Himachal Pradesh
| Author:Laxman Burdak, IFS (R) |
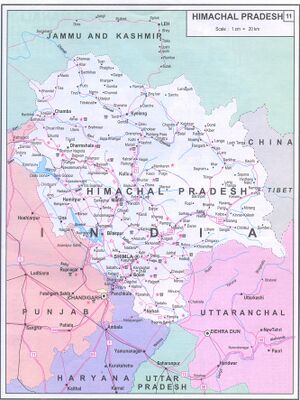
Himachal Pradesh (हिमाचल प्रदेश) is a state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen mountain states and is characterized by an extreme landscape featuring several peaks and extensive river systems. It is also known as Dev Bhumi. Manjit Singh Dogra was a Jat Mla in Himachal Pradesh
Location
Himachal Pradesh is the northernmost state of India and shares borders with the union territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh to the north, and the states of Punjab to the west, Haryana to the southwest, Uttarakhand to the southeast and a very narrow border with Uttar Pradesh to the south. The state also shares an international border to the east with the Tibet Autonomous Region in China. Himachal Pradesh is also known as Dev Bhoomi, meaning 'Land of God'[1] and Veer Bhoomi which means 'Land of Braves'.[2]
Districts
History
The predominantly mountainous region comprising the present-day Himachal Pradesh has been inhabited since pre-historic times having witnessed multiple waves of human migrations from other areas.[3] Through its history, the region was mostly ruled by local kingdoms some of which accepted the suzerainty of larger empires. Prior to India's independence from the British, Himachal comprised the hilly regions of Punjab Province of British India. After independence, many of the hilly territories were organized as the Chief Commissioner's province of Himachal Pradesh which later became a union territory. In 1966, hilly areas of neighboring Punjab state were merged into Himachal and it was ultimately granted full statehood in 1971.
Himachal Pradesh is spread across valleys with many perennial rivers flowing through them. Around 90% of the state's population lives in rural areas. Agriculture, horticulture, hydropower and tourism are important constituents of the state's economy.
Early history: The Mahabharata mentions the Janapadas in Himachal Pradesh such as Kuluta (Kullu), Trigarta (Kangra), Kulinda (Shimla hills and Sirmaur), Yugandhara (Bilaspur and Nalagarh), Gabdika (Chamba) and Audumbara (Pathankot).
Alexander Cunningham on Trigarta
Alexander Cunningham[4] describes about the Hill States of the Punjab as the Chinese pilgrim Hwen Thsang has noticed so few of the many hill-states of the Panjab.
According to popular opinion the petty states of the Alpine Panjab, at the present time, consist of twenty-two Muhammadan and twenty-two Hindu chiefships, the former lying to the west, and the latter to the east of the Chenab river. [5]
An older classification divides them into three groups, each named after the most powerful state which formed the head of the confederation[6]. These were:
- 1. Kashmir- consisted of the rich valley of Kashmir, and all the petty states between the Indus and Jhelam;
- 2. Dogra - included Jammu and the other petty states between the Jhelam River and the Ravi River,
- 3. Trigartta - comprised Jalandhar, and the various small states between the Ravi River and the Satluj River.
This division into three groups most probably existed prior to the seventh century, as we find that the states to the east of the Ravi were quite independent of Kashmir, while those of Urasa, Punach, and Rajapuri are spoken of in such a way as to show that they had kings of their own previous to their subjection by Kashmir.[7]
The Gakar chiefs hold the lower valley of the Jhelam, and the upper course of the Haro river to the south-west of Kashmir. The Gakars also occupy several portions of the eastern Doab, as Guliana, near Gujar Khan, and Bugial, under the lofty hill of Balnath. But these districts do not properly belong to the hills, although they were subject to Kashmir at the time of Hwen Thsang's visit in the seventh century. [8]
Alexander Cunningham[9]provides us the list which gives the names and positions of the various states attached to the eastern, or Jalandhar (Trigartta) division of the Alpine Panjab.
| Vansha | State |
|---|---|
| Somvansi | 1. Kangra, or Katoch. |
| 2. Guler, to S.W. of Kangra. | |
| 3. Jaswal, on Suhan River. | |
| 4. Datarpur, on lower Bias River. | |
| 5. Siba, on lower Bias River. | |
| Surajvansi | 6.Chamba, on Ravi River. |
| 7. Kullu, on upper Bias River. | |
| Pundir, or Pandayas. | 8.Mandi, on middle Bias River. |
| 9. Sukhet, to south of Mandi. | |
| 10. Nurpur, between Ravi River and Bias River. | |
| 11. Kotila, to East of Nurpur. | |
| 12. Kotlehar. |
Of these twelve states no less than five are mere subdivisions of the once rich kingdom of Jalandhar, which embraced the whole of the Doab, or plain country, between the Bias and Satlej, and all the hill country lying between the Ravi and the frontiers of Mandi and Sukket, to the south of the Dhaola-dhar mountains. This included Nurpur, Kotila, and Kotlehar ; and as Mandi and Sukhet were at first under one rule, there were originally only four chiefships in the eastern division of the Alpine Panjab, namely, Jalandhar, Chamba, Kullu, and Mandi.
Alexander Cunningham[10] writes that Since the occupation of the plains by the Muhammadans, the ancient kingdom of Jalandhara has been confined almost entirely to its hill territories, which were generally known by the name of Kangra, after its most celebrated fortress.
Alexander Cunningham[11] writes that The royal family of Jalandhara and Kangra is one of the oldest in India, and their genealogy from the time of the founder, Susarma Chandra, appears to have a much stronger claim to our belief than any one of the long strings of names now shown by the more powerful families of Rajasthan. All the different scions of this house claim to be of Somavanshi descent ; and they assert that their ancestors held the district of Multan and fought in the Great War on the side of Duryodhan against the five Pandu brothers. After the war they lost their country, and retired under the leadership of Susarma Chandra to the Jalandhar Doab, where they established themselves, and built the stronghold of Kangra.
Alexander Cunningham writes that In the seventh century, the Chinese pilgrim, Hwen Thsang, was courteously entertained for a whole month by Raja U-ti-to, or Udita,[12] whom I would identify with Adima of the genealogical lists. One hundred and sixty years later, in an inscription dated A.D. 804, the Raja of Jalandhara is named Jaya Chandra, who is the Jaya Malla Chandra of the lists, the seventh in descent from Adima. Lastly, Ananta, king of Kashmir, from A.D. 1028 to 1081, married two daughters of Indu Chandra, [13] Raja of Jalandhara, who is the Indra Chandra of the genealogical lists of Kangra. These instances are sufficient to show that Jalandhara existed as an independent State for many centuries before the Muhammadan conquest. [14]
The smaller chiefships of Guler, Jaswal, Datarpur, and Siba, are offshoots from the parent stem of Kangra. The independence of Guler, or Haripur, was established by Hari Chandra, about A.D. 1400, when he yielded Kangra to his younger brother, Karmma Chandra. [15]
The date of the foundation of the other principalities is unknown, but I believe that they were always tributary to the parent state until the time of the Muhammadans, when the capture of Kangra by Mahmud of Ghazni afforded them an opportunity of asserting their independence. [16]
Raja Utito, mentioned by Chinese pilgrim Hwen Thsang, was a tributary of Harsh Vardhana, who appear to have continued to rule over the country right up to the 12th century, with occasional interruptions, but their capital was Jalandhar and Kangra formed an important stronghold.
We find in above description provided by Alexander Cunningham that Guliana Rawalpindi (p.132) represented by Mohammadans and Guler state to S.W. of Kangra (p.136) represented by Hindu chiefs of Guler. We may believe that these were the ancestors of Guleria clan.
Nagas in Himachal Pradesh
Dr Naval Viyogi[17] writes....Most probably Nagas moved from Kashmir valley and settled in different valleys of Himachal Pradesh. Still today these Nagas can be Seen in numerous temples and heard in legends throughout the modern province of Himachal Pradesh.
Basuki Naga is worshipped in the ex-hill state ot Chamba,[18] which comprises the Ravi valley and a portion of the valley of the upper Chinab. It is said that the cult of Basuki was introduced from Bhadravah in the beginning of the nineteenth century because a disease ad spread among the cattle of the state. For some time, the Naga had a temple at the capital likewise, named Chamba, but unfortunately it was burnt down. Evidently the means of his devotees were insufficient to have it rebuilt; the Naga with his vazeir found refuge in a small shrine of the goddess Hirma or Hidimba, which belongs to the ancient temple of Champavati Devi, the family goddess of the king of Chamba. In the temple, the statue of Basuki Nag, the smaller one of the two, wears a royal crown surmounted by an eleven fold hood. In his right hand he holds a sword marked with a snake, and in his left hand a Damaru or hand-drum on each side of his feet is a cobra in an erect attitude. Basuki Naga also has a temple of Himgiri[19].
There is also another Naga in Chamba state called Indru Naga. This is the same as Nahusha whose story is told in the Mahabharata. Indru Naga is worshiped at several paces : at Kuārsi on the road leading to Dharmasala, at Samra in Ranhun kothi, at Chinota and Trehta. There is also another temple of Indru Naga at Kanhiarā in Kangra. [20]
Among the numerous other serpent deities found in Chamba we wish to mention only Mul Naga and Stūhr Naga. The shrine of Mul Naga is immediately above a very fine fountain at the village of Brehi.
The Stuhr or Satuhr Naga is worshipped at the village of Tur on the road to the Baleni pass by wich the Dhaolā Dhār is crossed[21].
This is to be noted[22] that Pujari and Chela attached to the Naga temples of Chamba commonly belong to the agricultural caste of the Rāthī, but in good many cases only the Pujari is a Rathi and the Chela is
[p.21]: a Hali. Naga temples are also found in the valley of the Chinab. At Kilār in Pāngi, there is a shrine Det Naga. It is said that he was originally located in Lahul and human sacrifices were offered to him. There is also a temple of Kalihar Naga (Kelang Naga) at (Dughi]], it is famous about this Naga that he also hailed from Lahul[23]. Similarly Eighteen Nagas or serpents are also worshipped in Kulu [24] valley.
In the local language of this area of Himalayas, 'Kir' or 'Kiri' means serpent, and the people of above area are called 'Kirata', a word used for the people of internal part of Kashmir. in Rajtarangini. Hence Kirat is another form of Kir[25]. Varahamir also has cited this word Kir. Similarly, in the copper plate, published by Prof Kilborn, this word also occurs.[26]
There is mention of the word Kirgrama the inscription of Baijnath temple of Kangra valley. This shows that Kirgram would have been local name of this place.[27] In the local language, the meaning of 'Kirgram' is "The village of serpent or Naga race". Till today serpent is the most loving deity of Baijnath. Not only this, the venerable deity of people of surrounding area of Baijnath is also serpent. It means that in ancient time this town was inhabited by the Naga people. Kir is synonymous of Nag or serpent and it is apparent these Naga worshipping Kir people of Himalaya are near relatives of Dravidian Cher, Ker or Keral of South.
According to Vogel-"The hilly area of Uttarpatha and Nepal is also a homeland of numerous snake shrines and temples and snake worship is a basis of religious life of people."
Jats in Himachal Pradesh
There are about 1,50,000 Jats in Himachal Pradesh, they are mainly Hindu Jats. They are about 1% (approx) of the total population of the state. Recently Jats in Himachal Pradesh got OBC status with the efforts of Mr. Harnam Singh Gill, State president of Himachal Jat Kalyan Parishad. He can be contacted at 01892-232283 for more information. Mostly Jats are in army or migrated to others states for work. Jats are not politically active. There is only one MLA but minister in Himachal Pradesh cabinet from Jats. Jats in Himachal Pradesh are economically poorer than Jats in other states. They speak bholi- pharhi. Mainly Hindu jats are known by Chaudhary and Ghirth people.
Jat gotras in Himachal Pradesh
Regarding gotra generly Himachal Pradesh Jats are same gotra like in Punjab & Haryana few of them are- Kundhal, Gill, Kaundal/Kondal, Syal, Riar, Chang, Kang, Randhawa, Sandhu, Sidhu, Sahota, Bhatti, Khaire, Badal, Chawala, Kangri, Nara, Bhakal, Dhayal, Kahalon, Nanda, Rasen, Bains, Dadwal, Rilach, Bagga etc.
District wise population is - Una: 20,000 Jats, Kangra: 12000
Jat Organization in Himachal Pradesh
Jats in Himachal are organised under Himachal Jat Kalyan Parishad:
- Ishar Singh Mann, State President, Jat Kalyaan Parishad, Himachal Pradesh
- Address: Village Valiwal (Heeran), Post Office Palkowah, Tehsil Haroli, District Una, Himachal Pradesh
- Mobile No. 09814212563, 09814611563, 09625486744
- E-Mail:- is.mann@yahoo.com
Places associated with Jats
हिमाचल प्रदेश
हिमाचल प्रदेश उत्तर-पश्चिमी भारत में स्थित एक राज्य है। यह 21,629 मील² (56019 किमी²) से अधिक क्षेत्र में फ़ैला हुआ है तथा उत्तर में जम्मू और कश्मीर और लद्दाख केंद्र शासित प्रदेशों के पश्चिम तथा दक्षिण-पश्चिम में पंजाब (भारत), दक्षिण में हरियाणा एवं उत्तर प्रदेश, दक्षिण-पूर्व में उत्तराखण्ड तथा पूर्व में तिब्बत से घिरा हुआ है। हिमाचल प्रदेश का शाब्दिक अर्थ "बर्फ़ीले पहाड़ों का प्रांत" है। हिमाचल प्रदेश को "देव भूमि" भी कहा जाता है। इस क्षेत्र में आर्यों का प्रभाव ऋग्वेद से भी पुराना है। आंग्ल-गोरखा युद्ध के बाद, यह ब्रिटिश औपनिवेशिक सरकार के हाथ में आ गया। सन 1857 तक यह महाराजा रणजीत सिंह के शासन के अधीन पंजाब राज्य (पंजाब हिल्स के सीबा राज्य को छोड़कर) का हिस्सा था।[28] सन 1956 में इसे केन्द्र शासित प्रदेश बनाया गया, लेकिन 1971 में इसे, हिमाचल प्रदेश राज्य अधिनियम-1971 के अन्तर्गत इसे 25 जनवरी 1971 को भारत का अठारहवाँ राज्य बनाया गया।
बारहमासी नदियों की बहुतायत के कारण, हिमाचल अन्य राज्यों को पनबिजली बेचता है जिनमे प्रमुख हैं दिल्ली, पंजाब (भारत) और राजस्थान। राज्य की अर्थव्यवस्था तीन प्रमुख कारकों पर निर्भर करती है जो हैं, पनबिजली, पर्यटन और कृषि। प्रमुख समुदायों में राजपूत, ब्राह्मण, घिर्थ (चौधरी), गद्दी, कन्नेत, राठी और कोली शामिल हैं।
हिमाचल प्रदेश का इतिहास उतना ही प्राचीन है, जितना कि मानव अस्तित्व का अपना इतिहास है। इस बात की सत्यता के प्रमाण हिमाचल प्रदेश के विभिन्न भागों में हुई खुदाई में प्राप्त सामग्रियों से मिलते हैं। प्राचीनकाल में इस प्रदेश के आदि निवासी दास, दस्यु और निषाद के नाम से जाने जाते थे। उन्नीसवीं शताब्दी में महाराजा रणजीत सिंह ने इस क्षेत्र के अनेक भागों को अपने राज्य में मिला लिया। जब अंग्रेज यहां आए, तो उन्होंने गोरखा लोगों को पराजित करके कुछ राजाओं की रियासतों को अपने साम्राज्य में मिला लिया।
शिमला हिल स्टेट्स की स्थापना: 1945 ई. तक प्रदेश में प्रजा मंडलों का गठन हो चुका था। 1946 ई. में सभी प्रजा मंडलों को एचएचएसआरसी में शामिल कर लिया तथा मुख्यालय मंडी में स्थापित किया गया। मंडी के स्वामी पूर्णानंद को अध्यक्ष, पदमदेव को सचिव तथा शिव नंद रमौल (सिरमौर) को संयुक्त सचिव नियुक्त किया। एचएचएसआरसी के नाहन में 1946 ई. में चुनाव हुए, जिसमें यशवंत सिंह परमार को अध्यक्ष चुना गया। जनवरी, 1947 ई. में राजा दुर्गा चंद (बघाट) की अध्यक्षता में शिमला हिल्स स्टेट्स यूनियन की स्थापना की गई। जनवरी, 1948 ई. में इसका सम्मेलन सोलन में हुआ। हिमाचल प्रदेश के निर्माण की घोषणा इस सम्मेलन में की गई। दूसरी तरफ प्रजा मंडल के नेताओं का शिमला में सम्मेलन हुआ, जिसमें यशवंत सिंह परमार ने इस बात पर जोर दिया कि हिमाचल प्रदेश का निर्माण तभी संभव है, जब शक्ति प्रदेश की जनता तथा राज्य के हाथ सौंप दी जाए। शिवानंद रमौल की अध्यक्षता में हिमालयन प्लांट गर्वनमेंट की स्थापना की गई, जिसका मुख्यालय शिमला में था। दो मार्च, 1948 ई. को शिमला हिल स्टेट के राजाओं का सम्मेलन दिल्ली में हुआ। राजाओं की अगवाई मंडी के राजा जोगेंद्र सेन कर रहे थे। इन राजाओं ने हिमाचल प्रदेश में शामिल होने के लिए 8 मार्च 1948 को एक समझौते पर हस्ताक्षर किए। 15 अप्रैल 1948 ई. को हिमाचल प्रदेश राज्य का निर्माण किया था। उस समय प्रदेश भर को चार जिलों में बांटा गया और पंजाब हिल स्टेट्स को पटियाला और पूर्व पंजाब राज्य का नाम दिया गया। 1948 ई. में सोलन की नालागढ़ रियासत कों शामिल किया गया। अप्रैल 1948 में इस क्षेत्र की 27,000 वर्ग कि॰मी॰ में फैली लगभग 30 रियासतों को मिलाकर इस राज्य को केंद्र शासित प्रदेश बनाया गया।
भूगोल: हिमाचल प्रदेश हिमालय पर्वत की शिवालिक श्रेणी का हिस्सा है। शिवालिक पर्वत श्रेणी से ही घग्गर नदी निकलती है। राज्य की अन्य प्रमुख नदियों में सतलुज और व्यास शामिल है। हिमाचल हिमालय का सुदूर उत्तरी भाग लद्दाख के ठंडे मरुस्थल का विस्ता है और लाहौल एवं स्पिति जिले के स्पिति उपमंडल में है। हिमालय की तीनों मुख्य पर्वत श्रंखलाएँ, बृहत हिमालय, लघु हिमालय; जिन्हें हिमाचल में धौलाधार और उत्तरांचल में नागतीभा कहा जाता है और उत्तर-दक्षिण दिशा में फैली शिवालिक श्रेणी, इस हिमालय खंड में स्थित हैं। लघु हिमालय में 1000 से 2000 मीटर ऊँचाई वाले पर्वत ब्रिटिश प्रशासन के लिए मुख्य आकर्षण केंद्र रहे हैं।
नदियां: हिमाचल प्रदेश में पांच प्रमुख नदियां बहती हैं। हिमाचल प्रदेश में बहने वाले पांचों नदियां एवं छोटे-छोटे नाले बारह मासी हैं। इनके स्रोत बर्फ से ढकी पहाडि़यों में स्थित हैं। हिमाचल प्रदेश में बहने वाली पांच नदियों में से चार का उल्लेख ऋग्वेद में मिलता है। उस समय ये अन्य नामों से जानी जाती थीं जैसे अश्किनि (चिनाब) पुरूष्णी (रावी), अरिजिकिया (ब्यास) तथा शतद्रु (सतलुज) पांचवी नदी (कालिंदी) जो यमुनोत्तरी से निकलती है उसका सूर्य देव से पौराणिक संबंध दर्शाया जाता है।
रावी नदी: रावी नदी का प्राचीन नाम ‘इरावती और परोष्णी’ है। रावी नदी मध्य हिमालय की धौलाधार शृंखला की शाखा बड़ा भंगाल से निकलती है। रावी नदी ‘भादल’ और ‘तांतागिरि’ दो खड्डों से मिलकर बनती है। ये खड्डें बर्फ पिघलने से बनती है। यह नदी चंबा से खेड़ी के पास पंजाब (भारत) में प्रवेश करती है और पंजाब से पाकिस्तान में प्रवेश करती है। यह भरमौर और चंबा शहर में बहती है। यह बहुत ही उग्र नदी है। इसकी सहायक नदियां तृण दैहण, बलजैडी, स्यूल, साहो, चिडाचंद, छतराड़ी और बैरा हैं। इसकी लंबाई 720 किलोमीटर है, परंतु हिमाचल में इसकी लंबाई 158 किलोमीटर है। सिकंदर महान के साथ आए यूनानी इतिहासकार ने इसे ‘हाइड्रास्टर और रहोआदिस’ का नाम दिया था।
ब्यास नदी: ब्यास नदी का पुराना नाम ‘अर्जिकिया’ या ‘विपाशा’ था। यह कुल्लू में व्यास कुंड से निकलती है। व्यास कुंड पीर पंजाल पर्वत शृंखला में स्थित रोहतांग दर्रे में है। यह कुल्लू, मंडी, हमीरपुर और कांगड़ा में बहती है। कांगड़ा से मुरथल के पास पंजाब में चली जाती है। मनाली, कुल्लू, बजौरा, औट, पंडोह, मंडी, कांढापतन (मिनी हरिद्धार), सुजानपुर टीहरा, नादौन और देहरा गोपीपुर इसके प्रमुख तटीय स्थान हैं। इसकी कुल लंबाई 460 कि॰मी॰ है। हिमाचल में इसकी लंबाई 260 कि॰मी॰ है। कुल्लू में पतलीकूहल, पार्वती, पिन, मलाणा-नाला, फोजल, सर्वरी और सैज इसकी सहायक नदियां हैं। कांगड़ा में सहायक नदियां बिनवा न्यूगल, गज और चक्की हैं। इस नदी का नाम महर्षि ब्यास के नाम पर रखा गया है। यह प्रदेश की जीवनदायिनी नदियों में से एक है।
चिनाव नदी: चिनाव नदी जम्मू-कश्मीर से होती हुई पंजाब राज्य में बहने वाली नदी है। पानी के घनत्व की दृष्टि से यह प्रदेश की सबसे बड़ी नदी है। यह नदी समुद्र तल से लगभग 4900 मीटर की ऊँचाई पर बारालाचा दर्रे (लाहौल स्पीति) के पास से निकलने वाली चन्द्रा और भागा नदियों के तांदी नामक स्थान पर मिलने से बनती है। इस नदी को वैदिक साहित्य में ‘अश्किनि’ नाम से संबोधित किया गया है। ऊपरी हिमालय पर टांडी में ‘चन्द्र’ और ‘भागा’ नदियां मिलती हैं, जो चिनाव नदी कहलाती है। महाभारत काल में इस नदी का नाम ‘चंद्रभागा’ भी प्रचलित हो गया था। ग्रीक लेखकों ने चिनाव नदी को ‘अकेसिनीज’ लिखा है, जो अश्किनि का ही स्पष्ट रूपांतरण है। चंद्रभागा नदी मानसरोवर (तिब्ब्त) के निकट चंद्रभागा नामक पर्वत से निस्तृत होती है और सिंधु नदी में गिर जाती है। चिनाव नदी की ऊपरी धारा को चद्रभागा कहकर, पुन शेष नदी का प्राचीन नाम अश्किनि कहा गया है। इस नदी को हिमाचल से अदभुत माना गया है। इस नदी का तटवर्ती प्रदेश पूर्व गुप्त काल में म्लेच्छों, यवन, शिवि आदि द्वारा शासित था।
हिमाचल प्रदेश में जाट
शिव की जटाओं से खास रिश्ता रखने वाले, पांडवों को महाभारत जिताकर ज्येष्ठ कहलाने वाले श्रीकृष्ण से गहरा नाता रखने वाला, हिमाचल का डेढ़ लाख आबादी वाला जाट समुदाय अपने शौर्य से दुनिया भर में देवभूमि को गौरवान्वित कर रहा है। हिमाचल जाट समुदाय की कुछ उपलब्धियां को बता रहे हैं:
- प्रदेश की तरक्की में अहम रोल अदा कर रहे हैं हिमाचल के जाट
- ऊना जिले में है समुदाय की सबसे ज्यादा 20 हजार आबादी
- सेना में जाना जुनून, खेती के लिए जान छिड़क मिलता सुकून
- राजनीति से दूर, अब तक मनजीत डोगरा ही बन पाए एमएलए
- हिमाचल में भले ही जाट समुदाय की आबादी डेढ़ लाख के करीब है, लेकिन अपनी दिलेरी और जुझारूपन के चलते यह देवभूमि की शान है।
कहने को संख्या में ये प्रदेश का एक फीसदी हैं, लेकिन ‘जय जवान जय किसान’ के नारे को साकार करने में जाटों का अहम रोल है। सेना में शामिल होना समुदाय के युवाओं की पहली पसंद है,तो खेती से खास प्यार है। रियासतकाल हो या मुगलकाल, अंग्रेजी हुकूमत हो या उसके बाद देश की खातिर कुर्बानी देने में हमेशा जाट समुदाय अग्रणी रहा है। माना जाता है कि हिमाचल से रियालच परिवार के कई सूरमां महाराजा रणजीत सिंह के सुरक्षा कर्मी रहे। शेर-ए-पंजाब के राज्य की सीमाओं को अफगानिस्तान से लेकर बर्मा तक पहुंचाने में इस वर्ग का बड़ा योगदान रहा है। बाद में ब्रिटिश हुकूमत से टक्कर लेकर आजादी की लड़ाई में कई जाट सूरमाओं ने कीर्तिमान स्थापित किए। आजादी के बाद अब तक विभिन्न क्षेत्रों में मेहनतकश जाट हिमाचल का मान बढ़ा रहे हैं। दूसरी ओर राजनीति से जाट खुद को दूर रखते हैं,यही वजह है कि समुदाय से हिमाचल में मनजीत डोगरा एकमात्र नेता हैं, जो दो बार विधायक बने हैं। ओबीसी के तहत आने वाली जातियों में जाट सनातन और सिख, दोनों धर्माें को मानते हैं।
मौजूदा समय में प्रदेश में हिमाचल जाट कल्याण परिषद कार्यरत है, जो दहेज-नशे के खिलाफ योजनाबद्ध तरीके से काम कर रही है। समुदाय से कई लोग डाक्टर, वकील और अन्य प्रशासनिक पदों पर रंहकर भी सेवाएं दे रहे हैं।
हिमाचल में जाट समुदाय का वितरण: हिमाचल के ऊना जिले में जाटों की आबादी 20 हजार से ज्यादा है। प्रदेश के किसी जिले से यह प्रदेश में सबसे ज्यादा आंकड़ा है। इसी तरह कांगड़ा जिले में जाटों की संख्या 12 हजार से ज्यादा है। इसके अलावा चंबा, हमीरपुर, सोलन, सिरमौर, कुल्लू और शिमला आदि के कई हिस्सों में जाट समुदाय के लोग हैं।
हिमाचल में जाट गोत्र: हिमाचल में जाट समुदाय में आने वाली कई गोत्र हैं। इनमें गिल, माहल, मान, बराड़, कौंडल, कोंडल, सयाल, रियार, कंग, रंधावा, संधू, सिद्दू, सहोता, भाटी, खैरे, बादल, चावला, कांगरी, नेरा, भक्कल, दयाल, काहलों, नंदा, बैंस, डढवाल, रियालच व बग्गा आदि हैं।
हिमाचल के जाटों का इतिहास: जहां तक जाटों के इतिहास का सवाल है, तो यह क्षत्रिय वर्ण के हैं। महाभारत काल में हिमाचल के जनपदों का जिक्र मिलता है। उस समय कुलूत (मौजूदा कुल्लू), और त्रिगर्त (अब कांगड़ा)) का जिक्र है। इसी तरह कुलिंडा का भी वर्णन है, यह क्षेत्र अब शिमला के पहाड़ी इलाके और सिरमौर के नाम से विख्यात हैं। चंबा-पठानकोट तक क्रमशः गब्दिका और औडुंबरा के नाम से जाने जाते थे। उक्त समुदाय के लोग मूल रूप से क्षत्रिय हैं। बाद में इन्हीं में से एक वर्ग अलग होकर जाट कहलाया। कद-काठी में बेहद आकर्षक-मजबूती इन्हें औरों से अलग बनाती है। महाराजा रणजीत सिंह की सुरक्षा गार्द का खास हिस्सा रहे जाट वीर हरि सिंह नलवा ने उनके राज्य की सीमा को अफगानिस्तान से लेकर बर्मा तक पहुंचाने में अहम रोल अदा किया। ब्रिटिश काल में इस वर्ग के लोगों ने दहेज और सती प्रथा का हर मंच से विरोध किया। बहरहाल हिमाचली जाट विभिन्न क्षेत्रों में देश-दुनिया में देवभूमि का नाम रोशन कर रहे हैं।
हिमाचल में महत्वपूर्ण जाट लोग:
- रमेश बराड़: कांगड़ा विधानसभा हलके की पलेरा पंचायत के टल्ला गांव निवासी रमेश बराड़ जाट समुदाय की शान हैं। अमूमन मीडिया से दूर रहने वाले सदर भाजपा मंडलाध्यक्ष बराड़ शांत रहकर अपने काम से पार्टी को आगे ले जा रहे हैं। यह बराड़ का ही दबदबा था कि पिछले चुनावों में उनके बूथ पर कुल पड़े 182 वोट में विरोधी पार्टी कांग्रेस को महज सात वोट मिले थे,जबकि 175 भाजपा को। यही नहीं, लोकसभा चुनावों में ही हलके से भाजपा को 19395 मतों की बढ़त मिली थी,जो बराड़ की ताकत को दिखाती है। पांच जुलाई 1962 को जन्में बराड़ समाजसेवा में हमेशा आगे रहते हैं। ओबीसी समेत पूरे समाज की तरक्की में विश्वास रखने वाले बराड़ कहते हैं कि अगर हाइकमान टिकट दे,तो वह एमएलए बनकर कांगड़ा हलके को आगे ले जाएंगे। खास बात यह है कि इन्हें 600 फोन नंबर टिप्स पर याद हैं।
- सर्बजीत पिंका: स्मार्ट सिटी धर्मशाला के रहने वाले सर्बजीत मलूहिया उर्फ पिंका समाजसेवा में बड़ा नाम हैं। निर्धन-जरूरतमंदों की मदद में हरदम आगे रहने वाले पिंका की गिनती शहर के नामी कारोबारियों में होती है। शहर से सटे निचले सकोह में नौ मई 1964 को जन्मे पिंका युवाओं को स्वरोजगार के लिए प्रेरित करते हैं। गगल-धर्मशाला एनएच पर निचले सकोह में नए खुले होटल चांदनी के मालिक बेरोजगार युवाओं को स्वरोजगार की राह दिखा रहे हैं।
- लक्ष्मण सिंह: 1914 से 1918 तक चले पहले विश्व युद्ध में लक्ष्मण सिंह ने शहादत पाई थी।
- लांस नायक हरनाम सिंह: लांस नायक हरनाम सिंह ने 1934 में शहादत पाई थी। इस जवान ने ब्रिटिश सरकार में जनरल करयापा के साथ कमीशन प्राप्त किया था। इसके बाद करयापा रायल अकादमी ऑफ डिफेंस गए और चीफ ऑफ आर्मी स्टाफ बने।
- बावन सिंह: 1934 में लड़ाई में हरनाम सिंह के दूसरे भाई बावन सिंह ने अदम्य साहस का परिचय दिया था।
- सूबेदार मान सिंह: लांस नायक हरनाम सिंह और बावन सिंह दोनों के चचेरे भाई सूबेदार मान सिंह ने 1965 की लड़ाई में पाक के सियालकोट में शहादत पाई। इनका कद छह फीट 10 इंच था।
- रामेश्वर सिंह नायक: सन् 1962 में चीन से लड़ाई हुई, तो हरनाम सिंह के बेटे रामेश्वर सिंह नायक ने शहादत का जाम पिया।
- कैप्टन शैलेष रियालच: सन् 1999 में कारगिल युद्ध हुआ में कैप्टन शैलेष रियालच ने अदम्य साहस का परिचय दिया, कैप्टन शैलेष इस युद्ध में वीरगति को प्राप्त हुए थे। इन्हें सेना शौर्य पदक मिला।
- कर्म सिंह - सन् 1971 की लड़ाई में हमीरपुर से कर्म सिंह देश पर कुर्बान हुए।
- महिमा सिंह - सन् 1971 की लड़ाई में पालमपुर से महिमा सिंह देश पर कुर्बान हुए।
- बुद्धि सिंह - सन् 1971 की लड़ाई में सराह के बुद्धि सिंह ने शहादत पाई।
- ज्ञान सिंह और सोहन सिंह भी दूसरे महायुद्ध के बड़े नाम हैं।
- ज्ञान सिंह और सोहन सिंह के छोटे भाई ब्लैक कैट कमांडो परस राम ने आपरेशन ब्लू-स्टार लीड किया था।
- कर्नल वीएस अटवाल पर भी जाट समुदाय को बड़ा नाज है।
- हवलदार हरनाम सिंह: जब इस सूरमा ने भगाया फिरंगी कर्नल: देश स्वतंत्रता की 70वीं वर्षगांठ मना रहा है। आजादी के परवानों को नमन करने का वक्त है। कई सूरमाओं के नाम सुनहरे अक्षरों में दर्ज हैं, तो कई गुमनामी में खो गए। कुछ ऐसी ही वीरगाथा है कांगड़ा जिला मुख्यालय धर्मशाला से सटे गांव सराह के जांबाज हवलदार हरनाम सिंह की, जिन्होंने फिरंगी अफसर द्वारा भारतीय सैनिकों को गाली देने पर बगावत कर दी थी। एक ऐसी बगावत, जिसके परिणाम में उन्हें कोर्ट मार्शल के बाद जेल जाना पड़ा, मेडलों के साथ नौकरी गंवानी पड़ी, लेकिन यह हिमाचली हौसला ही था, जिसने घर आने के बाद भी नौजवानों के दिलों में आजादी की मशाल अंग्रेजों की विदाई तक जलाए रखी। वर्ष 1912 में सराह गांव में जन्मे हरनाम 1932 में अंग्रेजी सेना की पंजाब रेजिमेंट में बतौर सैनिक भर्ती हुए तो महज चार साल में ही अपनी योग्यता के दम पर उन्होंने हवलदार का रैंक हासिल कर लिया। समय बीता और 1939 से 1945 तक चले दूसरे विश्व युद्ध में हरनाम ने बैल्जियम, सिंगापुर, बर्मा व मलाया जैसे देशों में लड़ाई लड़कर बहादुरी के लिए अनगिनत मेडल हासिल किए। सन् 1945 में वह अपनी बटालियन में मेरठ आए। यहां उनका रुतबा अस्थायी रूप से बटालियन हवलदार मेजर का था, जिन्हें 850 सैनिकों पर कमांड का अधिकार था। चूंकि पंजाब रेजिमेंट के बहुत सारे जवान नेताजी की आजाद हिंद फौज से जुड़ रहे थे, ऐसे में फिरंगी उनसे नफरत करते थे। इसी कड़ी में एक दिन परेड के दौरान कर्नल रैंक के फिरंगी अफसर ने दो भारतीय सैनिकों को गालियां निकालना शुरू कर दीं, इस पर हरनाम ने विरोध जताया, तो वह उन पर ही झपट पड़ा। बस फिर क्या था, भारत माता के जयकारे लगाकर उन्होंने रायफल उठा ली। जांबाज को गुस्से में देख फिरंगी ऐसा भागा कि उसने कर्नल बैरक में जाकर शरण ली। बाद में हरनाम को अरेस्ट कर 15 दिन जेल में रखा। कोर्ट मार्शल के बाद मौत की सजा (गोली मारने) दी। खैर, बड़ी बगावत के डर से अंग्रेजों ने उन्हें माफी मंगवानी चाही, लेकिन उन्होंने साफ इनकार कर दिया। इस पर उन्हें एक्सट्रीम कंपनसेट ग्राउंड पर बिना मेडल-पेंशन घर भेजा गया, जब वह घर आए तो मां-बाप और पत्नी की मौत हो चुकी थी। घर आने पर भी आजादी तक वह अंग्रेज पुलिस-सेना के राडार पर रहे, लेकिन इस गुमनाम हीरो ने अंग्रेजों को भगाने तक युवाओं में आजादी की मशाल जलाए रखी। वर्ष 2005 में उनका निधन हो गया, लेकिन इस जांबाज ने कभी सरकार से पेंशन-भत्ते और फ्रीडम फाइटर का दर्जा नहीं मांगा (See Harnam Singh Kular)
- नादौन से लीडिंग फार्मर तारा सिंह और प्रिंसिपल अनंत राम व केसी रंधावा शिक्षा के क्षेत्र में प्रेरणास्रोत हैं। एसएस गिल ने कालेज कैडर से प्रिंसिपल पद पर रहकर मिसाल कायम की है।
- न्यायपालिका में ऊना निवासी स्व. अर्जुन सिंह बड़ा नाम हैं। इसके अलावा मोनिका सोमल भी न्यायपालिका में हैं। वहीं सोमल आईएफएस आफसर रहे हैं।
- कमांडेंट जागीर सिंह: बीएसएफ से रिटायर्ड कमांडेंट जागीर सिंह नादौन से हैं। बर्ष 1982 में एशियाड में इन्होंने भारतीय टीम को लीड किया था। अभी वह संगठन के राष्ट्रीय सचिव हैं। इतना ही नहीं, वह 18 बार नेशनल खेल कर कई गोल्ड मेडल जीत चुके हैं। एशियन खेलों में जाने के अलावा नामी कोच भी हैं।
- बीएस माहल : तब होनहार फायर आफिसर, अब नदी बचा रहे, वर्ष 2010 में शिमला में हुए भीषण अग्निकांड में करीब 60 कश्मीरी युवाओं की जान बचाने वाले होनहार फायर आफिसर बीएस माहल को कौन नहीं जानता। चुनौती बने उस अग्निकांड में श्री माहल ने बड़ी बहादुरी से कीमती जानें बचाई थीं। मूल रूप से सराह के रहने वाले हैं, लेकिन अब भटेड़ (दोनों गांव धर्मशाला से सटे) में शिफ्ट हो गए हैं। पूर्व डिवीजनल फायर अफसर श्री माहल ने बैजनाथ से लेकर इंदौरा तक करीब 350 पीपल के ऐसे पेड़ सहेजे हैं,जो पूरी तरह से सुरक्षित हैं। श्री माहल ने कई लोगों को पेड़ गोद लेने में मदद भी की है। अब बाणगंगा की सहायक नदी मांझी के सबसे बड़े संरक्षक बनकर उभरे हैं। धर्मशाला शहर से निकाले गए प्रवासियों द्वारा भटेड़ में खड्ड किनारे ठिकाने बनाने से पानी दूषित हो रहा है। श्री माहल चाहते हैं कि हजारों लोगों को पालने वाली खड्ड दूषित नहीं होनी चाहिए। वह इसे लेकर कई बार सरकार से मांग उठा चुके हैं।
- सतवंत जोहल - यूके में मकान, देवभूमि में दिल, सतवंत जोहल बना रहे हिमाचल में 17 होटल. यूके (इंग्लैंड) में रहने वाले सतवंत सिंह जोहल का हिमाचल से खास लगाव है। धर्मशाला के खनियारा और पंजाब के होशियारपुर में रहने वाले श्री जोहल हिमाचल में 17 होटल की चेन बना रहे हैं। इनमें तीन होटल ज्वालामुखी, घाघस और शाहपुर में शुरू भी हो गए हैं,जबकि अन्यों पर काम जारी है। श्री जोहल का सपना है कि हिमाचल में सैकड़ों युवाओं के लिए रोजगार के अवसर प्रदान किए जाएं। समुदाय को इन पर नाज है। शहीद-ए-आजम भगत सिंह के परिवार के करीबी श्री जोहल की होटल चेन का नाम स्पॉट हाई-वे सर्विस है।
- हरनाम सिंह गिल: हिमाचल में जाट समुदाय को ओबीसी में शामिल करवाने में हरनाम सिंह गिल का बड़ा योगदान रहा है। कांगड़ा शहर से सटे बैदी गांव के रहने वाले हरनाम गिल हैडमास्टर के पद पर तैनात थे। दयाल बाग आगरा से एमएबीटी करने वाले गिल समुदाय की समस्याओं से भलीभांति परिचित थे। उन्होंने जाट कल्याण परिषद के फाउंडर सूबेदार विचित्र सिंह द्वारा छेड़ी गई मुहिम को आगे बढ़ाया। ओबीसी कमीशन के पास समुदाय का पक्ष रखा कि कैसे मुजारा एक्ट में जमीनें छिनने के बाद खेती पहले जैसी नहीं रही। उस समय प्रदेश में प्रो. पे्रम कुमार धूमल मुख्यमंत्री थे और साहिब सिंह बर्मा जाट संघ के राष्ट्रीय अध्यक्ष। श्री गिल द्वारा पुख्ता तरीके से पक्ष रखने का ही नतीजा था कि सन् 2002 में जाट समुदाय को ओबीसी में शामिल कर लिया गया। जाट समुदाय के ओबीसी में आने से अन्य पिछड़ा वर्ग जैसे संगठन को संभवतः मजबूती मिली है।
- पुरुषोत्तम पड्डा - शिक्षा में अव्वल, कांगड़ा जिला के बैदी गांव निवासी पुरुषोत्तम पड्डा सेवानिवृत्त शिक्षक हैं। इनकी गिनती समुदाय के गणमान्यों में होती है।
- प्रताप रियाड़: मलां निवासी प्रताप रियाड़ नामी शिक्षाविद हैं। यह स्टेट अवार्डी हैं। शिक्षा के क्षेत्र में इन्होंने कई मील पत्थर स्थापित किए हैं।
- नानक सिंह आजाद हिंद: मलाया, सिंगापुर की जेलों में युद्ध बंदी रहे नानक सिंह आजाद हिंद फौज से संबंधित रहे हैं। बताते हैं कि वह कैप्टन के पद पर थे। बैदी में जन्मे नानक चंद बेहतरीन सेवाओं के लिए जाने जाते हैं।
- गुरुबचन सिंह फौज में उच्च पद पर रहे हैं। इन्हें कई मेडल भी मिले हैं। इनकी गिनती जाटों की बड़ी हस्तियों में होती है।
- केसी ब्रमला म्यांमार से आए हैं। इंदौरा में रहते हैं। अब इनकी गिनती नामी कारोबारियों में होती है। समुदाय के लिए यह बड़ा नाम है।
- मनजीत सिंह डोगरा : पंडितों के गढ़ में लीडर, हमीरपुर जिले में नादौनता (अब बड़सर) विधानसभा हलके से मनजीत सिंह डोगरा दो बार एमएलए रहे हैं। डोगरा संभवतः जाट समुदाय से एकमात्र नेता हैं,जो विधायक जैसे पद तक पहुंचे हैं। खास बात यह कि यह इलाका ब्राह्मण बहुल है। यहां से उनका विधायक बनना बड़ी बात है।
प्रशासकीय अधिकारी: समुदाय से कई नामी हस्तियां उच्च पदों पर रहकर देश-प्रदेश की सेवा कर रही हैं। राखिल काहलों आईएएस हैं, सतवंत अटवाल बीएसएफ में हिमाचल कैडर से आईपीएस हैं। इसी तरह बीएस भारद्वाज बीएंडआर से एसई रिटायर्ड हैं। समुदाय से ब्रिगेडियर सुरजीत सिंह (ऊना), ब्रिगेडियर लाल सिंह (भोटा) कर्नल विक्रम अटवाल (घुरकड़ी) कर्नल नरेश सिंह (भोटा), कर्नल कुलदीप अटवाल (जलाड़ी) जांबाज समुदाय की शान हैं।
स्रोत: दिव्य हिमाचल
Notable persons
- Ishwar Singh Mann, State president, Himachal Jat Kalyan Parishad, Mobile No. 09814212563, 09814611563, 09625486744, E-Mail:- is.mann@yahoo.com From village - Hiran Una, Haroli Tehsil of Una district in the state of Himachal Pradesh

- Harnam Singh Kular (1912- 02.09.2005) was a freedom fighter from Sarah locality in Dharamshala city of Kangra district in Himachal Pradesh. He joined Punjab Regiment during British rule in 1932. He fought wars in Belgium, Singapore, Burma and Malaya during Second World War and was awarded many bravery medals. He rebelled against the British officer for his unbecoming behaviour in 1945 and as a result was sent back to his home without medals and pension on extreme compensate grounds. He has not been officially awarded with the status of Freedom Fighter by the Govt.
- Ramesh Barar (रमेश बराड़) : कांगड़ा विधानसभा हलके की पलेरा पंचायत के टल्ला गांव निवासी रमेश बराड़ जाट समुदाय की शान हैं। अमूमन मीडिया से दूर रहने वाले सदर भाजपा मंडलाध्यक्ष बराड़ शांत रहकर अपने काम से पार्टी को आगे ले जा रहे हैं। यह बराड़ का ही दबदबा था कि पिछले चुनावों में उनके बूथ पर कुल पड़े 182 वोट में विरोधी पार्टी कांग्रेस को महज सात वोट मिले थे,जबकि 175 भाजपा को। यही नहीं, लोकसभा चुनावों में ही हलके से भाजपा को 19395 मतों की बढ़त मिली थी,जो बराड़ की ताकत को दिखाती है। पांच जुलाई 1962 को जन्में बराड़ समाजसेवा में हमेशा आगे रहते हैं। ओबीसी समेत पूरे समाज की तरक्की में विश्वास रखने वाले बराड़ कहते हैं कि अगर हाइकमान टिकट दे,तो वह एमएलए बनकर कांगड़ा हलके को आगे ले जाएंगे। खास बात यह है कि इन्हें 600 फोन नंबर टिप्स पर याद हैं।[29]
- सर्बजीत पिंका: स्मार्ट सिटी धर्मशाला के रहने वाले सर्बजीत मलूहिया उर्फ पिंका समाजसेवा में बड़ा नाम हैं। निर्धन-जरूरतमंदों की मदद में हरदम आगे रहने वाले पिंका की गिनती शहर के नामी कारोबारियों में होती है। शहर से सटे निचले सकोह में नौ मई 1964 को जन्मे पिंका युवाओं को स्वरोजगार के लिए प्रेरित करते हैं। गगल-धर्मशाला एनएच पर निचले सकोह में नए खुले होटल चांदनी के मालिक बेरोजगार युवाओं को स्वरोजगार की राह दिखा रहे हैं।[30]
External links
References
- ↑ "Himachal Pradesh known as 'Dev Bhoomi' or 'Land of Gods and Goddess'". 8 August 2014.
- ↑ "Anurag Thakur pays tribute at Shaheed Sthal in Bilaspur, says Himachal Pradesh also known as 'Veerbhoomi'". www.aninews.in.
- ↑ https://hppanchayat.nic.in/About%20us.html
- ↑ The Ancient Geography of India/Singhapura,pp.130-136
- ↑ Alexander Cunningham:The Ancient Geography of India/Singhapura,pp.130
- ↑ Alexander Cunningham:The Ancient Geography of India/Singhapura,pp.131
- ↑ Alexander Cunningham:The Ancient Geography of India/Singhapura,pp.131
- ↑ Alexander Cunningham:The Ancient Geography of India/Singhapura,p.132
- ↑ Alexander Cunningham:The Ancient Geography of India/Singhapura,pp.136
- ↑ The Ancient Geography of India,p.136
- ↑ The Ancient Geography of India,p.138
- ↑ Julien's ' Hiouen Thsang,' i. 261.
- ↑ ' Raja Tarangini,' vii. 150
- ↑ Alexander Cunningham: The Ancient Geography of India,p.139
- ↑ Alexander Cunningham: The Ancient Geography of India,p.139
- ↑ Alexander Cunningham: The Ancient Geography of India,p.139
- ↑ Nagas, The Ancient Rulers of India, Their Origins and History, 2002, pp. 20-21
- ↑ Vogel P-252
- ↑ Vogel P-252
- ↑ 9. (a) Oldham "Sun and Serpent Worship" P-73; 9. (b) Rose H. A., "Glossary of the tribes and caste of Punjab" Vol I, P-154
- ↑ Vogel P-253
- ↑ Ibid
- ↑ Ibid
- ↑ Vogel P-255
- ↑ Stein, A. "Rajtarangini" Part VII, P-27-67
- ↑ Rapson E. J."JRAS" (July 1900) P-533
- ↑ Jane "JRAS" (1903) P-37
- ↑ https://www.webindia123.com/himachal/history/history.htm
- ↑ दिव्य हिमाचल
- ↑ दिव्य हिमाचल

