Malla
| Author:Laxman Burdak, IFS (R) |
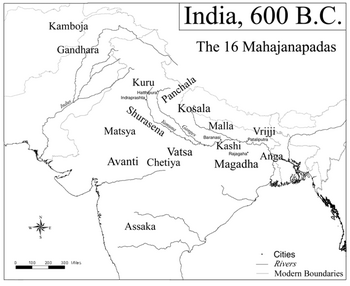
Malla (मल्ल) Malla (मल्ला) Mallah (मल्ला) Malay (मालय)[1] is a gotra of Jats found in Nimach district in Madhya Pradesh and Sindh province of Pakistan.
Variants
- Malladesha/Malla Desha (मल्लदेश)
- Mallarashtra/Malla Rashtra (मल्लराष्ट्र)
Origin
They are said to be originated from Chandravanshi King Malla (मल्ल) of the Mahabharata period.[2]
Mention by Panini
Mallaka (माल्लक) is mentioned by Panini in Ashtadhyayi. [3]
History
V. S. Agrawala[4] writes that The free clan called the Glaukanikoi (identical with the Glauchukāyanakas of Kashika on Panini IV.3.99) whose country lay in the fertile and populous regions lying in the south of Kashmir (the Bhimber and Rajauri districts) between the upper courses of the Jhelum and Chenab and the Ravi River, had as many as 37 cities, the smallest of which contained not less than 5000 inhabitants and up to 10000. Strabo affirms that in the territories of nine nations situated between Jhelum and Beas, such as the Malloi, Oxydrakai and others, there were as many as 500 cities.
They are Chandravanshi Jats. Malwa gets name after them. [5]They are mentioned in the Harivamsa and, as usual, a Mallāsura, (name of an Asura) is mentioned [6] Amarakosa defines Asura as Purvadeva i.e. a former god; obviously this must have been before the schism among the Aryans. [7] [8]
They have been mentioned in Mahabharata Bhisma Parva, along with Vahika, Vatdhan in shloka 45 as under:
In Rajatarangini
Rajatarangini[10] tells us....And when the stout Vijjaraja, hot with pride, struck Mallaka, he returned the blow, but both instantly fell on him. When the king appeared in view at the door of the four cornered room, Mallaka left his three antagonists and ran towards the king. At the time when the king was thus singled out, Kularaja ran swiftly in alarm and cut off the speed of Mallaka by cutting him in the bone of the buttocks. (p.208) (Mallaka→Malla)
Rajatarangini[11] tells us....Mallaraja had by queen Shveta three sons, Sahlana, &c, of whom the second had died before. Shamkharaja (Radda) had sought to kill the surviving Sahlana and Lothana and they fled in fear to the Navamatha. (p.32)
Rajatarangini[12] tells us....King Sussala shouted as he rode on his horse. When he was in the court-yard and had not yet seated himself on the throne, the voice of "Victory to Sussala," and the sound of drums were heard. In the family of Mallaraja, the, honor that was lost by Salhana and Lothana was won back again. Sussala embraced Salhana and Lothana who were on their horses, and clad in mail and addressed them both calling them as "boy" and "youth" and cunningly caused them to be disarmed. He then secured them and ordered them to be removed to another house. Thus he got the kingdom and entered the court. Salhana was captured after a reign of four months! minus three days, on the third day of bright moon in the month of Vaishakha of the year 88. (p.41)
Rajatarangini[13] tells...When the king Sussala learnt that Madava which had been to some extent pacified, had once more become disaffected, he again went to Vijayeshvara. The sons of Mallaraja (Sussala's father) created dangers for themselves by their evil tongue. ...Yashoraja who was from his boyhood used to flattering language became offended with the king for his harsh and insulting words. The vile Yashoraja was at Avantipura with a large army, and he thence marched and joined the enemy's party. On his going over to the enemies with the best part of the army, the king fled in distraction from Vijayakshetra. (VIII,p.97)
मल्ल या मालव जाट गोत्र
दलीप सिंह अहलावत[14] लिखते हैं: मल्ल या मालव चन्द्रवंशी जाट गोत्र है। रामायणकाल में इस वंश का शक्तिशाली राज्य था। सुग्रीव ने वानर सेना को सीता जी की खोज के लिये पूर्व दिशा में जाने का आदेश दिया। उसने इस दिशा के ब्रह्ममाल, विदेह, मालव, काशी, कोसल, मगध आदि देशों में भी छानबीन करने को कहा। (वा० रा० किष्किन्धाकाण्ड सर्ग 40, श्लोक 22वां) भरत जी लक्षमणपुत्र चन्द्रकेतु के साथ मल्ल देश में गए और वहां चन्द्रकेतु के लिए सुन्दर नगरी ‘चन्द्रकान्ता’ नामक बसाई जो कि उसने अपनी राजधानी बनाई। (वा० रा० उत्तरकाण्ड, 102वां सर्ग) इससे ज्ञात होता है कि उस समय मालव वंश का राज्य आज के उत्तरप्रदेश के पूर्वी भाग पर था। महाभारत काल में भी इनका राज्य उन्नति के पथ पर था। महाभारत सभापर्व 51वें अध्याय में लिखा है कि मालवों ने युधिष्ठिर के राजसूय यज्ञ में असंख्य रत्न, हीरे, मोती, आभूषण भेंट दिये। इससे इनके वैभवशाली होने का अनुमान लगता है। मालव क्षत्रिय महाभारत युद्ध में पाण्डवों एवं कौरवों दोनों की ओर से लड़े थे। इसके प्रमाण निम्न प्रकार हैं - महाभारत भीष्मपर्व 51वां, 87वां, 106वां के अनुसार मालव क्षत्रिय कौरवों की ओर से पाण्डवों के विरुद्ध लड़े। इससे ज्ञात होता है कि मालव (मल्ल) वंशियों के दो अलग-अलग राज्य थे। पाण्डवों की दिग्विजय में भीमसेन ने पूर्व दिशा में उत्तर कोसल देश को जीतकर मल्लराष्ट्र के अधिपति पार्थिव को अपने अधीन कर लिया। इसके पश्चात् बहुत देशों को जीतकर दक्षिण मल्लदेश को जीत लिया। (सभापर्व, अध्याय 30वां)। कर्णपर्व में मालवों को मद्रक, क्षुद्रक, द्रविड़, यौधेय, ललित्थ आदि क्षत्रियों का साथी बतलाया है। उन दिनों इनके प्रतीच्य (वर्तमान मध्यभारत) और उदीच्य (वर्तमान पंजाबी मालवा) नामक दो राज्य थे। इन दोनों देशों के मालवों ने महाभारत युद्ध में भाग लिया। (जाटों का उत्कर्ष पृ० 311, लेखक योगेन्द्रपाल शास्त्री।)
पाणिनि ऋषि ने इन लोगों को आयुधजीवी क्षत्रिय लिखा है। बौद्ध काल में मालवों (मल्ल लोगों) का राज्य चार स्थानों पर था। उनके नाम हैं - पावा, कुशीनारा, काशी और मुलतान। जयपुर में नागदा नामक स्थान से मिले सिक्कों से राजस्थान में भी इनका राज्य रहना प्रमाणित हुआ है। अन्यत्र भी प्राप्त सिक्कों का समय 205 से 150 ई० पूर्व माना जाता है। उन पर मालवगणस्य जय लिखा मिलता है। सिकन्दर के समय मुलतान में ये लोग विशेष शक्तिसम्पन्न थे। मालव क्षत्रियों ने सिकन्दर की सेना का वीरता से सामना किया और यूनानी सेना के दांत खट्टे कर दिये। सिकन्दर बड़ी कठिनाई से आगे बढ़ सका। उस समय मालव लोगों के पास 90,000 पैदल सैनिक, 10,000 घुड़सवार और 900 हाथी थे। मैगस्थनीज ने इनको ‘मल्लोई’ लिखा है और इनका मालवा मध्यभारत पर राज्य होना लिखा है। मालव लोगों के
जाट वीरों का इतिहास: दलीप सिंह अहलावत, पृष्ठान्त-254
नाम पर ही उस प्रदेश का नाम मालवा पड़ा था। [15]वहां पर आज भी मालव गोत्र के जाटों की बड़ी संख्या है। सिकन्दर के समय पंजाब में भी इनकी अधिकता हो चुकी थी। इन मालवों के कारण ही भटिण्डा, फरीदकोट, फिरोजपुर, लुधियाना के बीच का क्षेत्र (प्रदेश) ‘मालवा’ कहलाने लगा। इस प्रदेश के लगभग सभी मालव गोत्र के लोग सिक्खधर्मी हैं। ये लोग बड़े बहादुर, लम्बे कद के, सुन्दर रूप वाले तथा खुशहाल किसान हैं। सियालकोट, मुलतान, झंग आदि जिलों में मालव जाट मुसलमान हैं। मल्ल लोगों का अस्तित्व इस समय ब्राह्मणों और जाटों में पाया जाता है। ‘कात्यायन’ ने शब्दों के जातिवाची रूप बनाने के जो नियम दिये हैं, उनके अनुसार ब्राह्मणों में ये मालवी और क्षत्रिय जाटों में माली कहलाते हैं, जो कि मालव शब्द से बने हैं। पंजाब और सिंध की भांति मालवा प्रदेश को भी जाटों की निवासभूमि एवं साम्राज्य होने का सौभाग्य प्राप्त है। (जाट इतिहास पृ० 702, लेखक ठा० देशराज)। महात्मा बुद्ध के स्वर्गीय (487 ई० पू०) होने पर कुशिनारा (जि० गोरखपुर) के मल्ल लोगों ने उनके शव को किसी दूसरे को नहीं लेने दिया। अन्त में समझौता होने पर दाहसंस्कार के बाद उनके अस्थि-समूह के आठ भाग करके मल्ल, मगध, लिच्छवि, मौर्य ये चारों जाट वंश, तथा बुली, कोली (जाट वंश), शाक्य (जाट वंश) और वेथद्वीप के ब्राह्मणों में बांट दिये। उन लोगों ने अस्थियों पर स्तूप बनवा दिये (जाट इतिहास पृ० 32-33, लेखक ठाकुर देशराज।) मध्यप्रदेश में मालवा भी इन्हीं के नाम पर है।
मालव वंश के शाखा गोत्र - 1. सिद्धू 2. बराड़
Distribution in Punjab
Villages in Ludhiana district
- Mallah and Rasulpur Malla is village in Jagraon Tahsil in Ludhiana district, Punjab.
Distribution in Madhya Pradesh
Malla (मल्ला) gotra Jat sare found in Nimach district in Madhya Pradesh.
Villages in Nimach district
Distribution in Pakistan
Mallah are found in Districts Thatta (Sindh),
References
- ↑ O.S.Tugania:Jat Samuday ke Pramukh Adhar Bindu,p.55,s.n. 1999
- ↑ Mahendra Singh Arya et al.: Adhunik Jat Itihas, p.277
- ↑ V. S. Agrawala: India as Known to Panini, 1953, p.114
- ↑ India as Known to Panini, p.73
- ↑ Mahendra Singh Arya et al.: Adhunik Jat Itihas, p.277
- ↑ See Sanskrit English Dictionary ( M. Williams), p. 793
- ↑ cf. Rig Veda. viii, 25 , 4
- ↑ Bhim Singh Dahiya, Jats the Ancient Rulers ( A clan study), p. 286
- ↑ Bhisma Parva in Sanskrit
- ↑ Kings of Kashmira Vol 2 (Rajatarangini of Kalhana)/Book VIII (i), p.208
- ↑ Kings of Kashmira Vol 2 (Rajatarangini of Kalhana)/Book VIII, p.32
- ↑ Kings of Kashmira Vol 2 (Rajatarangini of Kalhana)/Book VIII, p.41
- ↑ Kings of Kashmira Vol 2 (Rajatarangini of Kalhana)/Book VIII,p.97
- ↑ जाट वीरों का इतिहास: दलीप सिंह अहलावत, पृष्ठ.254-255
- ↑ ठा० देशराज जाट इतिहास पृ० 702, इस मालवा नाम से पहले इस प्रदेश का नाम अवन्ति था।
Back to Jat Gotras
- Jat Gotras
- Ancient Jat Gotras
- Muslim Jat Gotras
- Jat Gotras in Pakistan
- Gotras after Places
- Madhya Pradesh
- Punjab
- Chandravanshi
- The Mahabharata Tribes
- Gotras in Nimach
- Gotras in Ludhiana
- Villages in Ludhiana
- Gotras in Thatta
- Rare Distribution
- Mahabharata People
- Mahabharata Places
- Mahabharata People and Places
- People and Places by Panini

