Gwadar
| Author:Laxman Burdak, IFS (R) |

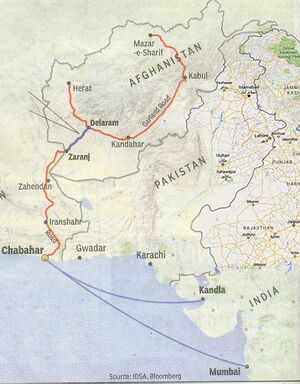
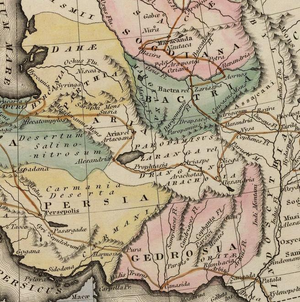
Gwadar (ग्वादर) is a city and district in Balochistan province of Pakistan.
Variants
Origin of name
- The word "Gwadar" is a combination of two Balochi words—"Gwat" ("wind") and "Dar" ("gateway"). So the meaning of Gwadar is "The gateway of wind".
- Another theory is that the name derived from the ancient name of Baluchistan, "Gedrosia", which was given by the Greeks to the arid area of southern Baluchistan.
Location
Gwadar is a port city on the southwestern coast of Pakistan's Balochistan province where the Arabian Sea meets the Persian Gulf just outside the Strait of Hormuz near key shipping routes in and out of the Persian Gulf. Under development as a free trade port, it is the district headquarters of Gwadar District. It is about 700 km from Karachi and 120 km from the Iranian border.
Jat clans
- Basoli: Basol River (Pakistan) may be the origin of clan. Basol River flows in Gwadar District of Balochistan Province, in southwestern Pakistan, drains a desert area of the Makran region.
Tahsils
Gwadar District is subdivided into five Tehsils or sub—districts:
History
Inhabitation of Gwadar, like most areas of Balochistan, appears to be ancient. The area shows inhabitation as early as the Bronze age with settlements around some of the area's oases. It is from this settlement pattern that word Makran, the original name of Balochistan, is derived. For a period, it was a region of the Achaemenid Persian Empire. It is believed to have been conquered by the founder of the Persian Empire, Cyrus the Great.
The capital of the satrapy of Gedrosia was Pura, which is thought to have been located near the modern Bampūr, in Iranian Balochistan. During the homeward march of Alexander the Great, his admiral, Nearchus, led a fleet along the modern-day Makran coast and recorded that the area was dry, mountainous, and inhabited by the "Ichthyophagoi" (or "fish eaters"), an ancient Greek rendering of the ancient Persian phrase "Mahi khoran," which has itself become the modern word "Makran".[1] After the collapse of Alexander's empire the area was ruled by Seleucus Nicator, one of Alexander's generals.
The region then reverted to Indian rule around about 303 BCE after Seleucus made peace with Emperor Chandragupta and ceded the territory to the Indian Empire.
Omani rule: The region remained on the sidelines of history for a millennium until the Arab-Muslim army of Umar captured Makran in 643 CE and over the intervening (and nearly equivalent) amount of time the area was contested by various powers. This was then followed by almost two centuries of local rule by the various Baloch tribes.
The city was visited by Ottoman Admiral Seydi Ali Reis in the 1550s and mentioned in his book Mirat ul Memalik (The Mirror of Countries), 1557.[2] According to Seydi Ali Reis, the inhabitants of Gwadar were Baloch and their chief was Malik Jelaleddin, son of Malik Dinar.
In the 15th century the Portuguese conquered many parts of India and Oman. They planned to proceed with annexation of the coastal area of Makran. They attacked Gwadar under the leadership of Vasco de Gama, but under the supervision of Commander Mir Ismaheel Baloch, the Portuguese were defeated by the Baloch. A few times the Portuguese looted and set the coastal villages on fire, but they failed to capture Gwadar. Cannons of the Portuguese army were found lying near the Central Jail of Gwadar, heirless. The grave of Mir Ismaheel Baloch is situated near the Mountain of Batal Gwadar, constructed by Mir Ismaheel Baloch himself during life. He died in 873 Hijri.[3]
ग्वादूर
विजयेन्द्र कुमार माथुर[4] ने लेख किया है ...ग्वादूर (मकरान, पाकिस्तान) (AS, p.311): ग्वादूर मकरान, पाकिस्तान में स्थित है। यह अरब सागर (फ़ारस की खाड़ी) के तट पर एक छोटा-सा बंदरगाह है, जिसका प्राचीन नाम 'बंदर' कहा जाता है। इसका उल्लेख टॉल्मी, आर्थोगोरस और एरियन (90 ई.-170 ई.) आदि प्राचीन विदेशी लेखकों ने भी किया है। मध्य काल में इस स्थान का बहुत महत्व था और ईरान की खाड़ी तथा भारत के पश्चिमी तट पर स्थित पत्तनों के व्यापारिक जहाज़ यहाँ रुकते थे। यूनानी लेखकों ने ग्वादूर के समीप समुद्र में अनेक प्रकार की विचित्र मछलियों का वर्णन किया है। 1581 ई में पुर्तग़ालियों ने इस नगर को जलाकर नष्ट कर दिया था। 17वीं शती में कलात के ख़ान ने इस बंदरगाह पर अधिकार कर लिया। उसने इसे ओमान के शासक सैयद सुल्तानबिन अहमद को सौंप दिया। इस प्रकार 1871 ई. तक इस पर मस्कट के सुल्तान का कब्जा रहा। इस वर्ष से ब्रिटेन का एक राजदूत भी यहाँ रहने लगा था। (दे. मकरान)
18वीं सदी के उत्तरार्ध में कलात के ख़ान नसीर ख़ाँ प्रथम ने ग्वादूर तथा पास की लगभग 300 वर्ग मील भूमि मस्कट के सुल्तान के भाई को आजीविका के लिये दे दी। पाकिस्तान का निर्माण होने पर ग्वादूर पत्तन तथा 'ओमान की खाड़ी' के उत्तर का कुछ क्षेत्र पाकिस्तान के अधिकार में आ गया है। ग्वादूर के अधिकांश निवासी मछुए हैं, जो 'मेद' कहलाते हैं। इस स्थान का व्यापार 'खोजा' मुसलमानों, जिन्हें 'लोटिया' कहते हैं, तथा हिन्दू गुजरातियों के हाथ में है। कराची तथा बंबई-बसरा-मार्ग पर चलने वाले जहाज़ यहाँ ठहरते हैं। कस्बे के पास ही पहाड़ी पर पत्थर से बना हुआ सुंदर बाँध है।[5]
Notable persons
External links
References
- ↑ Jona Lendering, Livius.org. "Gedrosia". Archived from the original on 2013-09-24.
- ↑ http://legacy.fordham.edu/halsall/source/16CSidi1.asp "Medieval Sourcebook: Sidi Ali Reis (16th Century CE): Mirat ul Memalik (The Mirror of Countries), 1557 CE". Fordham.edu. Archived from the original on 2014-03-10
- ↑ "GwÄdar - Imperial Gazetteer of India". p. 415. Archived
- ↑ Aitihasik Sthanavali by Vijayendra Kumar Mathur, p.311
- ↑ भारतकोश-ग्वादूर
Back to Jat Places in Pakistan

