Gaugamela
| Author: Laxman Burdak, IFS (R) |
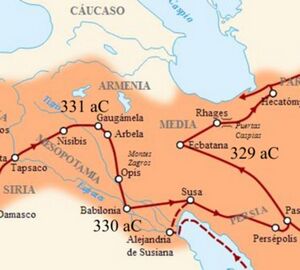
Gaugamela was the place near Arbela where the decisive battle of Alexander the Great's invasion of the Persian Achaemenid Empire was fought in 331 BC.
Location
Gaugamela was near the river Bumodus, about 600 stades distant from the city of Arbela. The river Bumodus is now called Ghasir, a tributary of the Great Zab. The village Gaugamela was in the district of Assyria called Aturia, about 69 miles from the city of Arbela, now called Erbil. [1]
Variants of name
- Gaugamēla (Anabasis by Arrian, p. 156, 334.)
- Gaugamēla (Greek: Γαυγάμηλα)
- Gaugamela (Pliny.vi.30)
Jat Gotras Namesake
Jat Gotras Namesake
- Gogh = Gaugamēla (Anabasis by Arrian, p. 156, 334.). Gogh is a village in Guhla tehsil of Kaithal district in Haryana.
History
The Battle of Gaugamela (/ˌɡɔːɡəˈmiːlə/; Greek: Γαυγάμηλα), also called the Battle of Arbela (Greek: Ἄρβηλα), was the decisive battle of Alexander the Great's invasion of the Persian Achaemenid Empire. In 331 BC Alexander's army of the Hellenic League met the Persian army of Darius III near Gaugamela, close to the modern city of Dohuk (Iraqi Kurdistan). Though heavily outnumbered, Alexander emerged victorious due to his army's superior tactics and his deft employment of light infantry. It was a decisive victory for the Hellenic League and led to the fall of the Achaemenid Empire.
Background
In November 333 BC Darius III had lost the Battle of Issus, resulting in the capture of his wife, his mother and his two daughters, Stateira II and Drypetis. Darius had retreated to Babylon, where he regrouped the remaining army from the previous battle. The victory at Issus had given Alexander control of southern Asia Minor. Following a victory at the Siege of Tyre (332 BC), which lasted from January to July, Alexander controlled the Levant. After his victory at Gaza Persian troop counts were low and the Persian satrap of Egypt, Mazaeus, peacefully surrendered to Alexander.[2]
Jat History
The various tribes came to the aid of Darius-III (the last king of the Achaemenid Empire of Persia) and were part of alliance in the battle of Gaugamela (331 BC) formed by Darius-III in war against Alexander the Great at Arbela, now known as Arbil, which is the capital of Kurdistan Region in northern Iraq. [3]
Some of Jat tribes associated with Darius-III fighting against Alexander the Great include:
- Bactrians:Takhar Jats who gave the name Tukharistan to the Country
- Sogdianians: Sogaria, Solanki Jats
- Sacians: Saka Jats
- Scythian: Jats
- Arachotians: Arak Jats
- Areians: Aryan Jats
- Parthians: Parad Jat clan, Bhim Singh Dahiya writes that the clan (Gotra) name of some of the seers of the Rigveda are derived from Rishis, which are identifiable with the existing Jat clans, e.g. Tanva Partha (X/193) may represent the present Parad clan, the well-known Parthians of Iran.
- Hyrcanians: Virk Jats
- Medes: Manda Jats
- Cadusians: Kadwa Jats
- Uxians: Ojla, Ujjihana Jats
- Susianians: Suswal Jats
- Babylonians: Babal Jats
- Carians: Kar, Kari, Karia, Kurka Jats
- Armenians: Armenia and Cappadocia were included in the Manda Jat empire.
- Cappadocians:Armenia and Cappadocia were included in the Manda Jat empire.
- Syrians: Asiagh Jats
The Jat tribes fighting against Darius-III and fighting in favour of Alexander the Great include:
- Paeonian : They were Paunia Jats - Herodotus mentions a people, Paeonia, a colony of Teucarians. [4] The paeonians were transferred from Hellespont to Asia, under the orders of Darius the great. Here we have the Pauniya and Tokhar Jats in Europe in sixth century BC.[5]
Ch.8 Description of Darius-III's Army at Arbela against Alexander

Uxians came to the aid of Darius-III (the last king of the Achaemenid Empire of Persia) and were part of alliance in the battle of Gaugamela (331 BC) formed by Darius-III in war against Alexander the Great at Arbela, now known as Arbil, which is the capital of Kurdistan Region in northern Iraq.
Arrian[6] writes....Alexander therefore took the royal squadron of cavalry, and one squadron of the Companions, together with the Paeonian scouts, and marched with all speed; having ordered the rest of his army to follow at leisure. The Persian cavalry, seeing Alexander, advancing quickly, began to flee with all their might. Though he pressed close upon them in pursuit, most of them escaped; but a few, whose horses were fatigued by the flight, were slain, others were taken prisoners, horses and all. From these they ascertained that Darius with a large force was not far off. For the Indians who were conterminous with the Bactrians, as also the Bactrians themselves and the Sogdianians had come to the aid of Darius, all being under the command of Bessus, the viceroy of the land of Bactria. They were accompanied by the Sacians, a Scythian tribe belonging to the Scythians who dwell in Asia.[1] These were not subject to Bessus, but were in alliance with Darius. They were commanded by Mavaces, and were horse-bowmen. Barsaentes, the viceroy of Arachotia, led the Arachotians[2] and the men who were called mountaineer Indians. Satibarzanes, the viceroy of Areia, led the Areians,[3] as did Phrataphernes the Parthians, Hyrcanians, and Tapurians,[4] all of whom were horsemen. Atropates commanded the Medes, with whom were arrayed the Cadusians, Albanians, and Sacesinians.[5] The men who dwelt near the Red Sea[6] were marshalled by Ocondobates, Ariobarzanes, and Otanes. The Uxians and Susianians[7] acknowledged Oxathres son of Aboulites as their leader, and the Babylonians were commanded by Boupares. The Carians who had been deported into central Asia, and the Sitacenians[8] had been placed in the same ranks as the Babylonians. The Armenians were commanded by Orontes and Mithraustes, and the Cappadocians by Ariaoes. The Syrians from the vale between Lebanon and Anti-Lebanon (i.e. Coele-Syria) and the men of Syria which lies between the rivers[9] were led by Mazaeus. The whole army of Darius was said to contain 40,000 cavalry, 1,000,000 infantry, and 200 scythe-bearing chariots.[10] There were only a few elephants, about fifteen in number, belonging to the Indians who live this side of the Indus.[11] With these forces Darius had encamped at Gaugamela, near the river Bumodus, about 600 stades distant from the city of Arbela, in a district everywhere level;[12] for whatever ground thereabouts was unlevel and unfit for the evolutions of cavalry, had long before been levelled by the Persians, and made fit for the easy rolling of chariots and for the galloping of horses. For there were some who persuaded Darius that he had forsooth got the worst of it in the battle fought at Issus, from the narrowness of the battle-field; and this he was easily induced to believe.
1. Cf. Aelian (Varia Historia, xii. 38).
2. Arachosia comprised what is now the south-east part of Afghanistan and the north-east part of Beloochistan.
3. Aria comprised the west and north-west part of Afghanistan and the east part of Khorasan.
4. Parthia is the modern Khorasan. Hyrcania was the country south and south-east of the Caspian Sea. The Tapurians dwelt in the north of Media, on the borders of Parthia between the Caspian passes. Cf. Ammianus, xxiii. 6.
5. The Cadusians lived south-west of the Caspian, the Albanians on the west of the same sea, in the south-east part of Georgia, and the Sacesinians in the north-east of Armenia, on the river Kur.
6. "The Red Sea was the name originally given to the whole expanse of sea to the west of India as far as Africa. The name was subsequently given to the Arabian Gulf exclusively. In Hebrew it is called Yam-Suph (Sea of Sedge, or a seaweed resembling wool). The Egyptians called it the Sea of Weeds.
7. The Uxians occupied the north-west of Persis, and Susiana was the country to the north and west of Persis.
8. The Sitacenians lived in the south of Assyria. ἐτετάχατο. is the Ionic form for τεταγμἑνοι ἦσαν.
9. The Greeks called this country Mesopotamia because it lies between the rivers Euphrates and Tigris. In the Bible it is called Paddan-Aram (the plain of Aram, which is the Hebrew name of Syria). In Gen. xlviii. 7 it is called merely Paddan, the plain. In Hos. xii. 12, it is called the field of Aram, or, as our Bible has it, the country of Syria. Elsewhere in the Bible it is called Aram-naharaim, Aram of the two rivers, which the Greeks translated Mesopotamia. It is called "the Island," by Arabian geographers.
10. Curtius (iv. 35 and 45) states that Darius had 200,000 infantry, 45,000 cavalry, and 200 scythed chariots; Diodorus (xvii. 53) says, 800,000 infantry, 200,000 cavalry, and 200 scythed chariots; Justin (xi. 12) gives 400,000 foot and 100,000 horse; and Plutarch (Alex., 31) speaks of a million of men. For the chariots cf. Xenophon (Anab., i 8, 10); Livy, xxxvii. 41.
11. This is the first instance on record of the employment of elephants in battle.
12. This river is now called Ghasir, a tributary of the Great Zab. The village Gaugamela was in the district of Assyria called Aturia, about 69 miles from the city of Arbela, now called Erbil.
Jat History
Bhim Singh Dahiya[7] writes that....The connection of Dahiyas with Persia is further supported by Anabasis who states that the Dahae were one of the Chief tribes of Persia.[8] Their fight at Arbela in 331 B.C., against Alexander, is mentioned by the same authority.[9] It is well known that Cyrus the Great, was killed in battle against the Massagetae, under their Queen Tomyris.
Mention by Pliny
Pliny[10] mentions Adiabene.... The kingdom of the Persians, by which we now understand that of Parthia, is elevated upon the Caucasian chain between two seas, the Persian and the Hyrcanian. To the Greater Armenia, which in the front slopes towards Commagene, is joined Sophene, which lies upon the descent1 on both sides thereof, and next to it is Adiabene, the most advanced frontier of Assyria; a part of which is Arbelitis,2 He alludes to the town of Arbela, where, as it is generally said, the army of Darius was defeated by Alexander the Great; by which engagement the conflict was terminated. It was the fact, however, that Darius left his baggage and treasures at Arbela, while the battle really took place near the village of Gaugamela, about twenty miles to the north-west of Arbela. This place still retains its name of Arbil, where Alexander conquered Darius, and which joins up to Syria. The whole of this country was called Mygdonia by the Macedonians, on account of the resemblance it bore to Mygdonia3 in Europe. Its cities are Alexandria,4 and Antiochia, also called Nisibis5; this last place is distant from Artaxata seven hundred and fifty miles. There was also in former times Ninus6, a most renowned city, on the banks of the Tigris, with an aspect towards the west. Adjoining the other front of Greater Armenia, which runs down towards the Caspian Sea, we find Atropatene7, which is separated from Otene, a region of Armenia, by the river Araxes; Gazæ8 is its chief city, distant from Artaxata four hundred and fifty miles, and the same from Ecbatana in Media, to which country Atropatene belongs.
1 35 See c. 10.
2 He alludes to the town of Arbela, where, as it is generally said, the army of Darius was defeated by Alexander the Great; by which engagement the conflict was terminated. It was the fact, however, that Darius left his baggage and treasures at Arbela, while the battle really took place near the village of Gaugamela, about twenty miles to the north-west of Arbela. This place still retains its name of Arbil.
3 A district in the east of Macedonia, bordering on the Thermaic gulf and the Chalcidic peninsula.
4 Nothing is known of this place. Hardouin suggests that it may have been built on the spot where Alexander defeated Darius.
5 Also known as Antiochia Mygdoniæ, the capital of Mygdonia. Its ruins are still to be seen near a place called Nisibin. It stood on the river Mygdonius, now the Nahral Huali.
6 Or Nineveh, the capital of the great Assyrian monarchy, destroyed by the Medes and Babylonians about B.C. 606.
7 There is great difficulty in ascertaining, from the accounts given by the ancient writers, the exact limits of this district, but it is supposed to have included a considerable portion of the province now known by the name of Azerbaijan. It derived its name from Atropates or Atropes, who was governor of this district under the last Darius.
8 Most probably the place now known as Gazæa, the royal residence of the Parthian kings, and, as its name would imply, their treasure city. Colonel Rawlinson thinks that this place underwent many changes of name according to the rulers who successively occupied it; among other names, it appears to have borne that of Ecbatana.
Mention by Pliny
Pliny[11] mentions Mesopotamia ...Up to the Gordyæi8 join the Aloni, through whose territory runs the river Zerbis, which falls into the Tigris; next are the Azones, the Silici, a mountain tribe, and the Orontes, to the west of whom lies the town of Gaugamela9, as also Suë, situate upon the rocks.
8 The mountains of the Gordyæi are mentioned in c. 12.
9 This, as previously mentioned in a Note to c. 16, was the scene of the last great battle between Alexander and Darius, and known as the battle of Arbela. It has been suggested that it may perhaps be represented by a place now called Karnelis. See p. 27.
External links
References
- ↑ Arrian:The Anabasis of Alexander/3a, Ch.8
- ↑ Arrian 1893, 3.1.
- ↑ Arrian:The Anabasis of Alexander/3a, Ch.8
- ↑ v, 12-27
- ↑ Bhim Singh Dahiya: Jats the Ancient Rulers (A clan study)/Jat Clan in India, p. 267-268
- ↑ Arrian:The Anabasis of Alexander/3a, Ch.8
- ↑ Bhim Singh Dahiya: Jats the Ancient Rulers (A clan study)/The Antiquity of the Jats,p.252
- ↑ Chapter XIII.
- ↑ Chapter III/2.
- ↑ Natural History by Pliny Book VI/Chapter 16
- ↑ Natural History by Pliny Book VI/Chapter 30

