Sindhu
- For river of this name see Sindhu River
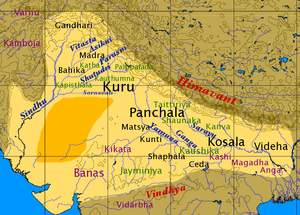
Sindhu (सिंधु)[1] Sandhu (संधू)[2] Sandhu (संधु)[3]/Sanddhu (सन्द्धु)[4] gotra Jats are found in Haryana, Punjab, Rajasthan,Uttar Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir in India and also in Pakistan. Sindhu is an ancient gotra. Dilip Singh Ahlawat has mentioned it as one of the ruling Jat clans in Central Asia. [5] The were also called Sindi (Sindicar of Herodotus). They fought Mahabharata War in Kaurava's side.
Origin
- This gotra seems to have originated from Sindhu Janapada of Mahabharata period. [6] Sandhus are considered descendants of King Satyasandhu (सत्यसंधु) . [7]Sindhu Raja Jayadratha, who had married Duryodhana's sister, fought for the Kauravas in the Mahabharat. Dilip Singh Ahlawat has mentioned Sindhu as one of the ruling Jat clans in Central Asia. [8]
- Tej Ram Sharma[9] writes....The term Sindhu was corrupted to Hindu in the old Persian inscriptions of Darius I (516-485 B. C.), and to Indus by the Ionian (=Panini's Yavana) Greeks. [10] The word 'India' is derived from the river Sindhu or the Indus. Taking its rise from the snows of Western Kailasa in Tibet, the Sindhu first flows north-west of Kashmir and South of little Pamir, and then takes a southward course along which lay some of the important cities of north India. Emerging from the Darad high-lands, the river (Daradi Sindhuh) enters the Gandhara country until it receives its most important western tributary the Kabul river at Ohind, a few miles north of Attock. [11]
- सिंध रावत के नाम पर सिंधु जाट गोत्र प्रचलित हुआ है.[12]
Variants
- Sindhu (Anabasis by Arrian,p. 263.)
Jat Gotras Namesake
- Sindhu = Sindus = Sindos (Greek: Σίνδος) (Pliny.vi.5)
- Sindhu = Sindhu (Anabasis by Arrian,p. 263.)
- Sindhu (Jat clan) = Sindhurani . Sindhurani is a name of queen mentioned in 'Chhapri Statue Inscriptions of Gopaladeva (Kalachuri) year 840 (=1048 AD)'. [13] Chhapri is village in Bodla tahsil of Kawardha (Kabirdham) district in Chhattisgarh.
Mention by Panini
Pare-Sindhu (पारे-सिंधु) is mentioned by Panini in Ashtadhyayi. [14]
Sindhu Janapada (सिंधु जनपद) is mentioned by Panini in Ashtadhyayi. [15]
Sindhu-vaktra (सिंधु-वक्त्र) is mentioned by Panini in Ashtadhyayi. [16]
Villages after Sindhu
- सिंधुकोपा (जाट गोत्र - सिंधु) : सिंधुकोपा नाम का गाँव झारखंड के सराइकेला खरसावाँ जिले की गम्हरिया विकास-खंड में है।
History
V. S. Agrawala[17] writes that Ashtadhyayi of Panini mentions janapada Sindhu, under Kachchhadi (कच्छादि) (IV.2.133) (शैषिक अण्। काच्छ:)[18] and Sindhvadi (सिन्ध्वादि) (IV.3.93) (सोअस्याभिजन:,अण्। सैन्धव:)[19]. Sindhu was originally the name of a river which gave its name to the country. The term Sindhu was corrupted to Hi(n)du in old Persian Inscriptions of Darius I (516-485 BC) and to Indus by Ionian (=Panini's Yavana) Greeks. Sindhu as janapada may be identified with Sind-Sagar Doab, the region between Jhelum and Indus. Most of it is now sandy desert of Thal.
Ram Swarup Joon[20] writes In the Sabha Parva, Mahabharata/Book II Chapter 48, while describing various Kings who attended a ceremony in the Durbar (court) of Maharaja Yudhisthira, seventeen names are mentioned which are today found as Jat gotras. These are Malhia, Mylaw, Sindhar, Gandhar, Mahity, Mahe, Savi, Bath, Dharan, Virk, Dard, Shaly, Matash, Kukar (Khokar) Kak, Takshak, Sand, Bahik (Bathi) Bije (Bijenia), Andhra, Sorashtra (Rathi) Mann, Ar, Sohat, Kukat, Othiwal (Othval).
Ram Sarup Joon[21] writes that ....There is a story in Karna Parva/Mahabharata Book VIII Chapter 23 of the Mahabharata that when Dron Acharya was killed in action, Karna was appointed Commander in Chief of Kaurava Army. He chose Raja Shalya of Sialkot as his charioteer. He was a Madrak Jat and a brother of Madri, mother of the Pandavas. When they were driving to the battle field Karan said, “0, Shalya, there is none equal to me in archery in the Pandava army. They will flee before my arrows”. Shalya was frank and said “No, my people don’t acknowledge your prowess with the bow and arrow as being superior to that of Arjuna.” Karan felt offended and remarked caustically’ “0 Shalya, what do you Jartikas living in the land of five rivers, know about archery and bravery. All your people, Arh, Gandhar, Darad, Chima, Tusar, Malhia, Madrak, Sindhaw, Reshtri, Kukat, Bahik and Kekay eat onion and garlic..... The gotras mentioned above are all Jats and are not found in any other community. However ungraceful the remark, it does prove the existence of Jats in that period and that people of Punjab were called Jatika or Jartika.
Ram Sarup Joon [22] writes that ... Ardas or Urdas Sindhu: This is a very old gotra of the Jats. They are mostly Sikh Jats. They are the descendants of King Jai Dratha. As they came from Sindh they were known as Sindhi. They have been mentioned in history for various praiseworthy deeds, which have been mentioned earlier. King Jai Dratha was the son of Drudabhanu in the 52nd generation of the Urdas Branch of King Yayati and was the brother-in-law of Duryodhana.
His capitals were Mathela Shorao, Mao and Shivasthan (Seistan). The Mahabharat Sabha Parva mentions Jai Daratha to be a Sindhu. About 600 years before Christ, the King of Sindhu helped the king of Cyprus, against Babylonia. But later on the king of Cyprus, on becoming very powerful drove them out of Sindh. The Sindhar gotra is a derivative of Sindhu. The people of this clan belonging to this gotra are found in Haryana.
Ram Swarup Joon[23] writes that Pliny has written that during a conflict between KhanKesh, a province in Turkey, and Babylonia, they sent for the Sindhu Jats from Sindh. These soldiers wore cotton uniforms and were experts in naval warfare. On return from Turkey they settled down in Syria. They belonged to Hasti dynasty. Asiagh Jats ruled Alexandria in Egypt. Their title was Asii
Ram Sarup Joon[24] writes that...about 70 Jat Gotras joined the Gujar force and started calling themselves Gujars. Sindher is one of them.
Bhim Singh Dahiya[25] writes that the ancient Greeks mentioned them as Sindi (Sindicar of Herodotus) and placed them on the Basphorus. In Indian literature they are mentioned as Sindhu or Saindhava and are associated with Sauvira-of the expression Sindhu-Saurira. In Kurma Purana and Vishnu Purana, they are mentioned with the Hunas : “Sauvirah Saindhava Hunan” (सैबीरा सैंधवाहूणाः) as residents of Sakala, Sialkot . Panini mentions a janapada (Republic) of the Sindhus between Jhelum and Indus rivers ([26] In Mahabharata war, they fought on the side of Kauravas. [27] A copper plate inscription of Gujarat, Chalukiya Pulakesi Raja Refers to Tajikas, i.e. Arabs who had defeated the Sandhus and other tribes in west India. Earlier, in 739 A.D. they had defeated the Arabs under their king Punyadeva. In 756 and 776 A.D., they twice repulsed the Arab naval attacks.
Ram Swarup Joon[28] writes that Sindhu is an ancient gotra. Sindhu Raja Jai Dhrata, who had married Duryodhana's sister fought for the Kauravs in the Mahabharat.
Nagendra Nath Bannerjee writes in his book 'Bangla Shabd Kosh' that Jaidhrata before becoming the ruler of Sindh Desh ruled Ceylon. Jai Dharat was born in the 52nd generation of Yayati's third son Ardas. His father was
History of the Jats, End of Page-101
Dardshanu. His capital in Sindhu Desh was Alwa and he had constructed forts at Mathela, Shiv Rao, Bhan and Shavistan. In 600 BC a Sindhu ruler helped Babylonia against Cyrus. Later another ruler helped Darius against Alexander. After having been ruled by Sindhus for many generations, Sindhu Desh came under the rule of Mauryas. Chach, a Brahmin courtier, assassinated the Mauryan ruler in conspiracy with his corrupt queen. The Sindhu and Midh Jats of Sindhu Desh resented it and consequently helped Khalifa Al Qasim against Chach. After Chach came to power, the Sindhu Jats left Sindhu Desh in large numbers and settled in the Punjab and established a big 'Khaap' there. In Haryana these people are called Sindhar. The majority of Sindhus are found in the districts of Lahore and Amritsar.
Shahzadpur Ambala

Shahzadpur Ambala () is a village in Naraingarh tahsil of district Ambala in Haryana.
Kunwarrani Rajinder Kaur Sandhu of Shahzadpur is direct Descendants of Amar Anokhay Shaheed Baba Deep Singh Sandhu of Shaheed Misl.
Credit:- Kunwar Sandeep Singh Sandhu of Shahzadpur (Ambala, Haryana).
Estate:- Shahzadpur Ambala
Dynasty:- Sandhu
Source - Jat Kshatriya Culture
In Rajatarangini
Rajatarangini[29] tells that during the reign of Abhimanyu II in Kashmir There lived a charioteer named Kupya who had two sons named Sindhu and Bhuyya, of whom the elder Sindhu was a flatterer. He had been treasurer of Parvvagupta, and afterwards became the treasurer and favorite of the queen.
Rajatarangini[30]tells....When the king's evil designs were rumoured, Uhlaṇa fled. The king in his anger exiled Mallakoshta. Ananda, lord of Dvara, son of Ananta, was imprisoned and Prajji, an inhabitant of Sindhu and born in a royal family, was made lord of Dvara by the king. Year 1121 AD (VIII,p.89)
Rajatarangini[31] tells that ....But when Sujji arrived with a few Kashmirians, with the Khashas and the men of Sindhu, they tried in vain to confront him.
Rajatarangini[32] tells that....Koshtaka imprisoned the chiefs of the several departments of government, and, like a king,- collected rent from the subjects in Dranga, in his own name, and left no money in Sindhu. (p.178)
Rajatarangini[33] mentions works done by various chiefs during the reign of king Jayasimha (1128 - 1155 AD) of Kashmir....The chief among the kings made his own matha a specially desirable object. He was without vanity, and gave away in gifts many villages, the principal among which was celebrated as Simhapura by those who knew of his gifts. In this place the son of the daughter of the lord of Kārapatha established a Colony of the twice-born who were going to Sindhu and of the rough out caste people of Dravida who formerly lived at Siddhachchhatra. (p.218-219)
Maratha Jat connections
Ranmal Singh pointed out Maratha Jat connections. Some of the Maratha clans evolved from Jat clans as under:
- Holkar - From Haga Jat clan
- Sindia - From Sindhu Jat clan
- Gayakwar - From Gawar Jat clan
- Bhosle - From Bisu Jat clan
- Pawar - From Panwar/Parmar Jat clan
This is based on oral History and needs Genealogical research to establish any Jat-Maratha Connection.
जाट इतिहास
ठाकुर देशराज[34] ने महाभारत कालीन प्रजातंत्री समूहों का उल्लेख किया है जिनका निशान इस समय जाटों में पाया जाता है....सिन्धू - यह नाम ही बताता है कि पंजाब के पास के वर्तमान सिंध में मद्रों के पड़ौसी थे और अब पंजाब में हैं । पंजाब में जाटों का यह प्रसिद्ध गोत्र है।
सिन्धु गोत्र का इतिहास
दलीप सिंह अहलावत[35] लिखते हैं:
सिन्धु जाटों का प्रसिद्ध, गौरवशाली और प्राचीनकाल से प्रचलित गोत्र है। इस वंश का शासन सिन्धु देश पर था। रामायण में भी इनका वर्णन है। सुग्रीव ने सीता जी की खोज के लिए वानरसेना को अपने श्वशुर ‘सुषेण’ के नेतृत्व में पश्चिम दिशा को भेजा और सिन्धु
जाट वीरों का इतिहास: दलीप सिंह अहलावत, पृष्ठान्त-265
देश में जाने का भी आदेश दिया (वा० रा० किष्किन्धा काण्ड, 42वां सर्ग)। सिन्ध मजम्मल-उल-तवारीख वाक़ातए पंज हजारी साला में लिखा है कि दुर्योधन से 5000 वर्ष पहले सिन्ध देश पर मेद1 जाटों का राज्य उन्नति के पथ पर था। जाट इतिहास अंग्रेजी अनुवाद पृ० 6 लेखक रामसरूप जून ने इसी लेख के आधार पर यही लिखा है। परन्तु वैदिक काल से ही इस देश पर जाटों का राज्य रहा है। (देखो इसी पुस्तक का तृतीय अध्याय, वैदिककाल में जाटवंशों का राज्य)।
द्वापर में सिन्धु नामक विशाल जनपद था जिस पर इसी नाम का वैभवशाली सिन्धु राजवंश राज्य करता था। इस वंश के अधीन दस राष्ट्र थे।
- “सिन्धु राष्ट्रमुखानीह दश राष्ट्राणि यानीह” (कर्ण पर्व 2-23)।
उस समय जयद्रथ नामक राजा इस प्रदेश पर कठोरतापूर्वक शासन करता था। महाभारत “सिन्धु-सौवीरभर्तारं दर्पपूर्णं मनस्विनम्” (सभपर्व 22-9), “पतिः सौवीरसिन्धूनां दुष्टभावो जयद्रथः” (वनपर्व 268-8), “जयद्रथो नाम यदि श्रुतस्ते सौवीरराजः सुभग स एव” (वनपर्व 266-12) आदि स्थलों पर जयद्रथ को सिन्धु सौवीर आदि जनपदों का नरेश लिखा है। कई ऐतिहासिकों ने उपरोक्त दस राष्ट्रों की कल्पना करते हुए शिवि, वसाति, काकुस्थ, सौवीर,2 (चारों जाटवंश) आदि वंशों को भी सिन्धु राज्य के अन्तर्गत होना माना है। इस विशाल सिन्धु राज्य का प्रबन्ध राजसभा, न्यायसभा और धर्मसभा के अधीन था। इसी कारण जयद्रथ अपने समय का उत्कृष्ट प्रबन्धक था। इसी योग्यता से प्रभावित होकर राजा दुर्योधन ने अपनी बहिन दुःशला का विवाह जयद्रथ से करके सिन्धुओं को अपना मित्र बना लिया था।
युधिष्ठिर के राजसूय यज्ञ के अवसर पर सिन्धु नरेश ने सुवर्णमालाओं से अलंकृत पच्चीस हजार सिन्धुदेशीय घोड़े उपहार में दिये थे। (सभापर्व, 51वां अध्याय)। महाभारत युद्ध में एक अक्षौहिणी सेना लेकर जयद्रथ दुर्योधन की ओर से लड़ा था। यह सबको विदित है कि अर्जुन ने सूर्यास्त होते-होते जयद्रथ का वध कर दिया था।
सिन्धु राज्य की ध्वजा वराह (सूअर) चिह्न वाली थी (द्रोणपर्व 43-3)। यही ध्वजा प्रायः पश्चिम के सभी आर्य जनपदों की मानी गई। जयद्रथ के मरने के बाद उसका पुत्र सुरथ सिंधु देश का राजा हुआ। महाभारत युद्ध के पश्चात् सम्राट् युधिष्ठिर ने अश्वमेध यज्ञ किया। उस अवसर पर अर्जुन सिन्धु देश में पहुंचा। अर्जुन के वहां पहुंचने की सूचना सुनकर ही सिन्धुराज सुरथ की हृदय गति के रुक जाने से मृत्यु हो गई।
अश्वमेध यज्ञ की स्मृति (यादगार) में अर्जुन ने मोहन (कृष्ण) और युधरो (युधिष्ठिर) के नाम पर मोहनजोदारो-मोहनजोदड़ो नामक नगर बसाया3। (जाटों का उत्कर्ष पृ० 296, लेखक योगेन्द्रपाल
- 1. अनटिक्विटी ऑफ जाट रेस पृ० 6 पर लेखक उजागरसिंह माहिल ने ठोस प्रमाणों द्वारा सिद्ध किया है कि ‘मेद’ शब्द गलत है, इसके स्थान पर मांडा (गोत्र) जाट पढ़ो।
- 2. जाट्स दी एन्शनट् रूलर्ज में बी० एस० दहिया ने पृ० 20 पर सौवीर को सोहल सिद्ध करके सोहल जाट गोत्र लिखा है।
- 3. जाट इतिहास पृ० 693, लेखक ठा० देशराज ने लिखा है कि जयद्रथ के बाद सिन्धुदेश के एक बड़े प्रदेश पर श्रीकृष्ण और युधिष्ठिर के पक्ष के लोगों ने अपना अधिकार जमा लिया और ज्ञातिराज्य की नींव डाली। जहां उनकी राजधानी थी वह (मोहन + युधिष्ठिर के नाम) मोहन + युधरा कहलाती थी जो कालान्तर में मोहनजुधारो अथवा मोहनजोदारो के नाम से प्रसिद्ध हुई। सिन्धुवंश शिववंश का ही एक अंग है।
जाट वीरों का इतिहास: दलीप सिंह अहलावत, पृष्ठान्त-266
शास्त्री)। इस समय से पहले भी सिन्धु देश में जाटों का प्रजातन्त्री शासन था। सिन्धु देश का साहित्य इसका साक्षी है। ‘बंगला विश्वकोष’ जिल्द 7 पृष्ठ 6 पर लिखा है कि “प्राचीनकाल में सिन्धु देश में जाटों का गणराज्य था और सिन्धु देश की जाट स्त्रियां अपने सौन्दर्य और सतीत्व के लिए सर्वत्र प्रसिद्ध हैं।”
महाभारत के बाद सिन्धु देश में विद्यमान सिन्धुवंश के जाटों ने महात्मा बुद्ध से प्रभावित होकर तथा मौर्य, कुषाण एवं धारण गोत्री गुप्त सम्राटों (तीनों जाटवंश) के प्रताप से सामूहिक रूप से बौद्ध-धर्म स्वीकार कर लिया और देर तक इसी धर्म में रहने से आने वाले नवीन ब्राह्मण धर्म की ओर अकस्मात् प्रवृत्त नहीं हुए। नवीन ब्राह्मण धर्म जब पश्चिम में फैला तो ये सिन्धु जाट, सिक्ख या मुसलमान हो गए। इसका विशेष कारण सिन्ध में ब्राह्मणों द्वारा जाटों पर किए गए अत्याचार थे। इसी कारण नवीन हिन्दू धर्म की ओर झुकने में अपना अपमान समझते थे। (जाटों का उत्कर्ष पृ० 296 लेखक योगेन्द्रपाल शास्त्री)। एक चच ब्राह्मण को सिन्धु राजा साहसीराय1 द्वितीय ने अपने दरबार में रख लिया। इस राजा की रानी सुहानदी से चच ने अनुचित सम्बन्ध स्थापित कर लिया और नमकहरामी करके रानी की मदद से राज्य को हड़प लिया। साहसीराय के मरने पर चच ने उस रानी से विवाह कर लिया। इस चच राजा ने सिन्धप्रदेश पर 40 वर्ष राज्य किया। यह जाटों का इतना कट्टर एवं निर्दयी शत्रु था कि इसने उनकी आर्थिक, सामाजिक तथा मानसिक दशा को कुचल डाला। (जाट इतिहास पृ० 14-15,लेखक कालिकारंजन कानूनगो; जाट इतिहास पृ० 697 लेखक ठा० देशराज; जाट्स दी एनशन्ट रूलर्ज पृ० 213 लेखक बी० एस० दहिया)। अधिक वर्णन महाभारतकाल के बाद सिन्ध में जाट राज्य के अध्याय में लिखा जाएगा।
बन्दा बैरागी के नेतृत्व के पश्चात् जब पंजाब में उच्चाकांक्षी वंशों ने 12 मिसलें (रियासतें) बनाकर प्रान्त से मुगल शासन समाप्त करके सिक्ख शक्ति स्थिर की तो सिन्धु वंश ने कन्हैया और सिंहपुरिया आदि कई मिसलों में प्रमुख भाग लेकर राज्यसत्ता प्राप्त कर ली। कर्नल जेम्स टॉड ने इन सिन्धु जाटों की प्राचीन प्रतिष्ठा एवं राज्यगौरव का ध्यान रखते हुए सिंधुवंश को 36 राजवंशों में गिनाया है। राजस्थान के 36 राजकुलों की सूची में टॉड समेत 6 लेखकों की सूची हैं। चन्द्रबरदाई ने भी अपनी सूची में सिन्धु वंश को राजकुलों में लिखा है।
लाहौर, लायलपुर, शेखूपुरा जिलों में सिन्धु जाटों की बहुत उन्नत स्थिति थी। स्वतन्त्रप्रियता इस वंश की विशेषता है। शान्तिकाल में क्रान्ति की प्रतीक्षा करते हुए उत्तम कृषि करना और क्रान्ति में अग्रगण्य भाग लेते हुए प्रमुखता प्राप्त कर लेना सिन्धु जाटों की अपनी विशेषता है। समस्त पंजाब में ब्रिटिश सत्ता के विरुद्ध सर्वप्रथम क्रान्ति करने वाले सरदार अजीतसिंह सिंधु थे जिन्होंने देशहित के लिए विदेशों में रहकर घोर कष्ट सहना स्वीकार किया। इन्हीं के भाई देशभक्त सरदार किशनसिंह के पुत्र अमरशहीद सरदार भगतसिंह के कारण भारतीय क्रान्ति का इतिहास अत्युज्जवल है। सिन्धु वंश के नायक रूप में इस वीर को स्मरण किया जाएगा। इस प्रकार सिंधुवंश जाटों में अत्यन्त प्रतिष्ठाप्राप्त राजवंश है। अमरशहीद भगतसिंह सिंधु पर ने केवल जाटों को ही, परन्तु समस्त भारतवासियों को गर्व है। आपका जीवन चरित्र दशम अध्याय में लिखा जाएगा।
- 1. ‘राय’ मौर्य (मौर) जाटवंश की शाखा है। इसका वर्णन, मौर्य (मौर) जाटों का भारतवर्ष में राज्य प्रकरण में किया जाएगा।
जाट वीरों का इतिहास: दलीप सिंह अहलावत, पृष्ठान्त-267
भारत की स्वतन्त्रता से पूर्व सिन्धु जाटों की रियासतें (जागीरें) कलसिया, फतेहगढ़, सिरानवाली, बड़ाला, भड़वाल, ठोठर, पधाना, चुनिया, भड़न, कालयावाला, मौकल आदि थीं। इस जाटवंश की अधिक संख्या सिक्खों में है। किन्तु इस वंश के हिन्दू जाट भी हैं। ये जि० मेरठ, मुरादाबाद, हिसार और रोहतक में बसे हैं। जि० मेरठ में अक्खापुर गांव सिन्धु जाटों का है। जि० हिसार में खांडा-खेड़ी, जि० रोहतक में खेड़ी साध व नौनोंद गांव सिन्धु जाटों के हैं। कई स्थानों पर यह गोत्र सिन्धड़ भी कहा जाता है। जि० करनाल में इस गोत्र के जाटों के गांव खेड़ी मानसिंह, गगसीना, जुल्लापुर हैं।
सिन्धुवंश के जाटों की अतिप्रसिद्ध घटनाओं का संक्षिप्त ब्यौरा -
- 1. ईसा से 600 वर्ष पूर्व महान् सम्राट् साइरस ने बेबिलोनिया के लोगों से युद्ध करना पड़ा था। साइरस ने सिन्धु जाटों के सम्राट् सिन्धुराज से इस युद्ध के लिए सहायता प्राप्त की। सिन्धु सेना की सहायता से साइरस की विजय हो गई। कर्नल टॉड ने इस समय की जाट जाति के वैभव के लिए निम्नलिखित शब्दों का प्रयोग किया है - “साइरस के समय में ईसा से 600 वर्ष पहले इस महान् जेटिक (जाट) जाति के राजकीय प्रभाव की यदि हम परीक्षा करें तो यह बात हमारी समझ में आ जाती है कि तैमूर की उन्नत दशा में भी इन जाटों का पराक्रम ह्रास (कम, नीचे) नहीं हुआ था।”
- 2. जिस समय सिकन्दर ईरान पर आक्रमण करने के लिए बढ़ रहा था, उस समय वहां के शासक शैलाक्ष (सेल्यूकस) ने सिन्धु देश के राजा सिन्धुसेन जो कि सिन्धु जाटों के गणतंत्र अध्यक्ष थे, से सहायता मांगी। महाराजा ने तीर-कमान और बर्छे धारण करने वाले सिन्धु जाट सैनिकों को उसकी सहायता के लिए ईरान भेज दिया। हेरोडोटस ने इस लड़ाई के सम्बन्ध में लिखा है कि “सिकन्दर की सेना के जिस भाग पर जेटा (जाट) लोग धावा बोलते थे, वही भाग कमजोर पड़ जाता था। ये योद्धा रथों में बैठकर तीर-कमानों से लड़ते थे। सिकन्दर को स्वयं इनके मुकाबले के लिए सामने आना पड़ा था।” इसी समय बलोचिस्तान में राजा चित्रवर्मा राज्य करता था जिसकी राजधानी कलात थी। (जाट इतिहास पृ० 695-696, लेखक ठा० देशराज)।
- 3. जाटवीरों द्वारा महान् सम्राट् अकबर के आदेश को ठुकरा देने का अद्वितीय उदाहरण - सिन्धुवंशी जाट चंगा ने लाहौर से 15 मील दूर पधान नामक गांव बसाया था। फिरोजपुर जिले में दोलाकांगड़ा नामक गांव में धारीवाल जाटगोत्र का चौधरी मीरमत्ता रहता था। उसकी पुत्री धर्मकौर बड़ी बलवान एवं बहुत सुन्दर थी। एक बार सम्राट् अकबर दौरे पर उस मीरमत्ता के गांव के समीप से जा रहा था। उसने देखा कि मीरमत्ता की इस सुन्दर पुत्री ने पानी का घड़ा सिर पर रखे हुए अपने भागते हुए शक्तिमान् बछड़े को उसके रस्से पर पैर रखकर उस समय तक रोके रखा जब तक कि उसके वीरमत्ता ने आकर उस रस्से को न पकड़ लिया। अकबर यह दृश्य देखकर चकित रह गया। सम्राट् अकबर इस लड़की के बल एवं सुन्दरता को देखकर मोहित हो गया और चौधरी मीरमत्ता को उसकी इस पुत्री का अपने साथ विवाह करने का आदेश दे दिया। मीरमत्ता ने जाट बिरादरी से सलाह लेने का समय मांग लिया। सर लिपैन ने लिखा है कि “मीरमत्ता धारीवाल जाट ने 35 जाटवंशों (खापों) की पंचायत एकत्रित की जिसके अध्यक्ष जाट चंगा चौधरी थे। पंचायत ने
जाट वीरों का इतिहास: दलीप सिंह अहलावत, पृष्ठान्त-268
- सर्वसम्मति से प्रस्ताव पास किया कि अकबर बादशाह को लड़की नहीं दी जायेगी। यह प्रस्ताव लेकर चौधरी चंगा और मीरमत्ता अकबर के दरबार में पहुंचे। सिन्धु जाट चंगा ने निडरता व साहस से अकबर को पंचायत का निर्णय सुनाया कि जाट आप को लड़की नहीं देंगे। इस अद्वितीय उदाहरण तथा चंगी की निडरता से प्रभावित होकर अकबर बादशाह ने चंगा जाट को ‘चौधरी’ का खिताब (उपाधि) दे दिया और आपसी मेलजोल स्थापित किया।” चंगा के पुत्र को भी यह उपाधि रही। परन्तु चंगा के पौत्र देवीदास से हत्या के अपराध में जहांगीर बादशाह ने यह उपाधि छीन ली1। जिस सम्राट् अकबर के सामने सिर झुकाकर राजस्थान के बड़े-बड़े कई राजपूत राजाओं ने अपनी पुत्रियों का डोला उसको दे दिया, साधारण ग्रामीण जाटों ने उसके जाटलड़की के साथ विवाह करने के आदेश को ठुकरा दिया। यह है जाटवीरों की अद्वितीय विशेषता। इतिहास में कोई ऐसा उदाहरण नहीं मिलेता कि जाटों व जाट शासकों ने अपनी पुत्रियों का विवाह किसी मुसलमान बादशाह या मुस्लिम व ईसाईधर्मी लोगों के साथ किया हो। मुसलमान बादशाहों के जाटों की सर्वखाप पंचायत के सामने झुकने के अनेक उदाहरण हैं, जो उचित स्थान पर लिखे जायेंगे।
Distribution in Delhi
- Pehladpur Banger Sindhu gotra in Delhi
Distribution in Punjab
The majority of Sindhus are found in the districts of Lahore Pakistan and Amritsar Indian Punjab.
Sindhus in Indian Punjab
In Malwa, along the Sutlej river and from Faridkot to Mukatsar, Sandhus have prominent villages of Saian Wala, Chughe Kalan, Vire Wala, Bhag Singh Wala, Marh, Sakka Wali, Kanian Wali and Khurhanj
Village in Bathinda
Jodhpur Bagga Singh Alias Phalran
Villages in Moga district
Villages in Jalandhar district
Villages in Nawanshahr district
Villages in Patiala district
Sandhu (34,500)in Patiala district: This clan claims to have migrated from the Amritsar area of the Punjab in the 16th century A.D. and holds villages in the sub-districts of Barnala, Bhatinda, Rajpura, Ghanaur, and Amargarh.[36]
Villages in Ludhiana district
Sidhu (24,741) in Ludhiana district: It is believed that this clan originally came from the Faridkot area of Punjab about 350 years ago and own a good many villages around the town of Jagraon.[37]
Villages in Jalandhar district
According to B S Dhillon the population of Sandhu clan in Jalandhar district is 15,000.[38]:
Villages in Hoshiarpur district
In Hoshiarpur district the Sandhu population is 3,675. [39]
Villages in Fazilka district
In Firozpur district the Sandhu population is 31,500. [40]
Villages in Faridkot district
Villages in Sangrur district
- Sandhu Kalan is Village in Barnala tahsil of Sangrur district in Punjab.
Villages in Amritsar district
Narli, Bhullari, Sathiala, Pahuwind ,
Villages in Gurdaspur district
Villages in Taran Taran district
Distribution in Haryana
Sindher in Haryana - In Haryana these people are called Sindher. Actually this is wrongly interpreted. Sandhu and Sindhar are different gotras. The biggest Sandhu Gotra villages in Haryana are Koth Kalan also called Koth Kalan and Koth Khurd. There is also one village near Panipat called Khotpura, which was inhabited by the decedents of Koth Kalan.The residents of Kheri Sadh (Rohtak) and Nunond (नौणंद) (Rohtak) are actually Sandhu not Sindhar.
Villages in Karnal district
Gagsina (गगसीना), Jaisinghpur, Get (गेट), Thari (ठरी), Kheri Mansingh,
Villages in Hisar district
Mahazat, Masudpur Hansi, Sindher, Khanda Kheri, Naloi, Satrod Khas,
Villages in Rohtak district
Garhi Ballab, Kheri Sadh, Mokhara, Nunond - pronunciation as Naunand (नूणंद, नूणोंद, नौणंद) - emerged from Kheri Sadh near Rohtak city.
Villages in Yamunanagar district
Sandhu gotra is in villages:-
Aharwala, Amadalpur, Cahadwala, Chuharpur, Damla, Jathlana, Ratuwala, Yamunanagar Town,
Villages in Panipat district
Villages in Ambala district
Berkhedi, Gorsian, Jansui, Mirpur Ambala, Mohdi (मोहड़ी), Naraingarh, Tharwa Majri,
Villages in Jind district
Village in Kaithal district
Villages in Charkhi Dadri district
Distribution in Uttar Pradesh
Villages in Bulandshahr district
Villages in Hapur district
Akdoli, Bachhrota, Dadayara, Dhana, Hafizpur, Shyampur Jatt,
Villages in Saharanpur district
Villages in Moradabad District
Maanpur, Ramnagar Urf Rampura,
Villages in Shambal District
SalaKhana(सलखना )
Villages in Meerut District
Akkhapur Meerut, Behlolpur, Chhabariya, Parichhatgarh, Chindauritappa Lawar, Rasulpur Zahid,
Villages in Rampur District
Villages in Ghaziabad District
Village in Pilibhit District
Distribution in Rajasthan
Villages in Churu district
Sindhar Jats live in:
Villages in Nagaur district
Merta city, Jaswantabad, Bhanwal, Surpura,
Locations in Jaipur district
Murlipura Scheme,
Villages in Ajmer district
Villages in Ganganagar district
Distribution in Maharashtra
Villages in Nasik district
Distribution in Jammu and Kashmir
Villages in Rajauri disrict
Distribution in Madhya Pradesh
Villages in Bhopal district
Villages in Sehore district
Distribution in Himmachal Pradesh
Village in Kangra district
Distribution in Pakistan
Sandhu - The Sandhu are the largest Muslim Jat clan. They are found throughout central Punjab in many villages. They have played a significant role in the social and political spectrum of Pakistan. Many renowned Sandhu families lives in Lahore District (also known as Majha). They also have a considerable presence in Sheikhupura District (Qila Sura Singh), Sialkot District, Gujranwala District, Gujrat District and Faisalabad District (although the Pakistani Sandhu Jatts are the descendants of Sandhus who migrated from Punjab and Haryana).
According to 1911 census the Sandhu were the principal Muslim Jat clan in districts:
- Sialkot District - Sandhu (5,054)
- Gujranwala District - Sandhu (3,192)
- Lahore District - Sandhu (9,965)
- Amritsar District - Sandhu (2,054)
- Gurdaspur District - Sandhu (783)
- Gujrat District - Sandhu (3,442)
- Shahpur (Sargodha District) District - Sandhu (504)
- Lyalpur District (Faisalabad District) - Sandhu (3,659)
Notable persons
- Raja Risalu (7th century) was a Sindhu Gotra Jat Ruler of Sialkot in Pakistan.
- Bhagat Singh Sandhu
- Bhai Bala
- Baba Tilkara (बाबा तिलकारा) - Sindhu Gotra
- Sardar Ajit Singh
- Balwinder Singh Sandhu
- Pradeep Sindhu
- Kartar Singh Sindhu
- Ajeetesh Sandhu - Golf Player
- K K Sindhu - IPS, Haryana
- Satinder Singh Sandhu, 18-10-1957, IFS, Punjab 1979
- Chaudhary Mitter Sen - Industrialist and founder of Hari Bhoomi daily, Rohtak.
- Capt. Abhimanyu Sindhu, Politician from Haryana
- Baba Deep Singh Sandhu, Celebrated Sikh Saint and warrior, Leader.
- Ranjit Singh of Lahore - Maharaja of Punjab
- Lachman Singh Shahzadpur - Sandhu - Jat, From Ambala was in the List of Punjab Chiefs.
- Kikar Singh - Great wrestler of 20th century, who shot fame due to uprooting kikar tree.
- Harpreet Singh Sandhu - IC-49602X Colonel Harpreet Singh Sandhu 5/1st Battalion The Gorkha Rifles Army. Awarded with Sena Medal (Devotion to Duty) on 26 January 2012.[41]
- IC-51797M Colonel Harminder Singh Sandhu Rajput Regiment / 44th Battalion The Rashtriya Rifles Army. Awarded with Sena Medal (Devotion to Duty) on 26 January 2012.[42]
- Col. O. P. Sandhu - Retd.Defence, 331 Sector 17-A, Defence Colony, Gurgaon, Haryana Ph: 0124-2340526, 9818062193 (PP-240)
- Mr. S. S. Sandhu - Govt. Service ACP-ACB Delhi Police, 545, Hanuman Mandir Road, Chirag Delhi, New Delhi, Ph: 011-26464485 (PP-482)
- Mr. R. S.Sandhu - Asstt. Director, Home Affairs & Cabinet Sect. B-316, Pragati Vihar Hostel, New Delhi Ph: 011-26173771, 011-24362045 (PP-512)
- Gulzar Singh Kalianwala, Sandhu - Jat, From Amritsar district was in the List of Punjab Chiefs.
- Atar Singh Bhakha, Sandhu - Jat, From Amritsar district was in the List of Punjab Chiefs.
- Nihal Singh Of Kot Sayad Mahmud, Sandhu -Jat, From Amritsar district was in the List of Punjab Chiefs.
- Gurdit Singh, Chichawala, Sandhu - Jat, From Amritsar district was in the List of Punjab Chiefs.
- Sarup Singh Kanhaya of Fatehgarh, Sandhu - Jat, From Gurdaspur district was in the List of Punjab Chiefs.
- Sardar Udham Singh, Nakai of Baherwal Kalan, Sandhu Jat, From Lahore district was in the List of Punjab Chiefs of Pakistan.
- Bhai Teja Singh Thatar, Sandhu - Jat, From Lahore district was in the List of Punjab Chiefs of Pakistan.
- Anup Singh Thepuria, Sandhu - Jat, From Lahore district was in the List of Punjab Chiefs of Pakistan.
- Gurbaksh Singh Pahuwindia, Sandhu - Jat, From Lahore district was in the List of Punjab Chiefs of Pakistan.
- Fatehyab Singh, alias Jiwan Singh, Padhania, Sandhu - Jat, From Lahore district was in the List of Punjab Chiefs of Pakistan.
- Sardar Kahan Singh Kanhaya, Sandhu - Jat, From Lahore district was in the List of Punjab Chiefs of Pakistan.
- Sher Singh of Marake, Sandhu - Jat, From Lahore district was in the List of Punjab Chiefs of Pakistan.
- Attar Singh Rosa - Rosa (Sindhu) - Jat, See-Rosa family in Punjab Chiefs by Griffin (1865), pp.342-348
- Gurdit Singh Rosa - Rosa (Sindhu) - Jat, See-Rosa family in Punjab Chiefs by Griffin (1865), pp.342-348
- Tegh Singh Rosa - Rosa (Sindhu) - Jat, See-Rosa family in Punjab Chiefs by Griffin (1865), pp.342-348
- Teja Singh, Nakai, Sandhu - Jat, From Montgomery district was in the List of Punjab Chiefs of Pakistan.
- Sardar Sheo Deo Singh of Siranwali, Sandhu - Jat, From Sialkot district was in the List of Punjab Chiefs of Pakistan.
- Sardar Hakim Singh, of Wadala, Sandhu -Jat, From Sialkot district was in the List of Punjab Chiefs of Pakistan.
- Dr. Rajender Sandhu and Dr. Surendra Sandhu, Sandhu clinic, Near ITI, Yamunanagar.
- Deepak Sandhu - Chief Information Commissioner of India
- पूर्ण भक्त उर्फ बाबा चौरंगीनाथ - संधु (सिन्धड़) गोत्री
- बाबा दीपसिंह - संधु गोत्री
- पीर बाबा काला मेहर - संधु गोत्री (खोथकलाँ, हिसार हरियाणा)
- ठाकुरसिंह सन्धानवाला - सिन्धु गोत्री जाट जिसने ‘सिंघसभा’ की स्थापना की।
- CH. Sarup Singh (Sindhu) - Politician from Haryana
- Lalit Sandhu - IAS-2014, Rank-167.[43]
- Jasmit Singh Sindhu: IAS-2015, Rank 3 Delhi B.Tech. IIT Rudki, Rajasthan Cadre, earlier in IAS-2014 he passed with Rank-332 and got IRS. [44]
- Major Dalip Singh Sandhu - Battle of Burki [45]
- Major Raghbir Singh Sandhu - Battle of Burki [46]

- Amarjeet Singh Sandhu (Sqdrn Leader) (23.01.1933 - 24.09.1971), Vira Chakra, did act of bravery on 18 September 1965 during Indo-Pak War-1965 for which hewas awarded Vira Chakra. He was from Moriwala is a village in District Sirsa in the Indian state of Haryana.

- Rajiv Sandhu(Second Lt) (12.11.1966 - 19.07.1988) became martyr during Operation Pawan in Srilanka on 19.07.1988. He was from Chandigarh, [Punjab]]. He was in Unit: 19 Madras batallion. He was awarded Mahavir Chakra for his act of bravery.
- Harpreet Singh Sandhu : Bronze Medal, Asian Wrestling Championship 2017
- Dhara Singh Sindhu(born:1896) (मास्टर धारासिंह सिंधु), from Meerut (मेरठ), Uttar Pradesh, was a social worker in Nagaur, Rajasthan.[47]
- Shri Phool Kumar Sindhu - Notable Hockey Player & Coach - Gurugram, Haryana (from Rohtak)
- Jagveer Singh Sindhu

- गुरतेज सिंह संधू, थॉमस एडिसन से ज्यादा पेटेंट वाले दुनिया के 7वें बेस्ट इन्वेंटर. गुरतेज संधू एक भारतीय मूल के आविष्कारक हैं, जिनके नाम थॉमस एडिसन - द फादर ऑफ इनवेंट्स की तुलना में अधिक पेटेंट हैं।एडिसन के नाम पर 1,084 पेटेंट थे, 63 वर्षीय गुरतेज संधू ने 1,325 पेटेंट हासिल किए हैं और दुनिया भर में सबसे अधिक खोज करने वालों की सूची में 7 वें स्थान पर हैं। वर्तमान में, संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका के इडाहो में रहने वाले, गुरतेज संधू एक आविष्कारक होने के साथ-साथ माइक्रोन प्रौद्योगिकी के उपाध्यक्ष हैं। IIT दिल्ली से इलेक्ट्रिकल इंजीनियरिंग में डिग्री हासिल करने के बाद, गुरतेज ने 1990 में यूनिवर्सिटी ऑफ नॉर्थ कैरोलिना से भौतिकी में पीएचडी की उपाधि प्राप्त की। गुरतेज स्व-ड्राइविंग कारों, बिग डेटा के साथ अन्य बड़ी परियोजनाओं में भी प्रयोग और नए अविष्कार कर रहे हैं, जिससे उनके पेटेंट की लिस्ट में उछाल आया है। संधू ने धातु को ऑक्सीजन तक उजागर किए बिना टाइटेनियम के साथ माइक्रोचिप्स कोटिंग का एक तरीका विकसित किया, जो चिप्स को बर्बाद कर देगा। प्रारंभ में, उन्होंने नहीं सोचा था कि उनका विचार एक बड़ी बात है, लेकिन अब अधिकांश मेमोरी-चिप निर्माता इस प्रक्रिया का उपयोग करते हैं। गुरतेज संधू वास्तव में इतने सारे पेटेंट को सुरक्षित करने वाले कुछ भारतीय अन्वेषकों में से एक बनकर हम सभी को बेहतर करने का भरोसा जगाया है।
- Gurpreet Singh Sandhu (born 03.02.1992) is an Indian professional footballer who plays as a goalkeeper for Indian Super League club Bengaluru and is the captain of the India national team.
- Amardip Sandhu became Martyr in Jammu and Kashmir. He was from Koth Kalan village in tehsil Narnaund of district Hissar in Haryana.
Gallery
-
Satnam Singh Sandhu
External links
References
- ↑ Jat History Dalip Singh Ahlawat/Parishisht-I, s.n. स-42
- ↑ B S Dahiya:Jats the Ancient Rulers (A clan study), p.243, s.n.207
- ↑ O.S.Tugania:Jat Samuday ke Pramukh Adhar Bindu,p.60, s.n. 2339
- ↑ Jat History Dalip Singh Ahlawat/Parishisht-I, s.n. स-42
- ↑ Jat History Dalip Singh Ahlawat/Chapter IV, p.342
- ↑ Mahendra Singh Arya et al: Adhunik Jat Itihas, p. 282
- ↑ Mahendra Singh Arya et al: Adhunik Jat Itihas, p. 284
- ↑ Dilip Singh Ahlawat: Jat viron ka Itihasa
- ↑ Personal and geographical names in the Gupta inscriptions/Names of the Rivers and the Mountains,p.296
- ↑ V S Agrawala, India as Known to Panini. p. 51
- ↑ V S Agrawala, India as Known to Panini. p.44
- ↑ Dr Ompal Singh Tugania, Jat Samuday ke Pramukh Adhar Bindu/Gotra, p.6
- ↑ Corpus Inscriptionium Indicarium Vol IV Part 2 Inscriptions of the Kalachuri-Chedi Era, Vasudev Vishnu Mirashi, 1905, p.580-582
- ↑ V. S. Agrawala: India as Known to Panini, 1953, p.43
- ↑ V. S. Agrawala: India as Known to Panini, 1953, p. 43, 44, 50
- ↑ V. S. Agrawala: India as Known to Panini, 1953, p.65, 66
- ↑ V. S. Agrawala: India as Known to Panini, 1953, p.50
- ↑ V. S. Agrawala: India as Known to Panini, 1953, p.497
- ↑ V. S. Agrawala: India as Known to Panini, 1953, p.498
- ↑ Ram Swarup Joon: History of the Jats/Chapter II,p. 32-33
- ↑ History of the Jats/Chapter II,p.33-34
- ↑ Ram Sarup Joon: History of the Jats/Chapter V, p.71, sn.7
- ↑ Ram Sarup Joon: History of the Jats/Chapter III, p.40-41
- ↑ Ram Sarup Joon: History of the Jats/Chapter VI,p.116
- ↑ Jats the Ancient Rulers (A clan study)/Jat Clan in India,p. 267
- ↑ V.S.Agrawala, op. cit, p. 50
- ↑ Bhisma Parva, p. 882
- ↑ Ram Swarup Joon: History of the Jats/Chapter V, p. 101-102
- ↑ Rajatarangini of Kalhana:Kings of Kashmira/Book VI,p.160
- ↑ Kings of Kashmira Vol 2 (Rajatarangini of Kalhana)/Book VIII, p.89
- ↑ Kings of Kashmira Vol 2 (Rajatarangini of Kalhana)/Book VIII (i),p.164
- ↑ Kings of Kashmira Vol 2 (Rajatarangini of Kalhana)/Book VIII (i),p.178
- ↑ Kings of Kashmira Vol 2 (Rajatarangini of Kalhana)/Book VIII (i), p.218-219
- ↑ Jat History Thakur Deshraj/Chapter V,p.139
- ↑ जाट वीरों का इतिहास: दलीप सिंह अहलावत, पृष्ठ.265-269
- ↑ History and study of the Jats, B.S Dhillon, p.126
- ↑ History and study of the Jats, B.S Dhillon, p.123
- ↑ History and study of the Jats, B.S Dhillon, p.127
- ↑ History and study of the Jats, B.S Dhillon, p.127
- ↑ History and study of the Jats, B.S Dhillon, p. 127
- ↑ http://netindian.in/news/2012/01/25/00018449/368-republic-day-gallantry-other-defence-decorations-announced
- ↑ http://netindian.in/news/2012/01/25/00018449/368-republic-day-gallantry-other-defence-decorations-announced
- ↑ 'Jat Privesh', July 2015,p. 18
- ↑ 'Jat Privesh', July 2015,p. 18
- ↑ R S Joon:History of the Jats/Chapter XIII, p-246
- ↑ R S Joon:History of the Jats/Chapter XIII, p-248
- ↑ Thakur Deshraj:Jat Jan Sewak, 1949, p.189-190
- Ram Swarup Joon: History of the Jats, Rohtak, India (1938, 1967)
Back to Jat Gotras
- Jat Gotras
- Gotras after Places
- Muslim Jat Gotras
- Jat Gotras in Pakistan
- Sikh Jat Gotras
- Madhya Pradesh
- Uttar Pradesh
- Haryana
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Maharashtra
- Jammu and Kashmir
- Himachal Pradesh
- Gotras in Amritsar
- Gotras in Jalandhar
- Gotras in Hoshiarpur
- Gotras in Firozpur
- Gotras in Lahore
- Gotras in Jaipur
- Gotras in Churu
- Gotras in Nagaur
- Gotras in Ajmer
- Gotras in Ganganagar
- Gotras in Saharanpur
- Gotras in Rohtak
- Gotras in Jind
- Gotras in Hisar
- Gotras in Kaithal
- Gotras in Moradabad
- Gotras in Meerut
- Gotras in Bhopal
- Gotras in Sehore
- Gotras in Nasik
- Villages in Jalandhar
- Gotras in Sangrur
- Gotras in Gurdaspur
- Gotras in Nawanshahr
- Villages in Sangrur
- Villages in Taran Taran
- Gotras in Kangra
- Chauhan History
- Jat History
- Ancient Jat Gotras
- Gotras in Sialkot
- Gotras in Gujranwala
- Gotras in Gujrat
- Gotras in Yamunanagar
- Gotras in Sargodha
- Gotras in Faisalabad
- Gotras in Khanewal
- Parihar History
- Mahabharata People
- Mahabharata People and Places
- People and Places by Panini
- Jat Gotras Namesake


