, पिक्ट्स और स्काट्स ने हमला कर दिया। ब्रिटेन निवासियों की इसमें भारी हानि हुई। इनमें इतनी शक्ति न थी कि वे इन हमलों करने वालों को रोक सकें। इसलिए मदद के लिए इन्होंने जूट लोगों को बुलाया। जूट्स ने उसी समय ब्रिटिश सरदार वरटिगर्न के निमन्त्रण को स्वीकार कर लिया। जटलैण्ड से जाटों की एक विशाल सेना अपने जाट नेता हेंगिस्ट और होरसा के नेतृत्व में सन् 449 ई० में केण्ट (Kent) में उतर गई। इन्होंने पिक्ट्स और स्कॉट्स को हराया और वहां से बाहर निकाल दिया। उन्हें भगाने के बाद जाट ब्रिटेन के लोगों के विरुद्ध हो गये और उन्हें पूरी तरह से अपने वश में कर लिया और 472 ई० तक पूरे केण्ट पर अधिकार कर लिया। यहां पर आबाद हो गये। इसके अतिरिक्त जाटों ने अपना निवास व्हिट द्वीप में किया1।
जटलैण्ड के जाटों की विजय सुनकर उनके दक्षिणवासी सेक्सन्स तथा एंगल्स भी ललचाये। सर्वप्रथम सेक्सन्स ब्रिटेन में पहुंचे और उन्होंने ऐस्सेक्स, मिडिलसेक्स और वेस्सेक्स नाम से तीन राज्य स्थापित किये। वहां पर इन्होंने कुछ बस्तियां आबाद कर दीं। ब्रिटेन की जनता ने बड़ी वीरता से सेक्सन्स का मुकाबला किया और 520 ई० में मोण्डबेडन ने उन्हें करारी हार दी। इस तरह से
- 1. आधार लेख - इंगलैण्ड का इतिहास पृ० 16-17, लेखक प्रो० विशनदास; हिस्ट्री ऑफ ब्रिटेन पृ० 21-22, लेखक रामकुमार लूथरा, अनटिक्विटी ऑफ जाट रेस, पृ० 63-66, लेखक: उजागरसिंह माहिल; जाट्स दी ऐन्शन्ट रूलर्ज पृ० 86 लेखक बी० एस० दहिया तथा जाट इतिहास अंग्रेजी पृ० 43, लेखक ले० रामसरूप जून।
जाट वीरों का इतिहास: दलीप सिंह अहलावत, पृष्ठान्त-399
सेक्सन्स का बढ़ना कुछ समय के लिए रुक गया। परन्तु 577 ई० में डियोरहम की लड़ाई में सेक्सन्स ने केब्लिन के नेतृत्व में ब्रिटेन लोगों पर पूरी विजय प्राप्त कर ली तथा उनको अपना दास बनाए रखा। यह कामयाबी जूट्स (जाटों) की सहायता से हुई थी जिसके लिए सेक्सन्स ने उनसे मांग की थी1।
अब प्रश्न पैदा होता है कि उन जूट्स (जाटों) का क्या हुआ जिन्होंने हेंगिस्ट और होरसा के नेतृत्व में ब्रिटेन के एक बड़े क्षेत्र पर अधिकार कर लिया था और सेक्सन्स को सहायता देकर उनका ब्रिटेन पर अधिकार करवाया। इसका उत्तर यही हो सकता है कि ब्रिटिश इतिहासकारों ने इनके इतिहास को लिखने में पक्षपात किया है।
सेक्सन्स के बाद एंग्ल्स पहुंचे जो जूट्स और सेक्सन्स की तरह ही लड़ाके तथा लुटेरे थे। सन् 613 ई० में नार्थम्ब्रिया के एंग्ल राजा ने ब्रिटेन पर आक्रमण करके विजय प्राप्त की। इसके बाद इन्हीं एगल्स के नाम पर ब्रिटेन का नाम इंग्लैंड हो गया। ये एंगल्स लोग भी जाट थे जैसा कि पिछले पृष्ठों पर लिखा गया है। इंग्लैंड में रहने वालों को अंग्रेज कहा गया।
एंगल्स लोग संख्या में दूसरों से अधिक थे इसी कारण से ब्रिटेन को एंगल्स की भूमि एवं इंग्लैंड कहा गया। इस तरह से ब्रिटेन पर जूट्स, सेक्सन्स और एंगल्स का अधिकार हो गया। इसी को ब्रिटेन पर अंग्रेजों की जीत कहा जाता है। इन तीनों कबीलों ने अपने अलग-अलग राज्य स्थापित किए। जूट्स ने केण्ट (Kent); सैक्सन्स ने सस्सेक्स (Sussex), एस्सेक्स (Essex), वेसेक्स (Wessex) और एंगल्स ने ईस्ट एंगलिया (East Anglia), मर्शिया (Mercia) और नार्थम्ब्रिया (Northumbria) के राज्य स्थापित किये। ये सातों राज्य सामूहिक रूप से हेपटार्की कहलाते थे। परन्तु ये राज्य स्वतन्त्र नहीं थे। इन सातों में जो शक्तिशाली होता था वह दूसरों का शासक बन जाता था।
ऊपर कहे हुए तीनों कबीले संगठित नहीं थे। नॉरमनों ने जब तक इस देश को नहीं जीता, इंग्लैंड में शक्तिशाली केन्द्रीय राज्य की स्थापना नहीं हो सकी। इन कबीलों ने देश से क्रिश्चियन धर्म और रोमन सभ्यता को मिटा दिया। आधुनिक इंग्लैंड एंग्लो-सैक्सन्स का बनाया हुआ है। आधुनिक अंग्रेज किसी न किसी रूप में इंग्लो-सैक्सन्स के ही वंशज हैं।
अंग्रेज जाति की उत्पत्ति और बनावट के सम्बन्ध में दो प्रतिद्वन्द्वी सिद्धान्त हैं।
- पलग्रोव, पियरसन और सेछम आदि प्रवीण मनुष्य रोमन केल्टिक सिद्धान्त को मानते हैं। उनका यह विचार है कि आधुनिक इंग्लैंड में रोमन-केल्टिक रक्त और संस्थाएं मौजूद हैं।
- ग्रीन और स्टब्स जैसे दूसरे प्रवीन मनुष्य ट्यूटानिक सिद्धान्त को मानते हैं। उनका यह विचार है कि ट्यूटानिक अर्थात् जूट, एंगल, सैक्सन और डेन लोगों का रक्त और संस्थाएं बहुत कुछ आधुनिक इंग्लैंड में पाई जाती हैं। इन दोनों में से ट्यूटानिक सिद्धान्त अधिक माना जाता
- 1. आधार लेख - इंग्लैण्ड का इतिहास पृ० 16-17, लेखक प्रो० विशनदास; ए हिस्ट्री ऑफ ब्रिटेन पृ० 21-22, लेखक रामकुमार लूथरा; अनटिक्विटी ऑफ जाट रेस, पृ० 63-66, लेखक: उजागरसिंह माहिल; जाट्स दी ऐन्शन्ट रूलर्ज पृ० 86 लेखक: बी० एस० दहिया तथा जाट इतिहास अंग्रेजी पृ० 43, लेखक ले० रामसरूप जून।
जाट वीरों का इतिहास: दलीप सिंह अहलावत, पृष्ठान्त-400
- है और आमतौर पर यह स्वीकार किया जाता है कि ब्रिटिश जाति मिले-जुले लोगों की जाति है। जिनमें ट्यूटानिक तत्त्व प्रधान है, जबकि केल्टिक तत्त्व भी पश्चिम में और आयरलैंड में बहुत कुछ बचा हुआ है1।
इसका सार यह है कि इंगलैंड द्वीपसमूह के मनुष्यों की रगों में आज भी अधिकतर जाट रक्त बह रहा है। क्योंकि केल्टिक आर्य लोग तथा जूट, एंगल, सैक्सन और डेन लोग जाटवंशज थे। आज भी वहां पर अनेक जाटगोत्रों के मनुष्य विद्यमान हैं जो कि धर्म से ईसाई हैं।
References
- ↑ As UK Census data past 2001 is unavailable through the ONS website, it has been recommended to use archival census collection websites to obtain data. Data is taken from United Kingdom Casweb Data services of the United Kingdom 1991 Census on Ethnic Data for England (Table 6)
- ↑ Office of National Statistics; 2001 Census Key Statistics
- ↑ 2011 Census: Ethnic Group, local authorities in England and Wales
- ↑ History of the Jats/Chapter X,p. 172
- ↑ Jat History Dalip Singh Ahlawat/Chapter IV, pp.399-401